Biology and computers
advertisement

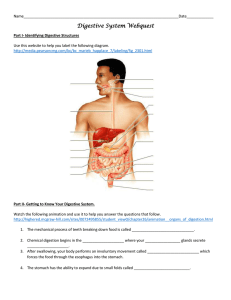
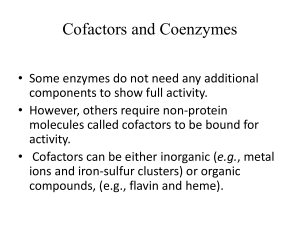
The digestive system, thermodynamics, enzymes, and transport across membranes April 28, 2003 Learning objectives Understand the major organs involved in the digestive system Understand the molecular difference between sugars and lipids Understand how enzymes break down complex molecules to derive energy ATP is the energy currency of the cell Understand how complex molecules are built up and know that this is an energy-requiring process Workshop-Work in groups to report on some aspect of digestion Homework-see last slide Grading 6 1 1 1 6 Quizzes (15%), Homework (10%), Midterm (25%), Writing assignment (15%), Final Exam (35%) Quizzes (each 10 points) = 60 Midterm = 100 paper = 60 final = 140 homeworks (ea. 6.67) = 40 Total = 400 points points points points points points 6 5 1 4 3 2 H (ATP) (warmth) First Law of Thermodynamics-Energy cannot be created or destroyed but it can change form. Second Law of Thermodynamics-Systems change in a way that increases disorder of the system and its surroundings + 6O2 + ADP + Pi 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP + heat energy •Enzyme action video 1 •Enzyme action video 2 •Enzyme action video 3 Characteristics of enzymes Globular proteins that function as biological catalysts to mediate specific biochemical chemical reactions Enzymes are not changed by the reactions they mediate Functional units of metabolism - responsible for all biochemical reactions May require cofactors/coenzymes for reaction to occur metal ions - e.g., Mn2+, Zn2+, Fe3+ coenzymes (NAD+, TPP, THF, etc.) Characteristics of enzymes (cont.) Apoenzyme - enzyme lacking essential cofactor Holoenzyme - intact & functional enzyme containing all cofactors/coenzymes Substrate (S) - molecules that enzymes react with Product (P) - molecules formed by enzymemediated reactions Obesity in America What is a calorie? The calorie (symbolized cal) is the unit of heat Heat is a form of kinetic energy transfer from one medium or object to another. An energy transfer of 1 cal will raise the temperature of one gram (1 g) of pure liquid water by one degree Celsius (1 oC) In nutrition, a unit called the diet calorie is sometimes mentioned; this unit is equivalent to 1000 cal, or one kilocalorie (1 kcal). Calorie content is measured with a bomb colorimeter H Workshop Work in assigned groups of two to give a 6 minute presentation to the class on a molecular aspect of human digestion prepare a 3 question quiz for the class Starch hydrolysis Protein digestion Fat emulsification Websites on human digestive system Site 1 Site 2 Types of transport 1. 2. 3. Passive-requires no energy Facilitated-requires no energy (put needs a protein transporter) Active transport-requires energy Video on transport systems Endocytosis vs. exocytosis Do the following exercises Homework Due May 5 Answer Reviewing Ideas on p. 74, problems 1, 2, 5-9, 11; Using Concepts on p. 75, problems 2, 3, 6, 8, 10 Answer Check and Challenge questions on p. 85 Reading for next week: 226-229; and familiarize yourself with the following website: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?call =bv.View..ShowSection&rid=gnd