Narrative has 5-8 quality sentences.
advertisement

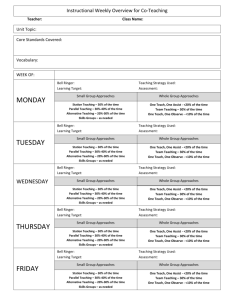
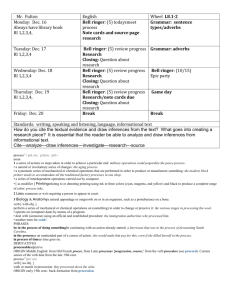
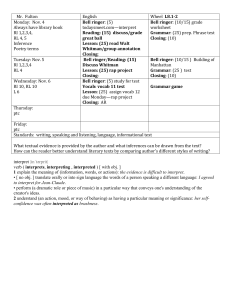
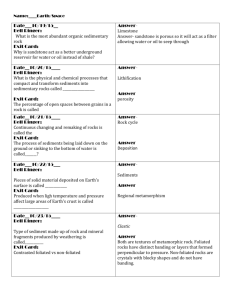
Bell Ringer #35 1/8/13 35. Briefly describe what each of these scientists contributed to the atomic model: Democritus, Lavoisier, Dalton, Thomson, and Rutherford. (You need your textbook for this one!) Bell Ringer #36 1/9/13 36. Compare and contrast the terms Element, Molecule, Atom, & Compound to each other. Bell Ringer #37 1/10/13 Describe these different parts of the atom; where are they located, what is their charge and so on. Draw an example of an atom with the parts labeled properly. Use your notes and book to help you. Bell Ringer #38 1/15/13 38. Name these elements based on their atomic number: A. 8 B. 19 C. 74 D. 86 E. 99 Bell Ringer #39 1/16/13 Explain how to and then solve for how many neutrons are in each element; name each element: A. Mg B. Zn C. Ag Bell Ringer #40 1/17/13 40. What is an isotope and explain how two isotopes of the same atom can be different. Bell Ringer #41 1/23/13 41. A chemical formula is written to indicate the makeup of a compound. What are the ratios of the individual atoms in the following compounds: Example: CO2= one carbon & two oxygen atoms A. SO2 (sulfur oxide) B. H2O (water) C. C6H12O6 (sugar) D. NaCl (salt) E. H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) Bell Ringer #42 1/24/13 42. Krypton has six naturally occurring isotopes. Complete the following table to solve for the number of protons, electron, and neutrons for each isotope. *HINT: You WILL need to be able to do this for your test! Atomic mass Kr 78 Kr 80 Kr 82 Kr 83 Kr 84 Kr 86 # of protons # of electrons # of neutrons Bell Ringer #43 1/29/13 Solve for the number of neutrons in each of the following elements and determine if they are isotopes or not. (Round the decimal of the atomic mass to the whole number.) Element Name Potassium (K) Boron (B) Arsenic (As) Lead (Pb) # of Neutrons Is it an isotope? Yes or No Bell Ringer #44 1/30/13 44. A. What is the difference between rotation and revolution? B. In relationship between the Sun, Earth, and Moon who does what? Sun, Earth, or Moon here Rotates or Revolves here Sun, Earth, or Moon here Earth Earth Bell Ringer #45 1/31/13 45. A. What are Earth’s seasons in order beginning with the season that we are currently in right now? B. What do you think is the cause for the different seasons? Bell Ringer #46 2/1/13 46. A. Explain how the Earth has its day & night, length of year, and seasons. You must use the following vocabulary words in you answer: Rotation Revolution Tilt Orbit Seasons Picture Swap 46. First off, good job with getting your work done! Explain on the other person’s paper how the Earth has its day & night, length of year, and that particular season. Also add something that you like about that person’s picture. You must use the following vocabulary words in your answer: Rotation Revolution Tilt Orbit Bell Ringer #47 2/4/13 A. If it is currently 112 degrees in Sydney, Australia, what season are they having and why? B. What season would we here in the United States be having and why? Bell Ringer #48 2/5/13 A. In regards to space, what is a satellite? B. Would the moon be considered one and why? Bell Ringer #49 2/6/13 A. What is the cause for the different phases of the moon that we see here on Earth? B. Why is it that we never see the “far side” of the moon? Bell Ringer #50 2/13/13 Why, in the Northern Hemisphere, do you think the wind patterns typically blow from the west to the east? Bell Ringer #51 2/14/13 50. A. What is a density current and how do they work? B. How is convection similar to a density current? Bell Ringer #52 2/19/13 52. Compare and contrast surface currents and density currents. You may use a Venn Diagram if you like. Bell Ringer #53 2/25/13 53. Why is the surface water cooler near San Diego, California, compared to that off the coast of Charleston, South Carolina? There was a question here. Bell Ringer #55 2/28/13 55. Without the atmosphere, the Earth’s surface would be very different. What are at least 3 ways that not having an atmosphere would affect or change on Earth’s surface? Bell Ringer #56 3/4/13 56. Identify one characteristic of each layer of the atmosphere, and explain how that characteristic affects life on Earth. Bell Ringer #57 3/5/13 57. A. What is global warming? B. What do you think may be a main cause of it? Bell Ringer #58 3/11/13 58. A. Explain the greenhouse effect. B. What are at least 3 consequences of what the results of the greenhouse effect might have on the Earth’s surface. Bell Ringer #59 3/12/13 59. A. What causes temperature changes in the atmosphere? B. What is the relationship between air temperature and density? Bell Ringer #60 3/13/13 What are the three forms of energy transfer and give an example for each of them. NOTE: Do NOT give the example from your notes or from this picture, come up with another one of your own. Bell Ringer #61 3/19/13 61. Suppose the stratosphere became covered in a thick blanket of volcanic dust that stayed suspended in the ozone. How would this affect the temperature of the air in the troposphere and why? Bell Ringer #62 3/21/13 62. A. How does the water cycle contribute to condensation? B. What are the forms that condensation can take in nature? Bell Ringer #63 3/25/13 63. Explain what humidity versus relative humidity is. Bell Ringer #64 3/26/13 64. What happens to relative humidity as the air temperature drops below the dew point? Use vocabulary terms in your answer. Bell Ringer #65 3/27/13 65. Name all of the steps of the water cycle in order and give one unique example for each step. Bell Ringer #66 3/28/13 66. Put all of the clouds in order from the highest in the atmosphere to the lowest in the atmosphere. There will be slight overlap in places. (Hint: pg. 41) B. Write one fact about EACH cloud type Cumulus Stratus Cirrus cumulonimbus Nimbostratus stratocumulus Altostratus altocumulus Cirrostratus cirrocumulus Bell Ringer #67 4/8/13 67. A. What is the difference between biotic and abiotic factors? B. List at least 3 biotic and 3 abiotic factors that you see in the picture. Bell Ringer #68 4/9/13 68. Explain what the 4 most important abiotic factors are and why they are necessary to an ecosystem. Bell Ringer #69 4/10/13 69. A. What does it mean to have a balanced ecosystem? B. Give at least 2 examples of events that might make an ecosystem unbalanced. Bell Ringer #69 70. A. What is a niche? B. What is a limiting factor? 4/10/13 2/8/13 Moon Phase Quiz today RIGHT after you enter. You should be sitting & studying! (Boys sit down & stop talking, girls you too. NOW.) Test today!!!!! Get out your assignments to be turned in. (They are listed on the board.) 4 -Grammar, capitalization, & punctuation is correct. -Narrative relates to the article. -Narrative has 5-8 quality sentences. -Does the narrative flow (makes sense)? *Has at least all of the 4 requirements with 3 or less mistakes 3 -Grammar, capitalization, & punctuation is correct. -Narrative relates to the article. -Narrative has 5-8 quality sentences. -Does the narrative flow (makes sense)? *Has at least 3 of the 4 requirements with 3 or less mistakes 2 -Grammar, capitalization, & punctuation is correct. -Narrative relates to the article. -Narrative has 5-8 quality sentences. -Does the narrative flow (makes sense)? *Has at least 2 of the 4 requirements with 3 or less mistakes 1 -Grammar, capitalization, & punctuation is correct. -Narrative relates to the article. -Narrative has 5-8 quality sentences. -Does the narrative flow (makes sense)? *Has at least 1 of the 4 requirements with 3 Time to reflect! You are to compare your Ecosystem Assessment score to the class average and reflect on several things: How you feel you did personally on the test. How did you do compared to the team average, compared to the classroom average. What can you do to prepare yourself for future assessments. Did you reach your goal that you set? If you did, explain what you did to get there. If you did not, explain what you did NOT do to prepare for the test. What is your goal (grade you want) for the next assessment? New Mineral & Rock Words (pg.256) mineral, rock, crystal, gem, ore, ingenous rock, extrusive, intrusive, sedimentary rock, metamorphic rock, foliated, nonfoliated, rock cycle, cleavage, streak, fracture, luster, hardness, lava, magma, detrital rocks, chemical rocks, organic rocks, fossils, compaction, sementation, weathering, erosion Exit Slip Question 4/23/13 Write this question down on a lined sheet of paper. At the end of class today, you should be able to answer the question from the notes and vocabulary discussed. Name and explain 3 of the physical properties of a mineral. Exit Slip Question 4/24/13 Write this question down on a lined sheet of paper. At the end of class today, you should be able to answer the question from the notes and vocabulary discussed. What are 3 of the 5 mentioned “special properties” that no other element has?