Sem3 Chp 3
advertisement

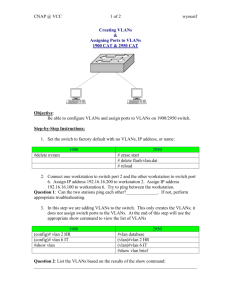
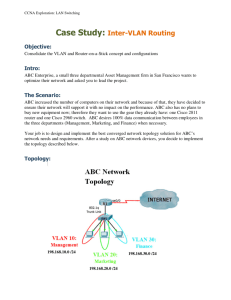
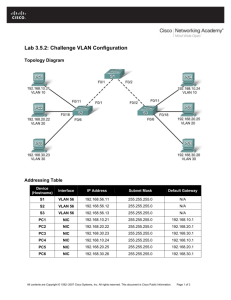
VLANs Semester 3, Chapter 3 Linda Stacy Table of Contents Go There! Virtual LANs (VLANs) Go There! Segmentation with Switching Architecture Go There! VLAN Implementation Go There! Benefits of VLANs Virtual LANs (VLANs) Table of Contents Existing Shared LAN Configurations In a typical shared LAN... Users are grouped physically based on the hub they are plugged into Routers segment the LAN and provide broadcast firewalls In VLANs... you can group users logically by function, department or application in use configuration is done through proprietary software Segmentation with Switching Architecture Table of Contents Grouping Users VLANs can logically segment users into different subnets (broadcast domains) Broadcast frames are only switched between ports on the switch or switches with the same VLAN ID. Users can be logically group via software based on: port number MAC address protocol being used application being used Differences between LANs & VLANs VLANs... work at Layer 2 & 3 control network broadcasts allow users to be assigned by net admin. provide tighter network security. How? VLANs Across the Backbone VLAN configuration needs to support backbone transport of data between interconnected routers and switches. The backbone is the area used for inter-VLAN communication The backbone should be high-speed links, typically 100Mbps or greater Router’s Role in a VLAN A router provides connection between different VLANs For example, you have VLAN1 and VLAN2. Within the switch, users on separate VLANs cannot talk to each other (benefit of a VLAN!) However, users on VLAN1 can email users on VLAN2 but they need a router to do it. How Frames are Used in a VLAN Switches make filtering and forwarding decisions based on data in the frame. There are two techniques used. Frame Filtering--examines particular information about each frame (MAC address or layer 3 protocol type) Frame Tagging--places a unique identifier in the header of each frame as it is forwarded throughout the network backbone. More on Frame Tagging Frame Tagging... is specified by IEEE 802.1q which states frame tagging is the preferred way to implement VLANs uniquely assigns a VLAN ID to each frame before it is forwarded across the backbone. is understood by switches prior to any broadcasts or transmission to other switches or routers places a tag in the frame...thus, frame tagging. So what layer? is removed by the switch after frame exits the backbone and before frame is forwarded to the end station VLAN Implementation Table of Contents Ports, VLANs, and Broadcasts Three methods for implementing VLANs Port-Centric Static Dynamic Each switched port can be assigned to a VLAN. This... ensures ports that do not share the same VLAN do not share broadcasts. ensures ports that do share the same VLAN will share broadcasts. Benefits of Port-Centric VLANs All nodes in the same VLAN are attached to the same router interface. (Note: curriculum says “switched port”) Makes management easier because... Users are assigned by router port VLANs are easy to admin. provides increased security packets do not “leak” into other domains 3 Port-Centric VLANs Static VLANs Defined Static VLANs are when ports on a switch are administratively assigned to a VLAN Benefits can be assigned by port, address, or protocol type secure, easy to configure and monitor works well in networks where moves are controlled Dynamic VLANs Defined Switch ports can automatically determine a user’s VLAN assignment based on either/or: MAC logical address protocol type When a station is initially connected to an unassigned port, the switch checks an entry in the table and dynamically configures the port with the right VLAN Benefits less administration (more upfront) when users are added or move centralized notification of unauthorized user Benefits of VLANs Table of Contents VLANs Make Changes Easier Traveling Users 20% to 40% of work force moves every year net admin’s biggest headache largest expense in managing networks. Moves may require... recabling readdressing and reconfiguration VLANs provide a way to control these costs. As long as the user still belongs to the same VLAN... simply configure the new switch port to that VLAN router configuration remains intact VLANs Control Broadcasts Routers provide an effective firewall against broadcasts Adding VLANs can extend a router’s firewall capabilities to the “switch fabric” The smaller the VLAN, the smaller the number of users that are effected by broadcasts VLANs Improve Security Shared LANs are easy to penetrate...simply plug into the shared hub. VLANs increase security by ... restricting number of users in a VLAN preventing user access without authorization configuring all unused ports to the “Disabled” setting control access by addresses application types protocol types VLANs Save Money Hub Replacement & Segmentation The ports on a non-intelligent hub can only be assigned one VLAN. Replacing hubs with switches is relatively cheap compared to the benefit gained. In the graphic, replacing the core hub in an extended star topology with a VLAN capable switch effectively microsegments one shared LAN into six. Table of Contents End Slide Show