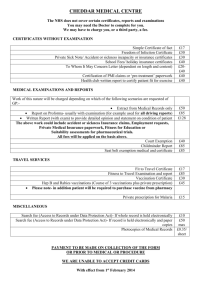
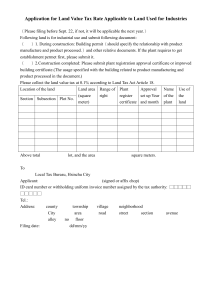
PKI Implementation in the Real World
Lessons Learned
Copyright 2003 Accenture. All rights reserved. Accenture, its logo, and Accenture Innovation Delivered are trademarks of Accenture.
Client CA Implementation
One of our current Government clients has implemented a
Certificate Authority to issue PKI certificates for Federal
Employees at participating Agencies.
Recently, they asked us to help them document and update their
processes, and help to expand their business.
We can use their example to understand a real world implementation
and gather some lessons learned.
We will call this client “US Certificate Authority,” or USCA.
Glossary
Public Key Crypto – key pairs used to encrypt/decrypt or sign/verify
Certificate – a digital method of binding a key pair or pairs to a specific
identity
Certificate Authority – the system that securely creates the certificates
Public Key Infrastructure – the whole system of creating, issuing,
managing, utilizing and revoking certificates
USCA’s CA
USCA has implemented a private Certificate Authority based
on Entrust software. It was built and is operated by USCA
employees, at a local datacenter with remote failover.
•The Certificate Authority’s primary responsibility is to ensure the
validity of each certificate and key pair that is issued.
• Secure architecture to generate keys and certificates
• Secure, enforceable processes to verify the users or systems to
whom it issues the certificates
• Unlike the Verisign model, each private Certificate Authority is part of
a closed system that is not automatically trusted by other systems or
external users.
• In order to trust the Certificates issued by the USCA, the end user has to
explicitly import and trust the Public Key of the CA or the system or
application has to trust the Public Key.
USCA’s Certificates
Each USCA User Certificate is issued with 2 key pairs and can
be used for:
•Authentication,
•Cryptography: Encryption / Decryption.
•Digital Signatures
•Enable Virtual Private Network using Checkpoint Firewalls,
•Encrypted/Digital Signature E-Mail,
•Encrypted E-Mail,
•Application Encryption and/or Digital Signature (non Web), and
•Desktop Encryption.
There have been about 5000 user certificates issued so far. In
addition, USCA can issue SSL certificates.
Overall Certificate Issuance Process
Become an NFC CA
Customer
Submit Required
Forms
Identity Proofing
Certificate Expiration
and Renewal
Certificate Recovery
Certificate Creation
Certificate Revocation
Certificate
Deactivation
User Activation
Certificate Use
Lessons Learned from this Implementation
The technology is NOT the problem. Once the technologies
are successfully implemented, the biggest problems are
user issues and process issues.
–
–
–
–
User registration
LRA identity proofing
User training
Use of certificates within applications
Identity Proofing
Once a new client group has been added to the closed
Certificate Authority, the CA is set up to issue certificates
for authorized members of the new group.
The first step is to validate who is requesting the new certificate by
identity-proofing. This is performed by a Local Registration Authority
from the client group.
–
Need to verify the identity of the new user. This is hard!
– Must be in person, which is hard for distributed organizations.
– What documents can a user present to prove they are John Doe?
– How much trust can you place on State Driver’s License and other
“breeder” documents?
User Registration
The next step is to collect information about the user and
verify that they have the approval of the client group to
receive a certificate.
–
–
–
The user information must match the information given to the
Local Registration Authority – this means that you can’t just
ask the user to type in their information, you have to build in a
process to double-check it.
The user registration process is also typically used to help
deliver the actual certificate, often by giving the user one of
multiple “tokens” that they will need to download the certificate.
Since the certificates cost the client group $$$, the approval is
important. How is this verified?
User Training
Another big problem is training the end user on how to
use their certificate.
–
–
Training is needed for end users, LRAs, RAs and Help Desk;
generally the people who actually run the system know how
things work, but using the PKI system interfaces is usually
confusing.
Users also need help actually using their certificate within their
PKI-enabled applications.
PKI Integration
Clients need to decide what are certificates used for within the
organization prior to purchasing services:
–
–
Often they get sold on the idea of PKI without a clear business
reason.
Applications must be modified in order to use certificates for signing,
encryption etc. Or, if the PKI system client is used, the client must
be embedded into the standard desktop build.
Contact Info
Dan Mellen
Daniel.W.Mellen@accenture.com
703 947 2226
Jennifer Combs
Jennifer.L.Combs@accenture.com
703 947 4093
Treb Farrales
Treb.S.Farrales@accenture.com
703 947 1942