Informative Speeches
advertisement

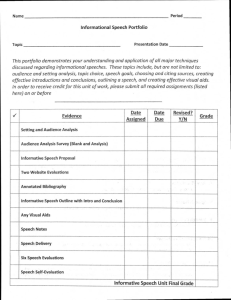
INFORMATIVE SPEECHES 9/23/14 Informative Speeches a speech that educates and informs an audience by explaining or describing facts in a way that stimulates interest and increases understanding GOAL: help listeners understand a topic by increasing their knowledge of the subject Informative Speeches – Your Topic 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Choose a type of speech. Choose a method of informing. Choose a subject. Choose a topic. Write a specific speech goal. TYPES OF SPEECHES PROCESS SPEECH explains how something is done, made, or works - a. b. you might only be able to demonstrate part of the process decide the steps and the order in which they need to be explained develop concrete explanations of each step EXPOSITORY SPEECH an informative speech that provides researched in-depth knowledge about a subject Has: - an in-depth knowledge of the subject - an organizational pattern - a variety of informative methods Sample Expository Subject Areas 1. political, economic, social ,religious, or ethical issues 2. historical events and forces 3. theories, principles, and laws 4. creative works METHODS TO INFORM 1. DESCRIPTION - - - gives an accurate and vivid verbal picture of an object, geographic feature, setting, image, etc. generally answers who? what? and where? size weight composition condition - shape color age spatial organization 2. DEFINITION explains something by identifying its meaning a. b. c. define a word or idea by classifying it and showing how it is different from similar words and ideas define a word by explaining its origin and history define a term by its use or function 3. COMPARE AND CONTRAST explains something by pointing out similarities and differences. 4. DEMONSTRATION shows how something is done by explaining the steps or by showing how something works SELECTING A SPEECH TOPIC STEPS IN CHOOSING A SPEECH TOPIC 1. CREATE A LIST OF SUBJECTS AND TURN THOSE SUBJECTS INTO TOPICS 2. COLLECT INFORMATION AND ANALYZE THE AUDIENCE 3. CHOOSE THE TOPIC THAT IS APPROPRIATE FOR THE AUDIENCE AND SETTING SUBJECT V. TOPIC SUBJECT – A BROAD AREA OF KNOWLEDGE TOPIC – KNOWLEDGE ABOTU A SPECIFIC PART OF A SUBJECT HOW TO FIND A TOPIC 1. MAKE A LIST OF ALL THE SUBJECTS YOU KNOW A LOT ABOUT. MOVIES BOOKS SUPERHEROES COOKING COMPUTERS SOCCER HOW TO FIND A TOPIC CONSIDER SOME OF THESE THINGS WHEN MAKING A LIST OF BROAD SUBJECTS: MUSIC, BANDS, SINGERS HOBBIES SPECIAL INTERESTS OR CONCERNS SPORTS ACTIVITIES AND CLUBS FAMILY, PETS, OR VACATIONS HOW TO FIND A TOPIC 2. USE BRAINSTORMING AN CONCEPT MAPS TO TURN BROAD SUBJECTS INTO SPECIFIC TOPICS THAT IDENTIFY A PART OF THE SUBJECT YOU WILL SPEAK ABOUT HOW TO FIND A TOPIC When picking a topic, remember: - which might be most interesting to your audience? - is the topic appropriate for the age of the audience and the speech location? - is the topic too broad or too narrow for the time allotted? - how much do you know about the topic? - is it something you can be passionate about? WRITING A SPEECH GOAL THE SPEECH GOAL GENERAL SPEECH GOAL: reflects the intent of the speech – do you want to entertain, inform, or persuade? Answers the question... what is the main purpose of the speech? “I want to inform my audience about illiteracy.” THE SPEECH GOAL SPECIFIC SPEECH GOAL: identifies the specific purpose of the speech - - a single statement that identifies the response you want from your audience exactly WHAT do you want them to know about your topic? “I want the audience to understand three ways illiteracy hurts someone in the workplace.”