6b-Diversity Protista 2015
advertisement
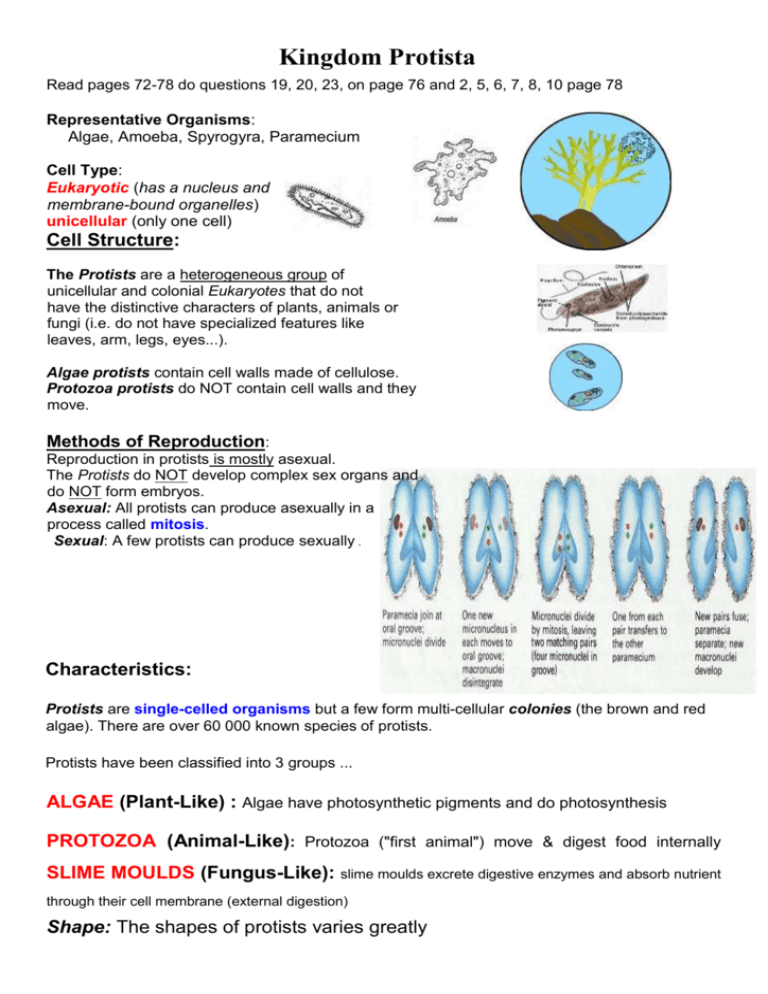
Kingdom Protista Read pages 72-78 do questions 19, 20, 23, on page 76 and 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10 page 78 Representative Organisms: Algae, Amoeba, Spyrogyra, Paramecium Cell Type: Eukaryotic (has a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles) unicellular (only one cell) Cell Structure: The Protists are a heterogeneous group of unicellular and colonial Eukaryotes that do not have the distinctive characters of plants, animals or fungi (i.e. do not have specialized features like leaves, arm, legs, eyes...). Algae protists contain cell walls made of cellulose. Protozoa protists do NOT contain cell walls and they move. Methods of Reproduction: Reproduction in protists is mostly asexual. The Protists do NOT develop complex sex organs and do NOT form embryos. Asexual: All protists can produce asexually in a process called mitosis. Sexual: A few protists can produce sexually . Characteristics: Protists are single-celled organisms but a few form multi-cellular colonies (the brown and red algae). There are over 60 000 known species of protists. Protists have been classified into 3 groups ... ALGAE (Plant-Like) : Algae have photosynthetic pigments and do photosynthesis PROTOZOA (Animal-Like): Protozoa ("first animal") move & digest food internally SLIME MOULDS (Fungus-Like): slime moulds excrete digestive enzymes and absorb nutrient through their cell membrane (external digestion) Shape: The shapes of protists varies greatly Size: • typically only 5 µm - 50 µm (0.01-0.5 mm) in size, • some protozoa grow as large as 5 cm • some "seaweed" algae grow large colonies • No specific size Motility (some are motile, some are NOT motile ) • some move using cilia • some move using flagella • some move using streaming (amoeba use "arms" called a pseudopods) cilia flagella streaming pseudopods The ALGAE Algae are plant-like protists that contain chlorophyll and do photosynthesis. - Algae have cellulose cell walls. - Algae have different pigments used to perform photosynthesis (they are autotrophs) Some algae move (are motile) using cilia. - Algae are producers that start many food chains. Plant-Like Protists 1. Green Algae 2. Brown Algae 3. Red Algae 4. Diatoms - major component of plankton 5. Dinoflagellata - have 2 flagella 6. Golden Algae - yellow/brown colour PROTOZOA Protozoa are animal-like protists are that must move to find and consume food. There are 4 phyla of protozoa a) ciliates - motile protozoa that use hair like projections called cilia to "swim" b) flagellates - motile protozoa that use a tail like projection called flagellum to "swim" c) cercozoans - motile protozoa that use "pseudopods" temporary cytoplasmic extensions that are used for feeding and movement d) sporozoans - generally non-motile but reproduce using spores Characteristics of Protozoa - They are heterotrophs (they must feed off other organisms to survive). - They are unicellular and are "hunters" or "gatherers" (feed). Digestion in protozoans is intracellular (inside the cell). - Protozoa lack cell walls. - Many protozoa cause diseases (are or parasitic.) - Most protozoa reproduce through mitosis (asexual). - Some protozoa utilize conjugation (sexual reproducuction). - Most protozoa are motile (they can move) using either cilia, flagella or pseudopods cilia flagella streaming SLIME MOULDS Fungus-like protists are called slime moulds. Characteristics of Slime Moulds - Slime moulds secrete chemicals that digest food in their environment and then absorb the digested chemicals and so they are considered heterotrophs (feed off other organisms). - Reproduction is asexual through fragmentation and the production of spores. - slime moulds have cell walls made of cellulose (not the same kind as plants) - Slime moulds are divided into three groups: 1. Myxomycota - produce spores to reproduce, they grow and eat as a mass 2. Acrasiomycota - solitary but can work together 3. Oomycota - "mildews and water moulds" Biological Role: - Photoplankton are the basis of many Food Chains - Algae produce O2 (photosynthesis) - Some work with termites (symbiosis) to help them digest wood fibre - Used by humans to make * fertilizer * ice-cream * paint * petroleum products * cosmetics * bioremediation in sediments Connection to Human Health: - Some protozoa are parasites (mostly the protozoa) - Plasmodium causes malaria - Amoeba proteus causes dysentery - Trichomonas hominis help break down materials in human intestines






