nsci_280_wk_5_www
advertisement

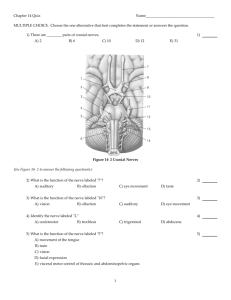
1. Name the bony structure through which each spinal nerve passes. 2. Which terminal branch of the spinal nerves contains motor innervation to muscles of the suboccipital triangle? 3. What do the dorsal and ventral roots at the same spinal cord level unite to form? 1. Name the four regions of the brain. 2. Describe the cerebrum. 3. How many cerebral hemispheres exist? 4. Name the five lobes of the cerebral hemispheres. 5. The cerebrum is considered responsible for 6. The cerebellum is composed of . . 7. The primary function of the cerebellum is . 8. The diencephalon is composed of three structures. What are they, and what are their functions? 9. Name and describe the three divisions of the brainstem. 10. Name the functions of each division of the brainstem. 11. Where do the cerebellar hemispheres attach to the brainstem? 12. The medulla oblongata extends from 13. The medulla oblongata is continuous with . . 1. List the three meninges in order from superficial to deep. 2. Name the two layers of the most superficial of the meninges. 3. Name the structures formed where these two layers split. 4. Name the space located between the middle and deepest meninges. What fills this space? 5. Name the four ventricles of the brain. 6. Describe the lateral ventricles. Where are they located? 7. Describe the third ventricle. How does it connect to the lateral ventricles? 8. Describe the cerebral aqueduct. 9. Describe the fourth ventricle. Where is it located? 10. Where is CSF located? How and where is it produced? 11. Describe the circulation of CSF. 1. In what brain structures would you expect to find (CSF)? 2. Where is this CSF produced? 3. What structure produces the CSF? 4. Beginning in the lateral ventricles, trace the flow of CSF. 5. What are arachnoid granulations? Animation: Dural Sinus Blood Flow After viewing the animation, answer these questions: 1. What are the dural venous sinuses? 2. Where are they located? 3. Name the two dural sinuses located along the midline. 4. Name the three sinuses that unite at the confluence of sinuses. 5. What vessels do the sigmoid sinuses become? 6. Name the division of the brain that includes the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. 7. Name the division of the brain that coordinates complex movements and smooths muscle contractions. 8. The primary hearing and smell areas are located in which lobe of the brain? 9. Memory is located in which lobe of the brain? 10. Speech perception and recognition areas are located in which hemisphere of which lobe of the brain? 11. What is the term that refers to the superficial gray matter of the cerebrum? 12. The reception of general sensory information from the body occurs in which lobe of the brain? 13. Tactile object recognition occurs in which lobe of the brain? 14. Language and verbatim repetition of terms occurs in which lobe of which hemisphere of the brain? 15. Name the structure that forms the floor of the longitudinal fissure. 16. Name the paired cavities containing cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. 17. Where is the falx cerebri located? 18. Name the crossing white-matter tracts between the optic nerves and the optic tracts. 19. Name two structures responsible for planning and execution of movement, muscle tone, and posture. 20. Name the slitlike, fluid-filled cavity that separates the right and left halves of the diencephalon. 21. Name the site of emotional behavior. 22. Name the structure that regulates body temperature, eating, and drinking. 23. Name the structure that controls the autonomic nervous system. 24. Name the lobe that is the primary visual area. 25. Name the lobe that controls voluntary motor activity. 26. Name the lobe that is the site of higher mental processing. 27. Name the structure continuous with the brain at the foramen magnum. 1. What are the three structures involved in vision? 2. The optic nerve runs between what two structures? 3. Describe the two parts of the retina. 4. Describe the light pathway from the eye to the brain. 5. Name the structure where the optic nerves converge. 6. Images are perceived in which lobe of the brain? 7. What structure do sound waves strike and cause to vibrate? 8. The vibrations are transferred to the three bones of the middle ear. From lateral to medial, what are those bones? 9. What structure transfers this vibration to the oval window? 10. The vibrations are then transferred to a fluid-filled chamber of the inner ear. What is that fluid, and what is the name of that chamber? 11. What is the difference in location for the detection of high-pitched and low-pitched sounds? 12. Which cranial nerve is composed of the ophthalmic, the maxillary, and the mandibular nerves? 13. Name the cranial nerve responsible for the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue. 14. Which cranial nerve has sensory fibers that monitor blood pressure at the carotid sinus? 15. Which cranial nerve is responsible for the constriction of the pupillary sphincter and accommodation of the lens for near vision? 16. Which cranial nerve is responsible for taste from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue and the muscles of facial expression? 17. Which cranial nerve has olfactory neurons on the mucosa of the anterosuperior nasal cavity? 18. Which cranial nerve controls the lateral rectus muscle of the eye? 19. Which cranial nerve is involved with hearing and balance? 20. Which cranial nerve is responsible for vision? 21. Which cranial nerve controls the extraocular muscle of the superior oblique? 22. Which cranial nerve controls all but one of the muscles of the palate, pharynx, and the intrinsic muscles of the larynx? 23. Which cranial nerve is the only one that extends beyond the head and neck?