TIMEFinalslides (1502348)
advertisement

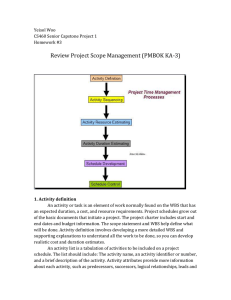
Project Time Management One Minute Thirty Second Overview My Favorite Triple Constraint View Think of it as Schedule Management • If Scope grows/changes, schedule must adapt • There will be unknowns do deal with – making it important to --define sequence of activities --estimate time needed for each one --build in some contingency time -- AND MONITOR, all the way through It is surprising how slow-going the route from 80% complete to 100% complete can be. Tools to help manage time with complex projects include GANTT Charts and Critical Path Analysis. What’s Critical Path Analysis? • The critical path is simply all the tasks that determine the end date in your project schedule. Float is…. • In project management, float or slack is the amount of time that a task in a project network can be delayed without causing a delay to: • subsequent tasks ("free float") • project completion date ("total float") • http://cms.chicostatepm.webnode.com/capm/ Time Management • Includes all the processes used to assure timely completion of the project. Most important output: the project schedule. • How it all relates…. Time • The scope planning process list of activities - Activity List is the input to activity sequencing, activity resource estimating, activity duration estimating processes. Time • The activity sequence process identifies the dependencies among the schedule activities that must be performed. Time • The main output of the activity seq. process are the diagrams used to used to show the timelines, schedule of work, and dependencies. Here’s a simple one - Time • The diagrams + activity resource requirements (simply, what you need) that you got from the resource estimating process …. • PLUS the activity duration estimates you got from the activity duration estimating process… Become the input item to the what? SCHEDULE DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Time • The schedule development process the project schedule; once approved, it becomes the schedule baseline, which becomes an input to….. SCHEDULE CONTROL PROCESS Understand How This is Fitting Together • Major task of the activity definition process is to generate the activity list by decomposing the WBS work packages into activities. • Major task of the activity sequencing process is to determine the dependencies among the activities in the activity list. This makes the list a “what-put” to the sequencing process? INPUT Time • The output of the activity sequencing process is a diagram or schema that displays the dependencies. • Once you figure out what the activity resource requirements are, you can estimate the duration of each activity. (Imagine your own schedule) Example – Activity Sequencing Example: Activity Sequencing IT Sequencing Example Any Activity Sequencing “Models real-world workflows of business processes…displays which actions need to take place, and what the dependencies are.” Time The approved project schedule acts as a baseline against which the project process is tracked. Things to be careful about… • Changing the quantity of a resource will affect the duration estimate (e.g. do more with less.) • Each activity on a critical path has zero (or negative) float time and thus poses a schedule risk. Monitor all critical path activities carefully. Also Remember • That the schedule activities are not the components of the WBS –they are components of the project schedule. • What are components of the WBS? WBS Remember for CAPM • The activity list, generated as an output of the activity definition process, becomes a component of the PM plan. Of course! • Fast-tracking compresses the schedule by performing activities in parallel which will otherwise be performed in a sequence whereas… Remember • Crashing compresses the schedule by assigning more resources. Can you think of an example of crashing, or tell us what it might look like? Have Knowledge of This for CAPM • You need to know what CRITICAL PATH refers to. • Know what “float” is and basically how to calculate it. • You can refer to the glossary on our site if needed.