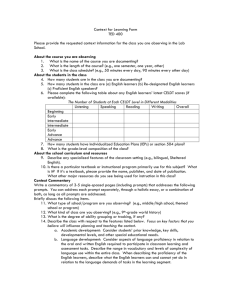
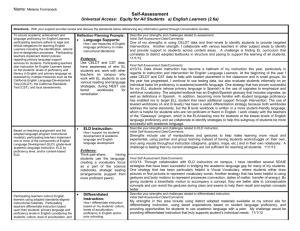
English Learner Master Plan - making
advertisement

Master Plan for English Learners Making Waves Academy -2- Master Plan for English Learners TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Identification, Assessment and placement procedures…………………………………………………………page 5 Registration and Home Language Survey English Language Proficiency Assessment Annual Fifth Grade Registration, Assessment, and Placement Primary Language Assessment Notification of Results of initial Assessment and Placement o Student Placement o Support Services o Program Placement o Annual Notification of Placement and Assessment Results Training for Staff and Administrators on Initial Identification, Placement and Parental Rights/Informed Consent Procedures for Parent Notification of Parental Exception Waivers Procedures for Approval/Denial of Parental Exception Waivers Section 311 of CA Ed. Code describes the three circumstances in which a Parental Exception Waiver may be granted 2. Instructional Programs 5-12……………………………………………………………………………………………….page 11 Achievement Goals for English Learners EL Instructional Programs Overview Structured English Immersion Program English Language Mainstream Core Curriculum (School Wide) Differentiation for Interventions English Language Development Progression through ELD Levels ELD Standards Intervention Plan Long-Term English Learners Mainstream Core content classes using Sheltered Instruction (SDAIE) Special Education Services for the English Learner Gifted and Talented Education (GATE) Monitoring Progress of English Learners with Benchmarks o Grading and Assessment o Directions for using EL Benchmark Reports Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix -3 Interventions for At-Risk English Learners Identifying ELs Who Are Not Meeting Expected Growth Monitoring of Student Progress: An Integral Aspect of the Intervention o Training on the Interventions o Evaluation of the Interventions Supporting and Monitoring Students 3. Monitoring of Student Progress and Reclassification………………………………………………………….page 22 Monitoring Student Progress School Assessment Initial Fluent English Proficient Students Overview of Reclassification Process Our School’s Reclassification Criteria: Steps to Reclassification Monitoring Procedures 4. Staffing and Professional Development…………………………………………………………………..………….page 28 Teacher Recruitment and Staffing Annual Staffing Report Recruitment Procedures for Teachers Hiring Priorities and Procedures Teacher Mis-assignment Administrative Staff Appropriate Use of Bilingual Para-educators Professional Development for Teachers needing EL Authorization EL Professional Development Plan Monitoring of Professional Development 5. Parent and Community Involvement……………………………………………………………………………….…page 32 Encouraging Parent and Community Participation Parent Advisory Committees English Learner Advisory Committee (ELAC) 6. Evaluation and Accountability………………………………………………………………………………..…………..page 35 Monitoring, Evaluation, and Accountability Program Evaluation Evaluation Design EL Program Goals EL Program Evaluation Questions Evaluating EL Program Effectiveness through Group Data Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix -4 Evaluation of Individual Student Progress 7. Funding and Resources………………………………………………………………………………………………….……page 40 Funding and Resources General Fund Resources Supplemental Funds 8. Curriculum of ELD Classes………………………………………………………………………………………………….page 43 ELD 1 ELD 2 ELD 3 ELD 4 9. State and Federal Laws pertaining to this Document Requirements for Categorical Program Monitoring…………………………………………………………….page 45 10. Glossary of Terms……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….page 53 11. Forms and/or Reference Material……………………………………………………………………………………….page 58 Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix -5- IDENTIFICATION, ASSESSMENT, AND PLACEMENT PROCEDURES Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix -6- Identification, Assessment and Placement Procedures Step 1 Parent Completes Home Language Survey Home Language other than English- Home Language is English Only- Place in Regular Mainstream Classroom Go to Step 2 Step 2 Assess English Language Fluency using CELDT Step 3 Language Classification Language Classification English Learner (EL) Language Classification Initial Fluent English Proficient(IFEP) if CELDT score is Beginning, Early Intermediate or Intermediate if CELDT score is Early Advanced or Advanced with all sub skill tests at Intermediate level or above Place in Regular Mainstream Classes Step 4 Assess Primary Language Step 5 Inform Parents of all instructional Options Parent signs Initial Placement Form at time of assessment. Step 6 Place Student in the Appropriate EL Placement Structured English Immersion English Language Mainstream CELDT overall score Begininning or Early Intermediate CELDT overall score Intermediate or Early Advanced Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix -7 Registration and Home language survey At the time of enrollment, California public schools are required to determine the language(s) spoken in the home by the student. In order to gather this information, all parents are required to complete, sign, and date the Home Language Survey for each student attending Making Waves Academy. The Home Language Survey is included in the registration packet and will remain on file for each student in the school. The registration packet is available in both English and Spanish. English Language Proficiency Assessment California regulations require that all students whose Home Language Survey indicates a language other than English on Questions 1, 2, or 3 of the Home Language Survey be assessed in 30 calendar days of their initial enrollment. A state approved assessment instrument, the California English Language Development Test (CELDT), is currently administered to determine English Proficiency Skills. The CELDT is a criterion-referenced test based on the English Language Development Standards that assess a student’s listening, speaking, reading, and writing abilities. The CELDT Assessment is administered in several parts: The speaking and listening portions are oral and are administered individually. The proctor scores as the student responds to each item. The reading and writing portions of the test are multiple-choice and are administered in a group setting. At Making Waves Academy, the CELDT is conducted by the EL Coordinator or a trained designee. A preliminary score is calculated at the school site for the purpose of placement and program options. Formal CELDT results and the Initial Parent Notification letter are placed in the EL Program folders of the student’s “Cumulative” (CUM) folder and in the Student Information System (PowerSchool). On the basis of CELDT scores, students are classified as: Initial Fluent English Proficient (IFEP) or English Learner (EL). The parents of IFEP students are informed of the results (See Parent Notification of Results Appendix 1) and student are placed in mainstream English classes. English Learner students proceed to the Primary Language Assessment. Annual Fifth Grade Registration, Assessment, and Placement Fifth grade registration begins in January when parents complete and submit a lottery packet. The lottery packet includes a questionnaire that asks about previous student programs and support services the students has received. After the student is selected from the lottery, the parent is given a registration packet that includes the Home Language Survey (HLS). If the HLS indicates a language other than English is spoken, the student will be given the CELDT test prior to the start of school. In addition, upon receipt of student transfer records from the originating school, the student’s previous language status will be honored. Primary Language Assessment All identified English Learners are assessed for primary language proficiency in listening, speaking, reading, and writing within 90 calendar days of the date of registration at the school site by a person trained in the test administration and who is a fluent speaker in the student’s primary language. At Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix -8MWA, these individuals would include but are not limited to EL teachers, para-educators or the EL Coordinator. In addition, MWA has the option of using a Primary Language Assessment, Las Links Espanol, which is available online. Results of the Primary Language Assessment are communicated to parents in the Initial Parent Notification Letter (See Parent Notification of Results), placed in the EL Folder of the student’s CUM folder and noted into the student information system (PowerSchool). The results of this testing are used to evaluate student’s literacy development in the primary language and to make program recommendations. Notification of Results of initial Assessment and Placement Parents are notified in writing using the Initial Parent Notification Letter of the results of the initial language assessment within 30 days of the receipt of the assessment scores. Additionally the letter includes, English Language proficiency, primary language proficiency, the various programs offered at MWA, and their child’s placement in the MWA programs. A copy of this letter is placed in the EL folder of the student’s CUM folder. The parents are provided a copy of all documents by the Data and Assessment Manager along with a Welcome letter from the EL Coordinator. At the start of school the EL Coordinator conducts an EL Parent Information Meeting. The purpose of this meeting is to explain English Proficiency and primary language assessment results, program options, placement at MWA, and the waiver process for an alternative program. The Data and Assessment Manager will enter the results for each student in the student information system, prepare the EL folder and places it in the Student’s CUM folder. A copy of the following form/letters are sent to the EL Coordinator: Home Language Survey, Preliminary CELDT scores, Primary Language Assessment results, Initial Parent Notification Letter, and any previous EL forms including transcripts, placement letters and reclassification forms. Student Placement In order to ensure that all students including English Learners have access to a quality education program, Making Waves Academy provides high quality English and Spanish Language Development classes as well as a comprehensive grade-level academic program in language arts, math, science, history/social studies, visual and performing arts and world languages. Once a student has been assessed EL Program Placement is determined by a student’s level of “reasonable fluency”. CELDT Score- Overall English Language Proficiency Beginner and Early Intermediate Less than reasonably fluent Intermediate (scale score ≤ 508) Less than reasonably fluent Intermediate (scale score ≥ 509) Reasonably fluent Early Advanced or Advanced Reasonably fluent Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix -9If a child is considered reasonably fluent by the above criteria a placement in the mainstream English program is recommended. Mainstream English instruction is only in English and the student is placed in classes with both EL and English only students. The EL student must also receive additional support services (See Support Services). The child continues with this placement until reclassified, the parent signs a waiver, or the program placement is deemed inappropriate. A program placement may be deemed inappropriate if the student is found to need support that is not available in the mainstream program. If a student is considered not reasonably fluent by the above criteria a placement in the Structured Immersion Program is recommended. In Structured Immersion classes, the instruction is overwhelmingly in English, with the primary language used to support the child’s learning as necessary. In addition, Structured Immersion classes consist of only EL students. The EL Student must also receive additional support services (See Support Services) Support Services These services include a class in English Language Development with the purpose of the EL students reaching full English proficiency within a reasonable period of time. In addition, one or more of the following to be determined by the MWA Response to Intervention (RTI) process: Content Instruction using SDAIE techniques Specialized instruction by a GATE certified teacher or a Resource Specialist Strategic or Intensive Intervention classes Primary Language Support Before, during and /or after school intervention programs Small group or one on one support Program Placement Once the parent is consulted about program options and the recommended placement is explained, an appropriate placement is assigned to the student based on the parent’s decision. A Program Placement Notification Form is completed and signed by the parent and the principal or designee. The program notification form is placed in the student’s EL folder in the student’s CUM folder. If the parent chooses to have their child participate in a bilingual program which is not offered at MWA then the parent completes and files a Parental Exception Waiver Form. In these circumstances the Head of School or designee will work with the home district to determine how a transfer will take place. Annual Notification of Placement and Assessment Results Once the official CELDT results have been received the parent is notified in writing using the Initial CELDT Results Parent Notification Form. A copy of this notification is placed in the Student’s EL folder in the student’s CUM folder. In addition, English Learners are tested annually with the CELDT until reclassification. Parents will receive an Annual Parent Notification Letter informing them of their child’s test results. This letter will also serve as a reminder of the program options for placement and the Parental Exception Waiver. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 10 Twice a year (September and February), teachers will receive an updated list of all English Learners with CELDT, CST and any other pertinent data available. Teachers should verify which of their students are EL’s and note the proficiency levels in their classroom list. NOTE: Although MWA has an updated database of annual EL’s CELDT scores, CELDT scores for new students may take up to 30 days from enrollment, either by obtaining scores from a former district or by administering the CELDT at MWA. Training for Staff and Administrators on Initial Identification, Placement and Parental Rights/Informed Consent To facilitate informed decision making and to improve home to school communication regarding program options and placement, MWA will provide ongoing training for staff and administrators on procedures relating to initial identification, and the use of the Parental Exception Waiver. Special Education staff will be trained in the process of appropriate placement of special education students who have language proficiency needs. Procedures for Parent Notification of Parental Exception Waivers PLEASE NOTE THAT MWA DOES NOT HAVE A PRIMARY LANGUAGE PROGRAM. IT IS STILL AN ED CODE REQUIREMENT TO INFORM THE PARENT OF THE PARENTAL EXCEPTION WAIVER. IF THE SCHOOL RECIEVES 20 AT THE SAME GRADE LEVEL IT WILL BE RESPONSIBLE FOR PROVIDING A PRIMARY LANGUAGE PROGRAM. On an annual basis, parents and guardians of English learners must be offered, through the Parental Exception Waiver process, the opportunity to request that their child(ren) participate in a program which includes instruction in the primary language. Information about these classes is provided through various District venues, including the school principal and/or designee, at Open House. It is the responsibility of the parents or guardians to apply for the waiver. Only where 20 or more approvable waivers for the same language are submitted at a grade level will a Transitional Bilingual Education or Subject Matter Bilingual Education Program (a.k.a. Alternative Primary Language) class be provided. Schools must keep a file of the waivers, and those with bilingual classes must monitor enrollees to ensure that all have waivers on file. The number of Parental Exception Waivers is reported annually on the Language Census. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 11 - INSTRUCTIONAL PROGRAMS Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 12 - Instructional Programs Achievement Goals for English Learners It is the mission of Making Waves Academy to educate and support English Learners in reaching their highest potential each school year. School resources will focus on enabling all students to achieve the following goals: Second Language Acquisition All English Learners will achieve English Proficiency as early as 8th grade and no later than 10th grade. All English Learners will meet the criteria for reclassification to Fluent English Proficiency within six years of enrolling in a California Public School. For those students that are identified as EL when entering MWA it is the goal to have all English Learners reach English Proficiency by 8th grade and no later than 10th grade. Academic Growth All students will make one or more years growth as measured using standardized tests (CST, CELDT. CAHSEE) EL Program Overview There are three types of program settings for ELs: Structured English Immersion (SEI), English Language Mainstream (ELM) and Bilingual Alternative Program (BAP). English Learner should be placed in the appropriate setting based on parent decision, CELDT score and other indicators of their ELD progress (see Student Placement). Each of these options is designed to ensure that students acquire English-language proficiency and make progress towards closing any academic deficits in all core content areas. Each option contains the following required components: Well-articulated, standards-based, differentiated English Language Development (ELD) instruction, specifically designed for English Learners and Long – term EL students Well-articulated, standards-based differentiated instruction in the core curriculum, with primary language support and/or Specially Designed Academic Instruction in English (SDAIE). Structured activities designed to develop multicultural proficiency and positive selfesteem. Administrative support is essential for a quality program that facilitates the successful academic and linguistic development of English Learners. Quality programs require support and collaboration among teachers. Articulation between grade levels is necessary for assuring a strong academic program as well as the successful acquisition of English for all English Learners. Parents are a critical component for successful programs. Their support is essential. Ongoing opportunities must be provided for both oral proficiency and literacy in English. Structured English Immersion Program A specialized process of teaching the English language to students whose first language is not English. The goal is for students to develop academic proficiency in English together with mastery of academic core content and multicultural proficiency. Instruction is nearly all in English. Primary language support is used for clarification and explanation when feasible. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 13 - Students Served: ELs who have NOT yet acquired “reasonable fluency” (reasonable fluency = CELDT overall score of early advanced (4) and intermediate (3) in all sub areas) Program Components: English Language Development (ELD) based on proficiency level for 45 minutes on Monday, Tuesday, Thursday, and Friday. No more than two consecutive levels of English proficiency may be combined for ELD instruction. Differentiated instruction in reading, writing, math, science and history/ social science, Specially designed academic instruction in English (SDAIE), GATE, or based on IEP Goals. Use state-approved, district-adopted, standards-based materials. Primary language support provided in order to motivate, clarify, direct and, explain concepts In compliance with CA Ed. Code Sections 300-400, students are placed in SEI for one year. However, if a student’s academic needs warrant it, the student may continue in an SEI classroom for up to three years. Possible Additional Support Options: Primary Language support Small groups or one on one instruction with Bilingual Instructional Assistants (BIAs) Specialized instruction from GATE or Resource Teacher Before, during and/or after school intervention/support programs (where available) Participation in strategic or intensive intervention classes Summer School Other appropriate services English Language Mainstream The goal for ELs in the English Language Mainstream Program is to develop academic proficiency in English together with mastery of academic core content and multicultural proficiency. Instruction is overwhelmingly in English. However, special support options are provided for ELs as needed. Students Served: Reclassified Fluent English Proficient students (RFEP- reclassified ELs) ELs whose parents/guardians have declined participation in the Sheltered English Immersion program ELs who have acquired “reasonable fluency” (reasonable fluency = CELDT overall score of early advanced (4) and intermediate (3) in all sub areas) Program Components: Daily English language development based on the assessed stage of acquisition, Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 14 Grouping for ELD as required to meet students needs based on ELD levels. No more than two consecutive levels of English proficiency may be combined for ELD instruction. Differentiated instruction in reading, writing, math, science and social science, delivered through specially designed academic instruction in English (SDAIE) methodology, utilizing state-approved, district-adopted, standards-based materials. Decreasing primary language support. Possible Support Options: Primary Language instruction/support Small group or one on one instruction with Bilingual Instructional Assistant (BIA) Specialized instruction by reading or literacy specialists Participation in strategic or intensive intervention classes Before and/or after school intervention/support programs (where available) Summer School Other appropriate services Core Curriculum (School Wide) At MWA, all teachers focus on a rigorous, standards based curriculum for each of the content areas. The ELD standards address skills English learners acquire during language acquisition to become proficient in the ELA Standards. All students receive the same instruction including ELs. However, additional teaching tools are utilized to provide universal access to the core content (visuals, graphic organizers, charts). Effective teaching strategies such as previewing/reviewing the lesson, paraphrasing, making frequent comprehension checks, and paired and small group instruction are essential to develop vocabulary, activate prior knowledge, build background knowledge, and promote higher level thinking and active participation of all students. Teachers differentiate instruction based on student need. Differentiation for Interventions In order to provide effective differentiation for English Learners, best practices indicate that grouping students by English language proficiency levels for ELD instruction allows ELs to develop English proficiency as quickly as possible. At MWA, students are grouped in the following ways to best support student learning: English Learners needing language support Students needing academic support Students needing Academic enrichment Opportunities English Language Development English Language Development (ELD) is a component of English Language Mainstream, and Sheltered English Immersion at MWA. It is based on the California English Language Development standards and provides a pathway to the English Language Arts (ELA) standards. ELD and ELA standards focus on developing skills related to cognitive academic proficiency in English. Instruction must develop an EL student’s full receptive and expressive proficiencies in the domains of listening, Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 15 speaking, reading and writing. ELD instruction provides a foundation to access English Language Arts curriculum. MWA supports the use of rigorous ELD instruction that includes both informal and formal language learning opportunities. A great deal of emphasis should be placed on natural language acquisition, with appropriate use of direct instruction of academic language. Teachers in the core content and ELD classes provide appropriate scaffolding to in order to make rigorous content accessible for all students. Scaffolding is a strategy that breaks concepts down into more understandable parts and assists learners to move toward new skills, concepts, or levels of understanding. Classroom instruction addresses the various levels of English proficiency. They build academic knowledge by using scaffolding, building on prior knowledge, and using academic language in a variety of ways. Making Waves Academy uses state adopted ELD materials or state recommended ELD materials that provide full access to the California ELD standards, and that can ensure effective and efficient mastery of English as a foundation for further success in mainstream English instruction. Various conditions help facilitate second language development. Language is comprehensible when: • • • • • • • • • It is in context It has real life purpose Prior knowledge is activated Background knowledge is developed The affective filter is low Risk-taking and approximations are encouraged Errors are accepted as part of the acquisition process Input is comprehensible through the use of real objects (realia), props, visuals, facial expressions, and/or gestures Positive feedback and correction by modeling are used ELD Time Requirements English Language Development is part of the daily program for every EL student. Students are assigned to classes based on individual levels of proficiency. The purpose of ELD is to teach second language learners to communicate with high levels of understanding in English. ELD also provides a foundation for literacy development (reading and writing). It is a planned, specific, explicit component of the student’s educational program. Students with EL scores 1-3 receive an average of 30 minutes of ELD instruction per day. Students with CELDT scores of 4-5 receive intervention services in Language Arts depending upon the student’s needs. ELs with CELDT levels 1 and 2 are clustered with the same teacher in order to receive Sheltered English Language Arts. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 16 - Middle School ELD Classes CELDT Levels (Approximate) ELD 1 Beginning- Early Intermediate ELD 2 Early Intermediate- Intermediate Literacy Boost- ELD Intermediate- Advanced Upper School ELD Classes CELDT Levels (Approximate) ELD 1 Beginning- Early Intermediate ELD 2 Early Intermediate- Intermediate ELD Pullout Intervention Intermediate- Advanced ELD Classes offered at MWA Progression through ELD Levels Change in ELD levels should be based on: CELDT scores ELD curriculum-based tests Classroom performance Teacher recommendation The expectation is that the majority of English learners will be reclassified by 8th grade. EL students who move to the upper school have progressed through all levels of ELD at the Middle school. These students would be considered long term English Learners (See Long Term English Learners). Students who master course content standards are promoted to the next level or exited from the program. Students may need to repeat an ELD level until they meet requirements to transition successfully to the next level. At the high schools, students receive credit toward graduation for all ELD courses, including any that are repeated. ELD Standards The ELD Standards provide guidelines for language acquisition at the Beginning, Early Intermediate, Intermediate, Early Advanced, and Advanced proficiency levels for English Learners. These address skills ELs must acquire to become proficient on the ELA Standards. The ELD standards are written as a pathway to the ELA standards. The ELD standards integrate listening, speaking, reading and writing and create a distinct pathway to reading and writing in English. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 17 Course Requirements for English Learners at MWA English Fluency (CELDT Level) Humanities Courses Math/ Science Courses Electives/ Health and Wellness Beginning CELDT 1-2` Early Intermediate CELDT 2-3 Intermediate- Advanced CELDT 3-5 Sheltered Sheltered Mainstream Sheltered Sheltered Mainstream Mainstream Mainstream Mainstream Long-Term English Learners Students classified as long term English Learners have more than six years with uninterrupted schooling in the United States. Students often have high oral fluency in English and in some cases are reasonably fluent proficiency (CELDT 4 and 5), but for a variety of reasons they have not yet achieved the academic requirements to qualify for reclassification. In determining the program placement of long term ELs, it is important to identify the student’s academic and linguistic needs and consider the following: Student’s number of years enrolled in U.S. schools Quality and consistency of English Language Development (ELD) instruction Consistency of student’s instructional program Student’s overall educational history Consideration of these factors will help determine if the student’s performance is related to his/her English Language Development, or other issues that affect the student’s academic performance. Student will need: English language learners at the upper school will need targeted intervention to address the lack of fluency achieved in grades 5-8th. Development through a SDAIE English class or an intervention class that address both language and literacy skills Sheltered or English Mainstream instruction in the core subjects provided by an appropriately CLAD certified teacher Counseling and monitoring to ensure that the students are enrolled in classes that meet high school graduation and post-secondary requirements Intervention support (before, during and/or after school) Mainstream Core content classes using Sheltered Instruction (SDAIE) All English learners receive core content instruction with English only students through the use of Sheltered Instruction called Specifically Designed Academic Instruction in English (SDAIE). SDAIE is a Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 18 methodology for maximizing students’ comprehension of English and core content by using special strategies and techniques. The basic features of SDAIE include: Liberal use of non-verbal language, visual support materials, graphic organizers (Cornell notes, T charts, Venn diagrams, etc.), Previewing text (ex: SQ3R method: Survey (titles, pictures, and bold-face vocabulary), Question, Read, Recite, and Review). Use of language modification such as pause time, questioning, pacing, and highlighting important words or concepts. Task-based instruction, allowing students to work with concepts and the language of those concepts in a variety of ways (such as acting, drawing or mapping out the concepts; using song, poetry, multimedia, chant, letters and journals to express and exemplify concepts). Language sensitive (slower pace, shorter sentences, etc.) and culture sensitive content teaching. Use of accommodations and modifications to help students access academic content. (Repeat/restate, preview key vocabulary; use a mix of large group/small group/pair activities; give a choice of assignments, peer tutors, etc.) Encouraging students to actively use language through a variety of classroom activities. Frequent checking for understanding; pausing longer for responses. Integrating assessment and instruction on an ongoing basis. Special Education Services for the English Learner English Learners have access to Special Education services just as all other students at MWA. Careful review by the Student Success Team (SST) of all referrals takes place first, to determine whether Special Education assessments (speech, language, social, emotional, or academic) are warranted or if student performance/behaviors are related to expected patterns of second language acquisition. When it is determined that an English Learner needs to be assessed, whether it be speech, academic or cognition, testing will be initiated upon parent’s written approval. When appropriate, assessment will be conducted in the primary language of the student, or English or both, making certain that cultural differences are taken into consideration when determining eligibility. Instructional decisions related to student’s language acquisition status must be described in the Individualized Education Plan (IEP) to the extent that the student’s English Language Development program relates to his/her need for Special Education services. The IEP must include a goal that addresses English Language Development. English Learners in grades K–12 with an IEP continue to receive ELD and SDAIE instruction from authorized teachers. Special Education staff, including Special Day Class staff, will receive the same training as general education staff in working with ELs. English Learners may also be served through team teaching/mainstreaming with authorized teachers. Bilingual para- Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 19 educators may be assigned to the program to provide direct support to English Learners with an IEP. Monitoring Progress of English Learners with Benchmarks MWA is in the process of developing benchmarks to monitor progress of ELs in language acquisition and academic content. Interventions for At-Risk English Learners The academic performance of ELs is monitored using Discovery Ed Benchmark Assessments in order to identify developing academic deficits. This monitoring of academic and language proficiency also continues throughout the year for two years following reclassification to ensure that students are continuing to make expected academic growth. State (CELDT, CST), MWA benchmarks (Discovery Ed), and text-embedded assessments provide information that informs instruction and alerts teachers to students that may be struggling. Students are assessed throughout the year and, if they are not performing on grade level, they are identified as in need of intervention. The state breakdown of academic proficiency is: Benchmark (approaching or at grade level) Strategic (less than 2 years below grade level) Intensive (more than 2 years below grade level) Students at the strategic or intensive level are provided extra support/classes. Their English language proficiency is also assessed to ensure that the intervention meets the student’s need, whether it is academic, linguistic or both. Identifying ELs Who Are Not Meeting Expected Growth No later than October, the EL Coordinator with the Language Review Team reviews the results of the previous spring CST results and revises or develops an English Learner Support Plan for EL students not meeting growth expectations. Parents are notified of changes and are asked for their input. Documentation is put in the ELL folder. Students are regularly monitored and adjustments and modifications to the intervention plan are made when necessary. If a student continues to make inadequate progress, they may be referred to the Student Study Team (SST) for monitoring of student progress. At the beginning of each quarter, the EL Coordinator reviews Discovery Ed, intervention assessments, and classroom performance of EL students and identifies students not meeting growth expectations. If necessary, the EL Coordinator will meet with the Language Review team to discuss possible changes to students English Learner Support Plan. Monitoring of Student Progress: An Integral Aspect of Intervention The Language Review Team will regularly monitor the progress of EL students by doing the following: • At minimum, the team will meet twice a year to review the most recent assessment data. • At this time, the LRT will possibly modify, extend, or replace interventions, when required. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 20 • In addition, the classroom teacher, EL Coordinator, and/or any other persons who have been assigned responsibility while developing the student’s English Learner Support Plan will closely and regularly monitor the student’s work to determine the efficacy of the selected interventions. • If the interventions are not offering appropriate support, the LRT will pursue other avenues of support until a correct match has been found for the referred student or other specialized assistance (i.e. Student Success Team for possible referral for Special Education testing) has been explored. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 21 - Benchmarks for English Learners in Structured English Immersion and Mainstream Programs CELDT Levels Beginning Early Intermediate CELDT Overall Score 1 2 3 4 5 4-5 CELDT Score 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 5th 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 4th 1st 2nd 3rd 3rd 1st 2nd 2nd 1st I-FEP the first year Intermediate Administered And Early Advanced Timeline toward Advanced Reclassification Criteria reclassification CST- ELA Far Below Basic Below Basic Basic Mid Basic/ Proficient Proficient/ Advanced Mid BasicProficient CST Score – Math Far Below Basic Below Basic Basic Mid Basic/ Proficient Proficient/ Advanced Mid BasicProficient MWA Benchmark Assessments Intensive Intensive/ Strategic Strategic Strategic/ Benchmark Benchmark Benchmark 275-300 300-329 330 and above 350 and above 350 and above 350 and above ELA/ Math CAHSEE Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 22 - MONITORING OF STUDENT PROGRESS AND RECLASSIFICATION Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 23 - Reclassifying a Student from English Learner to Fluent English Proficient Assessment of English Proficiency Review CELDT results NO Student remains an English Learner Student has an overall score of 4 or higher Comparison of Performance in Basic Skills Review CST-ELA results NO Student received a CST Scale Score greater than 325 Student has passed the ELA CAHSEE Teacher Evaluation of Student Academic Performance Review Student Grades Student has C’s or higher in all core classes Parent Opinion and Consultation Provide notice to parents of their right to participate in the reclassification process Encourage parents to participate in the reclassification process in a face to face meeting Reclassification of student to R-FEP Reclassify student to R-FEP Notify parents of reclassification in writing (parent signature required) Update student information system Monitor Progress for two years Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix NO Student remains an English Learner Student remains an English Learner - 24 - Monitoring of Student Progress and Reclassification Making Waves Academy reclassifies a pupil from English Learner (EL) to proficient in English by using a process and multiple criteria specified in law. MWA monitors reclassified student progress for a minimum of two years. MWA maintains key data on the process and assessments in the students’ permanent record documentation. Each English Learner (EL) who meets established reclassification criteria is reclassified as RFEP (Reclassified Fluent English Proficient). Each former EL student who has been reclassified as RFEP has demonstrated English-language proficiency comparable to that of the average native English speakers and can participate equally with them in the regular instructional program. Monitoring Student Progress Student progress is monitored annually based on a set of state and district-adopted assessments. These assessments are used to determine English language proficiency, and evaluate students’ language growth and academic performance. Formative assessments are used to monitor students ELD progress and are given throughout the school year in listening, speaking, reading and writing. School Assessment The assessments are equivalent to those used with English Only (EO) and IFEP students in the mainstream program. These include the state mandated STAR tests (California Standards Test (CST), California Alternative Performance Assessment (CAPA), California Modified Assessment (CMA), and California High School Exit Exam (CAHSEE) which are taken by all students regardless of their language classification. CELDT is taken each year by ELs to measure language proficiency until they are reclassified. In addition to state mandated tests all students take the Discovery Education Think Link assessments which are used for program placement, determination of progress in acquiring English and academic skills. Curriculum-embedded assessments in language arts are taken in English by ELs. These benchmark assessments are administered tri-annually. Students also take curriculum embedded (CE) assessments and school developed quarterly benchmarks. Teachers use the language arts and mathematics curriculum-embedded assessments to review student progress, and plan modifications in instruction and classroom interventions as appropriate. CELDT data is used for placement in appropriate ELD/SDAIE courses at the middle and high school level. Formative assessments are used by teachers to identify areas of progress and continuing needs for all groups of students. Instruction is modified to meet the needs that are revealed by the examination of this data. CST test results are used in conjunction with placement tests in language arts and mathematics to appropriately place students in benchmark, strategic or intensive intervention classes and assign them to appropriate instructional schedules. Initial Fluent English Proficient Students According to the California Department of Education definition, students who score at the early advanced or advanced proficiency level overall without any skill area below the intermediate proficiency level should be identified as Initial Fluent English Proficient (I-FEP). I-FEP students who Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 25 incur academic deficits may be monitored by the Academic Intervention Services Team to plan and oversee academic progress. Overview of Reclassification Process Making Waves Academy has adopted a reclassification process to enable students initially identified as English Learners to exit the specialized EL program services and participate without further language assistance as Fluent English Proficient students. ELs shall be reclassified as Fluent English Proficient (R-FEP) when they have acquired the skills necessary to receive instruction and achieve academic progress in English only. The reclassification criteria include multiple measures to ensure both proficiency in the English language and participation equal to that of a native speakers in the school’s regular instructional program. The reclassification criteria validate each student’s readiness to exit from specialized English learner programs, by demonstrating mastery of grade-appropriate standards in English language proficiency and academic achievement in reading and writing. Making Waves Academy’s Reclassification Criteria: Overall CELDT score of 4 or 5 (Early advanced or Advanced) with no more than one 3 (intermediate) in one sub area, CST Score of 325 or higher in English Language Arts, English Language Arts grade of “C” or better, Teacher recommendation, and Parent consultation Steps to Reclassification Each fall, the EL Coordinator with the assistance of the Data Coordinatorcollects STAR test results, the most current official CELDT scores, other assessment data, student grades, and teachers’ recommendations, for all EL students at 5th grade and above. The EL Coordinator shares the data with the Data Coordinator, Literacy Coordinator, Director of Curriculum and Instruction, and the Head of School to review and identify those students who are eligible for reclassification. Reclassification Criteria are based on multiple measures, including (See Reclassification Criteria): English language proficiency, including listening, speaking, reading and writing, Academic achievement in reading and writing in English, Teacher’s evaluation, Teacher recommendations regarding any academic performance deficits, and Parent’s recommendation In October and January of each year, the EL coordinator notifies parents/ guardians and invites them to participate in the reclassification process by providing an opportunity for the parent/ guardian to attend the Reclassification meeting.If the parent/guardian wishes to attend, the meeting is scheduled at a time convenient for the parent/guardian. The school site must make every attempt to involve the parent/guardian in the Reclassification Process through letters, phone calls, and, if possible, home visits. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 26 The reclassification decision is made at the Reclassification meeting after considering the evidence regarding the student’s performance and consulting with the parent. At the end of the Reclassification meeting decisions and recommendations are documented on the MWA Reclassification Form. 1. The EL coordinator fills out the MWA Reclassification form in the appropriate home language. 2. The classroom teacher adds their comments and signs with their initials. 3. Two copies are sent home to the parents with a request that parents sign one form and return it to school. 4. If a form is not returned then the EL Coordinator calls home to inform the parent of the reclassification process and to receive parent input or set up a date for a group conference. 5. After the conference and/or phone call, the EL coordinator signs on the form that parent comments and consent were obtained. 6. A copy of the completed form is added to the student’s CUM folder. 7. A copy of the completed form is added to a reclassification binder at the school site 8. A copy of the reclassification form is sent to the Data and Assessment office, where student information will be updated in the database.” Monitoring Procedures Students who have been reclassified as R-FEP receive follow-up monitoring for a minimum of two years after reclassification by the EL Coordinator. CST Scores in ELA and Math and academic grades must be kept for R-FEP students for two years (do not have to be consecutive) to show that each RFEP has maintained academic success. The school’s EL Coordinator maintains a roster of R-FEP students who need to be monitored while attending MWA. Follow-up occurs in November, March, and June and is done by the EL Coordinator and administration with the Language Reclassification Follow-up Form. Reclassified students having difficulty in the core curriculum will have access to the support services offered at the site to all students who are not meeting standards. Those support services will be reviewed and determined by the Academic Intervention Services Team and communicated with parents at the time of the parent conference. The AIS will use MWA’s academic support plan for at-risk students, to determine appropriate intervention measures, which may include but are not limited to any of the following: Student/teacher/parent conference Specialized academic assessment Specialized reading, writing or math instruction Placement in reading, writing or math support class Before, during or after school academic support programs Summer school Assessments of English Learners Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 27 MWA will use standards-based assessments and procedures to gather information on language acquisition and academic progress for ELs. The following are examples of assessments used: State Mandated Assessments CELDT (California English Language Development Test) STAR (CST, California Writing Assessment) CMA (California Modified Assessments) CAHSEE (California High School Exit Exam) MWA Generated Assessments: o English Language Arts: Discovery Ed Benchmark Assessments Text-embedded assessments Formative assessments Intervention curriculum embedded assessments Writing assessments Portfolio assessments o Math: Discovery Ed Benchmark Assessments Teacher-developed math assessments Intervention Math assessments Text-embedded assessments Course specific exams Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 28 - STAFFING AND PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 29 - Staffing and Professional Development Teacher Recruitment and Staffing Teachers assigned to provide English language development or access to core curriculum instruction for English Learners are appropriately authorized or are actively in training for an English Learner authorization. All newly hired teachers who do not have the required authorization are required to sign Intent Letter as a part of their contract indicating their intentions to complete the CLAD or BCLAD requirement in a specified time. MWA provides high quality professional development to classroom teachers, principals, administrators, and other school or community-based personnel that qualify existing and future personnel to provide appropriate instructional services to EL students. Annual Staffing Report Each spring, during the preparation of the Language Census Reports, the Data and Assessment Office collects information from teachers who are not certified to teach English Learners. The teachers who have made a commitment will submit information on their progress in fulfilling the requirements to the Data and Assessment Office no later than April. The English Learner Staffing Report will be completed each April by the Data and Assessment Office. This report will be shared at an ELAC meeting and kept on file. The annual staffing report will document the number of teachers who are fully credentialed and the number in training as well as results of hiring and staff training efforts each year. Recruitment Procedures for Teachers MWA ensures that all teaching personnel whose assignment includes English Learner students will hold appropriate certification to provide necessary instructional services to ELs. Teachers assigned to provide ELD, SDAIE and primary language instruction must be properly authorized or “actively pursuing” authorization as allowed by law. Hiring and placement of teachers is based on student and program needs. Proper Authorization - Multiple or Single Subject Teaching Credential with CLAD/BCLAD Emphasis CLAD/BCLAD BCC/LDS General teaching credential (ELD only) Supplementary Authorization in ESL (ELD only) University or District Internship Credential with CLAD Emphasis SB 395 or SB 1969 Proper Authorization - Primary Language (Bilingual) Multiple or Single Subject Teaching Credential with CLAD/BCLAD emphasis BCLAD BCC University or District Internship Credential with BCLAD emphasis Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 30 - Hiring Priorities and Procedures 1. Highest priority is placed on hiring teachers who have completed their EL authorization training and their placement in an appropriate classroom. 2. The second priority is to teacher candidates who are in the process of obtaining an EL authorization (candidates have one year to acquire their authorization). Teacher Mis-assignment Data and Assessment will provide the Head of School a list of certified teachers and their particular authorizations to serve English Learners. Teachers are placed according to student need. Teachers who are assigned to classrooms requiring EL Authorization but are not actively pursuing appropriate authorization are notified that if completion of needed authorization is not pursued, they will be reassigned or displaced. Administrative Staff In order to support the implementation of EL Programs and services at the school, MWA makes it a hiring priority to staff the school with administrators who possess the CLAD or BCLAD, or who are working toward this as part of their professional development. Currently employed administrators are encouraged to complete the EL Authorization. Appropriate Use of Bilingual Para-educators Bilingual Instructional Assistants contribute specialized skills in an English Learner program and work and plan closely with the full instructional team. The Bilingual Instructional Assistant (BIA) works with an EL authorized teacher to provide primary language support to motivate, clarify, direct, support and explain facts and concepts to the English Learner. The most important priority for BIAs is to be in the classroom, helping ELs understand core content instruction in language arts, math, social studies and science. BIAs are not responsible for English Language Development (ELD) instruction. This is the responsibility of the classroom credentialed teacher. BIAs, also, assist with a full spectrum of language needs outside the classroom: Parent-teacher/parent-administrator conferences and notifications ELAC and DELAC meetings CELDT testing Clerical duties (as needed) Primary language testing Oral and written translations Professional Development for Teachers needing EL Authorization The school provides training through the neighboring county offices for teachers enrolled in the program leading to California Teachers for the English Language (CTEL) Exam preparation or AB 2913 authorization. Training for BCLAD and CLAD may also be completed as part of a teaching credential program, institutions of higher learning, or other California Commission for Teacher Credentialing CTC approved programs. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 31 - EL Professional Development Plan As a means of providing access to the curriculum for all students and developing language abilities of our English Learners, MWA supports ongoing staff development to meet the needs of all school personnel that support English Learners. All school staff will receive professional development to increase awareness and sensitivity to the cultural and linguistic diversities of our student population as well as services necessary to ensure equal access of all students to the total curriculum. Our school offers and supports professional development opportunities that include but are not limited to: Procedures and Policies 1. State and Federal Mandates and Compliances 2. Fluent English Proficiency 3. Monitoring Student Achievement EL Program Design 1. EL Program Effectiveness 2. Instructional Settings Curriculum and Instruction 1. English Language Development 2. Access to the Core Curriculum 3. Assessment and Evaluation Cultural Awareness and Sensitivity Monitoring of Professional Development The EL Coordinator will report to the Head of School the professional development opportunities offered and review staff participation. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 32 - PARENT AND COMMUNITY INVOLVEMENT Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 33 - Parent and Community Involvement Encouraging Parent and Community Participation It is the goal of MWA that parents of English Learners will participate meaningfully in the education of their children. To accomplish this, the following types of activities may be carried out: • The school will provide translations and interpretation of school information. • All parents who have limited English proficiency will be provided with oral translations in the primary language. Translators are made available for parent/teacher conferences, report card night, back-to-school night, Individualized Education Plan meetings (IEP), Student Success Team Meetings (SST) and other parent meetings, school safety meetings, suspension and expulsion conferences and hearings, and for all due process actions held at the district level. • MWA has a bilingual translator (Spanish-English) who coordinates other BIAs tofunction as interpreters/translators for school/district parent meetings and events. • Parent meetings should be parent friendly: held at convenient meeting times, with childcare and food (when possible) and translation services. • The school can encourage parent volunteerism by providing opportunities for parents to volunteer and to provide training on how parents can effectively participate in school. • Training on school advocacy may be provided. Such trainings can include informational sessions on school operations and for assistance related to problems or concerns. MWA will review the EL Program with parents at the beginning of the year. The following topics will be reviewed: Placement, Reclassification, Monitoring of student language and academic progress. Parent Advisory Committees English Learner Advisory Committees at the school level provide an integrated school/parent/community group to help ensure that MWA’s program for EL students is wellplanned, effectively implemented, and ultimately successful in achieving its goals for EL students. English Learner Advisory Committee (ELAC) • Each school with 21 or more English Learners must establish a functioning ELAC. • Members are chosen by election. All parents/guardians of English Learners have an opportunity to vote. • Members receive materials and training related to carrying out their legal responsibilities. • ELAC advises the Head of School and staff on topics related to English Learners, including: 1. Development of a Single School Plan for Academic Achievement by advising site council of the goals and action plans for English Learners 2. Administration of the annual language census and the ELAC’s needs assessment Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 34 3. Efforts to make parents aware of the importance of regular school attendance. 4. The school’s program for English Learners All site ELAC documentation (calendar of ELAC dates, agendas and minutes) must be kept at the site. See Appendix for samples Implementation of ELAC The Head of School, with support from the ELD Coordinator, is responsible for establishing the ELAC. The ELD Coordinator coordinates meetings and communication/documentation between the site and district office of EL programs. Meeting dates are determined and publicized in English and Spanish in advance. Elected officers conduct the meetings. Elections for ELAC are conducted at the school site by November 1st each year. Membership composition must reflect the percentage of English Learners in the school. Membership includes parents and school staff (fewer than the number of parents.) ELAC Roles and Responsibilities: The EL Coordinator plans the ELAC meetings, attends the meetings, arranges the agenda and publicizes the agenda at least 3 days prior to the meeting. Conducts meetings (a minimum of four per year) with agendas and minutes. Meeting dates are determined collaboratively between the school and ELAC Committee and publicized in advance. The ELAC will develop and revise bylaws and elect officers every two years. Childcare and refreshments will be provided at all meetings. ELAC members receive training in EL programs, Single School plan and Annual language Census. Copies of ELAC minutes and agendas are kept on file in the EL office. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 35 - EVALUATION AND ACCOUNTABILITY Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 36 - Evaluation and Accountability Monitoring, Evaluation, and Accountability MWA is committed to working collaboratively to provide effective instructional programs for English Learners. The programs will be evaluated regularly. English Learners receive ongoing support throughout the cycle of instruction, assessment, monitoring and evaluation. By monitoring student achievement through on-going analysis of achievement data of English Learners, academic needs will be addressed, instructional needs will be identified and implemented, and program effectiveness will be continually evaluated. Program Evaluation The purpose of evaluation of the program: 1. To determine to what extent English Learners are learning English and achieving the state’s academic standards 2. To determine the effectiveness of programs and services for English Learners. 3. To determine the extent to which English learners have equitable access, including pathways to higher education 4. To inform and guide instruction. The process of monitoring, evaluating, and providing accountability will commence with the following actions: 1. School will establish academic goals for English Learners 2. The evaluation team will utilize the sample questions to guide program effectiveness based on the Master Plan for English Learners 3. Data is analyzed in order to develop appropriate instructional goals for the upcoming school year and match student needs with staff development options. Evaluation Design The Language Review Team is composed of an administrator, the ELD Coordinator, a classroom teacher, and other staff when appropriate. Parents are invited and encouraged to participate in the process. Students are invited to participate when appropriate. One purpose of the Language Review Team is to monitor the progress of EL and R-FEP students. The team recommends programs, interventions, and strategies for EL students. The Language Review Team oversees the process of reclassification of students from EL to R-FEP based on the district-established process and criteria. Evaluation of the English Learner program is the other purpose of the Language Review Team. The team will review school-wide assessment data of EL and R-FEP students, answer evaluation questions, and finally, make program recommendations to the school leadership team. The Language Review Team is expected to meet at least twice a year. EL Program Goals o Goal 1: Monitor Implementation of Master Plan for English Learners Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 37 o o o o o Goal 2: Steady progress toward and attainment of academic English language proficiency Goal 3: Steady academic progress toward and attainment of grade level academic proficiency Goal 4: Strengthen parent participation and engagement in their child’s academic plans Goal 5: EL participation in advanced academic program and enrichment opportunities Goal 6: Engage English Learners in meaningful cultural, social, and academic activities. EL Program Evaluation Questions On an annual basis the LRT will come together to analyze the effectiveness of MWA programs for English Learners and devise any modifications required to enhance student learning. Below is a set of questions that will guide the evaluation of instructional programs and services: Goal 1: Monitor Implementation of Master Plan for English Learners o Are EL Programs fully and consistently implemented in ways that meet or exceed requirements of State and Federal Law? o To what extent is the Master Plan for English Learners useful to teachers, administrators and parents as a tool to meet the needs of ELs and staff? o Are ELs at the Upper School gaining access to academically rigorous core classes? Goal 2: Steady progress toward and attainment of academic English language proficiency o Do ELs meet the State’s Title III Annual Measureable Achievement Objective 1 with regard to progress in learning English? o Do ELs meet the State’s Title III Annual Measureable Achievement Objective 2 with regard to attaining English Language Proficiency? o Are there overall proficiency gains on all sub skill tests on the CELDT for: Students residing 1-3 years in the US? Students residing 4-5 years in the US? Students residing 5 or more years in the US? Goal 3: Steady academic progress toward and attainment of grade level academic proficiency o Are increasing percentages of ELs making steady academic progress on the CST-ELA? o Are increasing percentages of ELs making steady academic progress on the CST-Math? o Are ELs who are not making steady progress being identified and provided with other support services? o Are increasing percentages of ELs meeting all criteria required for reclassification? o Does the EL sub-group meet the state’s Title I Adequate Yearly Progress target for English Language Arts? o Does the EL sub-group meet the state’s Title I Adequate Yearly Progress target for Mathematics? o Are ELs in high school making expected progress towards graduation? o Are ELs proportionately represented in : Passing the CAHSEE by 10th grade? Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 38 Meeting UC/CSU course requirements at high school graduation? Goal 4: Strengthen parent participation and engagement in their child’s academic plans o Are parents of ELs and FEP students as likely as parents of EOs to participate in school activities? o Is the rate of parent engagement increasing? Goal 5: Increase EL participation in advanced academic program and enrichment opportunities o Are ELs/R-FEPs in high school making expected progress towards graduation? o Are ELs/R-FEPs proportionately represented in : Passing the CAHSEE by 10th grade? Meeting UC/CSU course requirements at high school graduation? Goal 6: Engage English Learners in meaningful cultural, social, and academic activities. o Are ELs/ R-FEPs proportionately represented in : Extracurricular activities Athletics Clubs Community events Evaluation of Program Based on Group Data MWA’s evaluation plan for determining program effectiveness is based on the adopted state standards and includes multiple measures for each content area. The following data are reviewed by site staff: • Longitudinal CELDT results for cohort groups by school and by grade • CST (STAR) assessment data for EL Learners relative to native English-speaking peers by site and by grade level • Formative and summative curriculum assessments • Standards-aligned grades for Math and Reading/Language Arts based on multiple, local assessments The rates at which EL students are meeting the “No Child Left Behind (NCLB) Title III Annual Measurable Achievement Objectives (AMAOs)”: o AMAO 1: ELs will make progress in learning English (move up one CELDT level in overall score per academic year) o AMAO 2: ELs will attain English Proficiency based on AMAO 1. ELs move one CELDT level (overall score) per year until Reclassified Fluent English Proficient (RFEP). o AMAO 3: ELs will make steady academic progress/achieve grade level proficiency on the CST (move from far-below basic/below basic/basic/proficient in a timely fashion) • Parent feedback regarding the program implementation Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 39 • Data for R-FEP students for two years (do not have to be consecutive) to show that each R-FEP student has maintained proficient level on CST for at least two years. Evaluating EL Program Effectiveness The district has established a process and criteria to determine the effectiveness of the program(s) provided to English Learners. Site results of the assessment/evaluation are reported to parents, site staff, and the Board of Education. Program evaluation results, analyses, and planned improvement are included in the school plan. District-wide results give comprehensive direction to members of the Board of Education and district staff. Evaluation of Individual Student Progress Teachers regularly assess student progress. With this information it is determine if the student is mastering their skill level at the grade capacity. This information is also utilized to plan future instruction. This process ensures that the teachers are properly monitoring the progress of EL students by providing each student the core curriculum and making sure that they’re meeting grade level standards. The progress of EL students is formally assessed each year. Formal assessment includes the statemandated CELDT (California English Language Development Test), CST, CAT/6 and APRENDA tests, formative assessments, site developed assessments, teacher-made tests, and/or publishers’ curriculum-embedded assessments. These assessments are used to determine if individual students are making expected progress based on English Language Development standards, and content area standards. These results will also be considered when making student assignments for the next school year. Students failing to meet program goals are referred to the Language Review Team. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 40 - FUNDING AND RESOURCES Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 41 - Funding and Resources Funding and Resources The following process is used to develop plans for program operations and improvement and the allocation of funds. 1. The Heads of School and Leadership team identifies and prioritizes needs based on school goals, data analysis and allocates funds and other resources to support those needs. 2. The Head of School coordinates development of the school plan and prioritization of needs based on data, meets with school site council and ELAC committees before they approve school plan and budget. 3. Site advisory committees perform the following duties: a. The School Representative Council (SRC) participates in the school plan’s development and revisions and approves the school plan. b. English Language Acquisition Committee (ELAC) members advise and give input on the school level plan and school budget. General Fund Resources MWA uses general funds to provide the base program for all students. This includes curricular materials, teachers’ salaries, and other school services such as special education, transportation, library, food, health and counseling. Supplemental Funds Economic Impact Aid/ Limited English Proficient (EIA/LEP) Funds EIA/LEP funds are used to supplement the base program. These are integrated with other supplemental funding sources and are used for supplemental services such as: • Employment of supplemental teachers • Para-educators (BIAs) • Purchase of supplemental teaching materials • In-service training for teacher and Para-educators for developing instructional skills • Support for parent involvement activities • Parent training • Translation services • Other reasonable expenses related to the EL program Services provided through EIA/LEP funds are designed to ensure that ELs develop full proficiency in English as rapidly and effectively as possible, and to ensure that they recoup any academic deficits that may have developed in other areas of the core curriculum as a result of language barriers. Each site receives an annual entitlement of EIA/LEP funds, based on their number of identified ELs to purchase supplemental instructional materials and other supports. Title III Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 42 The federal Title III program provides funds for supplementary programs and services for English Learners. Required activities include providing instruction and instructional support services related to English language development and academic progress in the core curriculum in a manner that allows ELs to meet grade level and graduation requirements. Programs must provide professional development opportunities to school staff assigned to teach ELs. Title III funds may also be used for a variety of instructional support, curriculum development, parental involvement and related EL program activities. • • ELAP The state ELAP program provides funds for supplementary programs and services for English Learners in grades 4-8. Required activities include: • Before/After school, summer school supplemental instruction for English Learners • Tutors/Mentors • Supplemental materials Any other supplemental activity that supports English acquisition Programs must provide professional development opportunities to school staff assigned to teach ELs. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 43 - CURRICULUM OF ELD CLASSES Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 44 - Curriculum of ELD Classes MWA is in the Process of developing curriculum for all ELD classes with a completion goal of May 2013. This section will be added May 2013. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 45 - LEGAL REFERENCES STATE AND FEDERAL REQUIREMENTS (CPM) Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 46 - Legal References The complete list of State and Federal regulations or other legal mandates governing the program may not be included within this document. Applicable legal citations for this program include, but are not limited to, the following: Federal Law 20 USC 1703(f); 42 USC 2000(d); 34 CFR 100.1-100.13, 300.300, 300.343(d), 300-346(a), 300.532(a)(c), 300.552; Castañeda v. Pickard (5th Cir. 1981) 648 F.2d 989, 1009-1013; Gómez v. Illinois State Board of Education (7th Cir. 1987) 811 F.2d 1030, 1041-1042. State Law EC 305-306, 310-311, 313, 33051(a)(3), 44253, 44253.1, 44253.2, 44253.3, 44253.10, 48985, 54032, 60810-60811, 62002, 62002.5; former EC 52161, 52164.1, 52164.6, 52168, 52176; 5 CCR 3942(3), 4304-4306, 4312, 4320, 11300-11305; 83 Ops. Cal. Atty. Gen. (2000) 40. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 47 - State and Federal Requirements for Categorical Program Monitoring (CPM) Master Plan for English Learners 5.1 To help English learners meet challenging achievement academic standards, each Local Educational Agency (LEA) plan shall include a description of high-quality student academic assessments that the LEA and schools use: a. To determine the success of children in meeting the state student academic achievement standards, and to provide information to teachers, parents, and students on the progress being made toward meeting the state student academic achievement standards b. To assist in diagnosis and instruction in the classroom and to determine what revisions are needed so that English learners meet the state student academic achievement standards 5.2 Minimum required components of the plan: a. Description of programs and activities to be implemented b. Description of how funds will be used to meet all annual measurable achievement objectives c. Description of how school sites will be held accountable for: i. Meeting the annual measurable achievement objectives ii. Making adequate yearly progress for English learners iii. Annually measuring the English proficiency of English learners d. Description of how school sites will promote parental and community participation in programs e. Description of how all English learners’ programs will be carried out to ensure that English learners are served f. Assurance that the EL program is based on scientificallybased research enabling English learners to meet challenging state academic content and student academic achievement standards. Documentation: Master Plan I. Identification, Assessment and placement procedures CPM EL 4: The district has properly identified, assessed, and reported all students who have a primary language other than English. CPM EL 17: All pupils are placed in English language classrooms unless a Parent Exception Waiver has been granted for a Bilingual Alternative Program. CPM EL 18: Parents and guardians of English Learners are informed of the placement of their children in an English language classroom and are notified of an opportunity to apply for a Parental Exception Waiver for their children to participate in a Bilingual Alternative Program. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 48 - Documentation: Master Plan of Policies and Procedures, Sample Notifications (initial and annual), Sample of waivers II. Instructional Programs 5-12 CPM EL 20 & 21: The district is providing services to ELs to ensure they are acquiring English language proficiency and recoup any academic deficits that may have been incurred in other areas of the core curriculum. Each English learner receives a program of instruction in English language development in order to develop in English as rapidly and effectively as possible. The district provides additional and appropriate educational services to English Learners in Kindergarten through grade twelve in all classroom situations. These services are designed to enable ELs to overcome language barriers and must be provided until they have demonstrated English language proficiency comparable to that of the average native English speaking students and recouped any academic deficits that may have been incurred in other areas of the core curriculum as a result of language barriers. Academic instruction for ELs is designed and implemented to ensure that they meet the District’s and State’s content and performance standards for their respective grade levels in a reasonable amount of time. The district has developed and is implementing a plan for monitoring and overcoming any academic deficits ELs incur while acquiring English. Actions to overcome academic deficits are taken before the deficits become irreparable. Documentation: ELD Course and curriculum descriptions, list of ELD material used, grade level course descriptions III. Monitoring of Student Progress and Reclassification CPM EL 14: The district reclassifies a student from English Learner to proficient in English by using a process and multiple criteria as specified by law. The district monitors for a minimum of two years the progress of students reclassified to ensure correct classification, placement, and additional academic support, if needed. The district maintains key data on the process and assessments in the student’s permanent record documentation (CUM). Each English Learner who meets the established reclassification criteria is Fluent English Proficient (R-FEP). Each former EL who has been reclassified as FEP has demonstrated English language proficiency comparable to that of the average native English speakers and can participate equally with them in the regular instructional program. Documentation: Master Plan; Policies and procedures, documentation that students have met criteria, criteria for reclassification, list of EL by CELDT level, time spent in program, academic achievement, List of students reclassified as IFEP, record of two year follow-up of R-FEP IV. Staffing and Professional Development Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 49 CPM EL 15: Teachers assigned to provide English language development or access to core curriculum instruction for English Learners are appropriately authorized or are actively in training for an English Learner authorization. CPM EL 16: The district provides high-quality professional development to classroom teachers, principals, administrators, and other school or community-based personnel that qualify existing and future personnel to provide appropriate instructional services to English Learners. Documentation: Policies and procedures, list of teachers instructing ELs and their authorization, MOU’s for teachers in training, professional development records V. Parent and Community Involvement CPM EL 1: The LEA outreach to parents of English Learners includes all the required items. The LEA sends notice of and holds regular meetings for the purpose of formulating and responding to the parents’ recommendations. The LEA informs the parents how they can be involved in the education of their children and be active participants in assisting their children to: 1. Attain English proficiency 2. Achieve at high levels in core academic subjects 3. Meet challenging state academic content and achievement standards expected of all students A LEA or consortium that has failed to make progress on the annual measurable achievement objectives (AMAO) shall inform parents/guardians of English learners of such failure no later than 30 days after such failure occurs. CPM EL 2: A school site with 21 or more English learners has a functioning English Learner Advisory Committee (ELAC) that meets all requirements. CPM EL 3: An LEA with 51 or more English learners has a functioning ELAC or a subcommittee of an existing district committee in which at least 51 percent of the members are parents (not employed by the district) of English learners. CPM EL 4.3: Parents/guardians of English learners and fluent English proficient students have been notified of their child’s initial English language and primary-language proficiency assessment results and program placement. CPM EL 4.9: Parents/guardians of English learners have been notified annually of their child’s English language proficiency assessment results within 30 calendar days following receipt of results of testing from the test contractor. CPM CP 7: The LEA provides parents with information on school and parent activities in a format and, to the extent practicable, in a language the parents can understand. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 50 CPM CP 7.1: When 15 percent of students enrolled in a public school speak a single primary language other than English, as determined by language census data from the preceding year, all notices, reports, statements, and records sent to parents of such students are written in English and the primary language. Documentation: Policies and procedures, sample letter AMAO notification if school fails to meet objectives, calendar of regular scheduled parent meetings, sample of school-home communications in home languages, ELAC; bylaws, meeting calendar, notices, agenda, minutes and sign in sheets, Member roster, training materials VI. Evaluation and Accountability CPM EL 13: The LEA has implemented a process and criteria to determine the effectiveness of programs for English learners, including: a. A way to demonstrate that the programs for English learners produce, within a reasonable period of time: English language proficiency comparable to that of average native speakers of English in the district Academic results indicating that English learners are achieving and sustaining parity of academic achievement with students who entered the district’s school system already proficient in English b. An ongoing mechanism for using the procedures described above to improve program implementation and to modify the program, as needed, to ensure that each English learner achieves full proficiency in English and academic achievement at grade level. Documentation: Master Plan, Evaluation reports, LEA Plan addendum (year2) VII. Funding and Resources CPM EL 9 (See also CPM CP items 8, 10, 11 and 12): Adequate general fund resources are used to provide each English Learner with learning opportunities in an appropriate program, including English language development, and the rest of the core curriculum. The provision of such services is not contingent on the receipt of state or federal categorical aid funds. Economic Impact Aid-Limited English Proficiency (EIA-LEP) funds are used only to supplement, not supplant, the district’s general funds as well as any other categorical funds the district receives. Documentation: Consolidated Application, SPSA, Fiscal records of EIA, Job Descriptions, list of personnel funded by EIA VIII. Curriculum of ELD Classes 5.2 Minimum required components of the plan: Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 51 f. Assurance that the EL program is based on scientifically based research enabling English learners to meet challenging state academic content and student academic achievement standards. Documentation: Course descriptions and sample lesson plans Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 52 - GLOSSARY Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 53 - Glossary of Terms AMAOs: Annual Measurable Achievement Objective API: Academic Progress Index AMAO: Adequate Measurable Achievement Objective (as required by federal Title III of“No Child Left Behind” Act. APRENDA 3: Norm referenced test: Part of STAR testing program. Administered to Spanish speaking students who have: (1) been in public school 12 months or less; (2) received academic instruction in Spanish during the same school year AYP: Academic Yearly Progress BICS: Basic Interpersonal Communication Skills: language used in daily social interactions. BCC: Bilingual Certificate of Competency Bilingual, Cross-cultural, Language and Academic Development (BCLAD) Authorization: Authorizes the holder to provide English Language Development (ELD); Specially Designed Academic Instruction delivered in English (SDAIE); Instruction in the primary language and instruction for primary language development. BTSA: Beginning Teacher Support and Assessment. Purpose of BTSA as set forth in the California Ed Code, Section 44279.2 (b) is to “provide an effective transition into the teaching career for first- year and second-year teachers in California and improve the educational performance of pupils through improved training and assistance for new teachers”. CABE: California Association for Bilingual Education. CAHSEE: California High School Exit Examination CAPA: California Alternate Performance Assessment Catch Up Plan: A plan to assist ELs or RFEPs with any language or academic deficiencies. CATSOL: California Association of Teachers of Speakers of Other Languages. CDE: California Department of Education CELDT: California English Language Development Test CPM: Categorical Program Monitoring. A modification of the process previously known as the CCR (Coordinated Compliance Review). State process to monitor academic program implementation. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 54 Cross Cultural, Language and Academic Development (CLAD): Authorizes the holder to provide the student with English Language Development and Specially Designed Academic Instructiondelivered in English (SDAIE). CST: California Standards Tests CTEL: California Teacher of English Learners Examination. DELAC: District English Learner Advisory Committee. An advisory committee that advises the district’s governing board on programs and services for English Learners. EIA: (Economic Impact Aid). Supplemental state funding used for ELs. EIA/LEP: Economic Impact Aid / Limited English Proficient EL Learner: English Language Learner; also known as LEP (Limited English Proficient). Used in many state documents. ELA: English Language Arts ELAC: (English Learner Advisory Committee). A committee that advises the principal and school staff on programs and services for English Learners. ELAP: (English Language Acquisition Program) State program to supplement EL services for ELs in grades 4-8. ELD: English Language Development. A broad term encompassing all aspects of language development for English Language Learners. It includes speaking and listeningas well as reading and writing at developmentally appropriate language levels. EO: English only student ESL: English as a Second Language FEP: Fluent English Proficient. Students with a home language other than English, whose oral and written skills approximate those of English Speakers. Green (curriculum) Folder: A folder which contains all relevant information regarding the language and academic progress of ELs. GATE: Gifted and Talented Education HLS: Home Language Survey (in registration form) IEP: Individualized Educational Plan IFEP: Initially Fluent English Proficient LRT: Language Review Team. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 55 LEA: Local Education Agency LEP: Limited English Proficient L1: The language that has been identified as the student’s primary or home language. L2: Second language student acquires (usually refers to English) LDS: Language Development Coordinator Certificate. Mainstream English Program: The goal for English Learners in the mainstream program is to develop academic proficiency in English. Instruction is overwhelmingly in English. However, special support options are provided for as needed. Newcomer: A student who is a recent immigrant to the United States. OCR: Office for Civil Rights Overwhelmingly in English: Overwhelmingly in/nearly all in English is not defined in Prop 227, but its use strongly implies that some instruction be provided in the students primary language. Teachers or other instructional support personnel use the student’s primary language to motivate, clarify, direct, support, and explain. Parental Exception Waiver: Parents or legal guardians must apply in writing and in person annually. This waiver requests that the child be transferred to classes where they are taught English and other subjects through bilingual education techniques or other generally recognized educational methodologies permitted by law. Primary Language: (L1) The first language the student learns to speak at home or the most often spoken language Primary Language Support: The use of the primary language of students by a teacher or paraprofessional to facilitate teaching/learning when English is the primary medium of instruction. R-30: Annual language census report Reclassification: When a student has met all district criteria, he/ she are reclassified from EL to Reclassified Fluent Proficient (RFEP) student. RFEP: Reclassified Fluent Proficient. SRC: Site Representative Council Second Language: (L2) The second language a student learns to speak. SDAIE: Specially Designed Academic Instruction in English. A methodology used by teachers who possess the competency to make academic content comprehensible to students in English. SIP: School Improvement Program Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 56 SST: Student Study Team Structured Immersion Program: A specialized process of teaching the language to students whose first language is not English. The goal is for students to develop academic proficiency in English. Instruction is nearly all in English. Primary language support is used for clarification and explanation when available. Title III: A program providing funding to improve the education of ELs by assisting them in learning and meeting state academic standards. Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 57 - FORMS AND/OR REFERENCE MATERIALS Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix - 58 - FORMS/ REFERENCE MATERIAL FOR IDENTIFICATION, ASSESSMENT, AND PLACEMENT PROCEDURES Page Home Language Survey CELDT Proficiency Level Descriptors Sample CELDT Schedule MWA CELDT Responsibilities CELDT Skill Area Proficiency Level Descriptors by grade levels Initial Parent Notification Letter/ Initial Placement Letter Program Placement Notification EL Program Information Parent Brochure Annual Parent Notification Form Parental Exception Waivers Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix 1 2 3 4 5 10 14 15 17 18 - 59 - FORMS/ REFERENCE MATERIAL FOR INSTRUCTIONAL PROGRAMS ELD Standards CELDT Blue Prints Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix Page 1 69 - 60 - FORMS/ REFERENCE MATERIAL FOR MONITORING OF STUDENT PROGRESS AND RECLASSIFICATION Invitation for parent to attend reclassification Reclassification Criteria Reclassification Form Language Reclassification Follow- up Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix Page 1 2 3 5 - 61 - FORMS/ REFERENCE MATERIAL FOR STAFFING AND PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT Commitment Letter Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix Page 1 - 62 - FORMS/ REFERENCE MATERIAL FOR PARENT AND COMMUNITY INVOLVEMENT State Description of ELAC and its requirements Recommended 6 Meeting topics for agendas Sample ELAC Ballot Sign In Sheet Sample ELAC Bylaws Language Census Report (R-30) Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix Page 1 2 4 5 6 10 - 63 - FORMS/ REFERENCE MATERIAL FOR EVALUATION AND ACCOUNTIBLITY EL Program Evaluation Questions Red print indicates there is documentation in the appendix Page 1