What is the tool? (PPT) - Insight Assessment Portal
advertisement

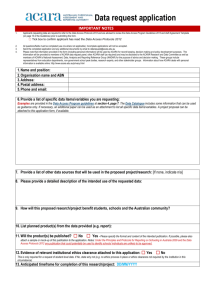
Critical and Creative Thinking Assessment Tool Session 1: What is the tool? 18 February 2015 Outline of the session • Welcome - Victoria Hall, Department of Education and Training • The Critical and Creative Thinking Assessment Tool - ACER Julian Fraillon and Ray Philpot • Questions and discussion • Next steps Accessing the Tool • The tool is available from the Insight Assessment Portal and includes: – Teacher Site, where teachers can preview and assign tasks to students and mark student responses – Student Site, where students can complete their assigned task. Valuing Critical and Creative Thinking • Thinking that is productive, purposeful and intentional is fundamental to students becoming effective and successful learners. (MCEETYA, 1999, 2008) • Critical and Creative Thinking is necessary ‘to compete in a global economy that demands innovation’ (Partnership for 21st century skills, 2013). • Responding to the challenges of the C21st – with its complex environmental, social and economic pressures – requires CCT (ACARA 2012) Valuing Critical and Creative Thinking • When information is readily accessible from a handheld device, recall of knowledge is less important than the ability to critically analyse masses of data and come up with innovative, open-ended solutions to problems. (McCurry, 2013). http://images.bwbx.io/cms/2012-06- Purpose of the Critical and Creative Thinking Assessment Tool • Provide support for the assessment of Critical and Creative Thinking by teachers (formative/summative assessment for/as learning) • Assess Critical and Creative Thinking using a standardised, trialled and quality assured set of tasks • Support assessment of Critical and Creative Thinking across the years of schooling AND in contexts across the curriculum • Provide a model to support teachers to create their own assessments of Critical and Creative Thinking Developing the Tool The Critical and Creative Thinking Construct What is critical and creative thinking? • Critical and Creative Thinking involves the ability to generate and evaluate knowledge, clarify concepts and ideas, seek possibilities, consider alternatives and solve problems. (ACARA, 2013). • The tool was developed with reference to the ACARA Critical and Creative Thinking general capability http://www.examiner.com/images/blog/wysiwyg/image/iStock_000007651615XSmall.jpg The Critical and Creative Thinking Construct • Critical and Creative Thinking can be thought of as: – dispositions (Tishman, Perkins and Jay; Ritchhart, Church and Morrison) – taxonomies of skills (Bloom; Anderson, Krathwohl et al.) – habits and frames of mind (Costa and Kallick; Gardner; de Bono) – thinking strategies (Marzano, Pickering and Pollock) – philosophical inquiry (Lipman, Sharp and Oscanyan). http://educationaljargonschs.wikispaces.com/file/view/blooms_revised_taxomony.jpg/197905582/blooms_revised_taxomony.j The Critical and Creative Thinking Construct • Critical thinking is at the core of most intellectual activity that involves students in learning to recognise or develop an argument, use evidence in support of that argument, draw reasoned conclusions, and use information to solve problems. • Creative thinking involves students in learning to generate and apply new ideas in specific contexts, seeing existing situations in a new way, identifying alternative explanations, and seeing or making new links that generate a positive outcome. (ACARA CCT General Capability) The Critical and Creative Thinking Continuum • The Critical and Creative Thinking learning continuum includes four strands: – Inquiring – Generating – Reflecting – Analysing The Critical and Creative Thinking Continuum • Inquiring – Identifying, exploring and clarifying questions and issues – Gathering, organising and processing information – Transferring knowledge into new contexts • Generating – Imagining possibilities and considering alternatives – Seeking and creating innovative pathways and solutions – Suspending judgment to visualise possibilities The Critical and Creative Thinking Continuum • Reflecting – Reflecting on thinking – Reflecting on procedures and products • Analysing – Applying logical and inventive reasoning – Drawing conclusions and designing a course of action Sample Tasks/Items • Examples from the Critical and Creative Thinking Assessment Tool Sample Task: Year 5/6 Playground • The slide in a playground is broken. Who broke it, what should replace it and how can the playground be made safe? Sample Item: Year 5/6 (Inquiring) Sample Task: Year 3/4 In the cave • An antelope becomes trapped in a cave with a lion. What strategies will help the antelope escape? Sample Item: Year 3/4 (Inquiring) Sample Item: Year 3/4 (Generating) Sample Task: Year 1/2 Possum • Information about a possum and its predators is provided. Keep Possum safe from the predators! Sample Item: Year 1/2 (Reflecting) Sample Task: Secondary – Maths/Science Detective • Assist an on-screen detective identify a mystery liquid. Sample Items: Secondary – Maths/Science (6-Generating; 7-Analysing) Sample Task: Secondary – Humanities/Social Studies Movie Star • Critically examine source material, evidence and arguments in the context of a (fictitious) movie star. Sample items: Secondary – Humanities/Social Studies (Inquiring) Sample Task: Secondary – Art Sheep Stealer • Compare and contrast two visual representations of James McKenzie, a sheep-stealer from New Zealand. Sample item: Secondary – Art (Generating) Next steps • Session 2: How do I use the tool? 4 March 2015, 4:00 – 5:00pm • Session 3: How could schools use the tool? 18 March 2015, 4:00-5:00pm • Register for the CCT Online Collaborate sessions by emailing: studentlearning@edumail.vic.gov.au. • Provide any feedback to: studentlearning@edumail.vic.gov.au.