MYP 10 EnergeticsWS4
advertisement

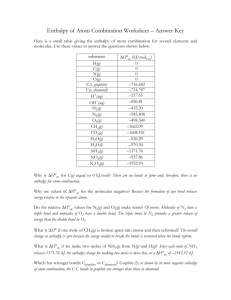
MYP 10 Chemistry 2013-14 Energetics Worksheet 4 Average Bond Enthalpy Name: _________________________________ ( ) Class: _________ Date: _____________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 1. The table below shows some bond energies. Bond C=O C-H H-Cl O-H C=C C-C O=O Bond Enthalpy in kJ/mol 743 412 431 463 612 348 496 (a) Butene, C4H8 reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water only. Write a balanced equation for the reaction. (b) The structural formulae of but-1-ene, oxygen, carbon dioxide and water are given below. H H H H H—C = C—C—C—H O=O H butene oxygen O=C=O H—O—H H carbon dioxide water Based on the balanced equation in part (a), and the structural formulae given, state the number of each type of bonds broken during the reaction. (c) Calculate the enthalpy change, ΔH for the reaction. [(c) -2068kJmol-1 ] 2(a)(i) Define the term average bond enthalpy. (ii) Explain why the fluorine molecule, F2, is not suitable as an example to illustrate the term average bond enthalpy. (b)(i) Using values from Table 10 of the IB Chemistry data booklet, calculate the enthalpy change for the following reaction: CH4(g) + F2(g) CH3F(g) + HF(g) (ii) Sketch an enthalpy diagram for the reaction. 3(a) Ethyne is commonly called acetylene. It is used in an oxy-acetylene flame which is hot enough to cut through steel. Ethyne completely combusts as shown in the equation below. 1 Calculate the enthalpy change of combustion of ethyne using the average bond enthalpies in the table below. (b) Ethyne is formed when water reacts with calcium carbide, CaC2. CaC2(s) + 2H2O(l) Ca(OH)2(s) + C2H2(g) The standard enthalpy change of this reaction can be determined indirectly using standard enthalpy changes of formation. (i) What is meant by the term standard enthalpy change of formation, ΔHfƟ? You should state the standard conditions in your answer. (ii) Standard enthalpy change of formation are shown in the table below. Calculate the standard enthalpy change of the reaction: CaC2(s) + 2H2O(l) Ca(OH)2(s) + C2H2(g) [(a)-1236kJmol-1(b)(ii)-128kJmol-1 ] 2