File
advertisement

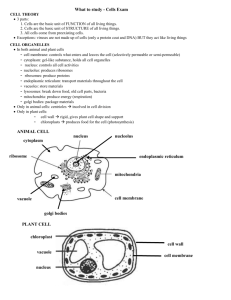
Unit Two – God’s Living Creation Chapter Four – Cells and Classification Organism – a complete living thing Life span – for living things, the process of birth, growth, reproduction and death Life cycle – another name for the life span Life comes only from life Living thing respond to their environments to protect themselves. Environments – surroundings Energy – the ability to do work Genesis 2:16-17 God commanded Adam and Eve not to eat of the tree of the knowledge of good and evil. If they ate of that tree, they would “surely die.” Rom 5:12 When Adam sinned, he brought sin into the world. The punishment for sin is death. Because Adam sinned, every descendant of Adam is born a sinner and will receive the punishment for sin. Rom 5:19, 1 Cor 15:12 Yet Jesus Christ obeyed God by dying on the cross. He made it possible for all men to be saved from sin and punishment of sin. Robert Hooke – first to observe and name cells Examined a small piece of dried cork with a microscope and observed small, empty chambers that he called cells Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden – formed the basis of the cell theory Found that all living things are made of cells Cell Theory – the theory developed by Schwann & Matthias that cells can function as individual living organisms or as the smallest units in a larger organism Some characteristics of living things are also characteristics of people that are spiritually alive in Christ. To be spiritually alive, a person must accept Jesus Christ as his Savior from sin and be born into God’s family. Living things grow and develop Spiritually alive people grow and develop in Christ Gal 5:22-23, 1 Peter 2:2 Living things reproduce Spiritually alive people spread the gospel to others Prov 11:30, Matt 28:19-20 Some characteristics of living things are also characteristics of people that are spiritually alive in Christ. To be spiritually alive, a person must accept Jesus Christ as his Savior from sin and be born into God’s family. Living things respond to their environments Spiritually alive people respond to their environments by fleeing temptation and doing what’s right 1 Cor 10:13, James 4:7 Living things use energy Spiritually alive people need energy (strength) from the Lord Phil 4:13, Ps 27:1 Microscope – an instrument that uses lenses to magnify objects Zacharias Jansen – credited with inventing the first microscope His father, Hans, was a lens maker and probably began making the first compound microscope. Cell – a tiny unit of living material surrounded by a thin membrane Unicellular – organisms that consist of one cell Multicellular – organisms made of more than one cell Most living things are multicellular and made of millions and millions of cells. Tissue – a group of cells working together Organs – formed by tissues working together Heart, lungs, liver, kidneys Systems – formed by organs working together In order, from smallest to largest Cells – Tissues – Organs – Systems Just as cells, tissues, organs and systems work together in the body to perform specific functions, Christians should work together in Christ’s church to glorify His name and do His will. Cell membrane – surrounds every cell and provides the external boundary for the material inside the cell Cytoplasm – a jellylike substance inside the cell membrane Organelles – tiny structures inside the cytoplasm that help carry out the functions of the cell Nucleus – a large, circular structure that contains DNA Chromosomes – Tight little bundles of DNA The cell follows the DNA code as it grows, reproduces, and builds substances for the organism. Mitochondria – breakdown the cell’s food and releases energy Endoplasmic reticulum – the cell’s transportation system Ribosomes – make the proteins that cells need Vacuoles – bubble-like storage organelles in the cytoplasm Cell wall – not found in animal cells; helps the plant cell stay rigid and firm Chloroplasts – structures found in plant cells that contain a green pigment Chlorophyll – a green pigment found in plant cells that absorbs energy from sunlight 2 1 8 7 3 4 5 6 1. Chromosomes 2. Endoplasmic Reticulum 3. Ribosomes 4. Cell Membrane 5. Cytoplasm 6. Mitochondrion 7. Vacuole 8. Nucleus 1 2 10 9 3 4 5 6 7 8 1. Cytoplasm 2. Chromosomes 3. Nucleus 4. Mitochondrion 5. Cell Membrane 6. Cell Wall 7. Endoplasmic Reticulum 8. Ribosomes 9. Chloroplast 10.Vacuole Cell division – the process of an individual cell dividing into two cells Mitosis – process through which organisms grow and replace cells Chromosomes duplicate once and the cell divides once Process produces two cells identical to the parent cell Sexual reproduction – the process of creating new life using cells from male and female organisms Meiosis – process through which reproductive cells are formed Each reproductive cell ends up with only half as many chromosomes as the parent cell Chromosomes duplicate once and the original cell divides twice The process produces four reproductive cells Classification – putting organisms with similar characteristics into groups Carolus Linnaeus – developed the method of classification into six kingdoms Bacteria – the smallest living things knows to man Unicellular microscopic organisms that are almost everywhere Colonies – same kind of groups of organisms living together Bacteria do not have well-defined nuclei Bacteria can make you sick Some bacteria can be helpful Your intestines contain bacteria that help digest your food Yogurt contains bacteria Archaebacteria are also unicellular, but they have a unique chromosome structure. Archaebacteria live in conditions that are poisonous to other living things. Like Eubacteria, Archaebacteria do not have a true nuclei. Unicellular organisms that have cell membranes and true nuclei Two kinds of organisms in this kingdom Protozoans – can move around and often live in water Paramecium – common protozoan that uses tiny hairlike structures called cila to propel it through the water Amoebas – move around by constantly changing their shape Algae – like plants, they have chlorophyll in their cells and therefore use sunlight for energy; not as mobile as protozoans Some species are unicellular, and some exist in colonies. Common examples of a fungus Mushroom Mold Yeast Exodus 12:15, 1 Cor 5:6 The Bible uses the word “leaven” for yeast, which often represents sin. Just as a little yeast can cause a whole loaf of bread to rise, a little sin is able to grow and affect others. Group of multicellular organisms (plants) that provide food and oxygen to all living things. Have chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll which helps a plant make its own food. Photosynthesis – a process of converting sunlight energy into a usable source of energy (sugar). Through photosynthesis, plants also release oxygen. Multicellular and do NOT have cell walls Cannot manufacture their own food Are dependent on the ability to move to find and gather food for their needs Man is in a class by himself. God created man in His own image and gave him specific instructions about how to live and rule over the earth. Common names – names that are widely recognized Different in different languages Carolus Linnaeus – developed the ordering system to help classify plants and animals according to common characteristics Seven levels of classification: Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species Kate Poured Coffee On Father’s Good Suit. King Phillip Came Over For Good Steak. Scientific names – Latin names that are unique and are not attached to any other organism Made up of two names Genus name – always capitalized Species name The scientific name must be underlined. The classification system makes learning about living things much easier. Looking at classifications helps us appreciate the orderliness of God’s creation. Every creature is exactly how God planned it to be!