File
advertisement

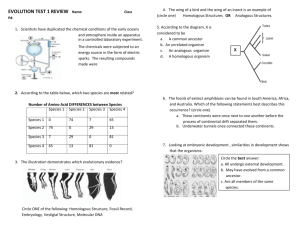
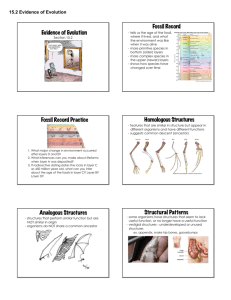
Bell Bell Ringer Ringer – 09/08 1. What are three pieces of evidence for evolution? 2. Add the following words to your flash cards: endosymbiosis, hominid Voice Level 0 Learning Target: We will investigate how comparative anatomy is used as evidence for evolution. Closure task: I can define and give examples of homologous, analogous and vestigial structures Agenda Bell Ringer 1.Radiometric dating handout 2.Flashback! 3.Evolutionary biologist notes Radiometric Dating What information is shown on the graphs? What can the graphs tell you? Compare & contrast the two graphs using a Venn Diagram. Radiometric Dating Worksheet Fossil Reflection ◉ How can you determine how old a fossil is? ◉ What do fossils tell us about evolution? ◉ Which form of dating fossils is more valuable? ◉ Create a story that explains the evolution of the fossils found in the strata model. Flashback! What was the result of endosymbiosis? A. Prokaryotes became larger B. Prokaryotes were able to move onto land C. Some prokaryotes evolved into eukaryotes D. Some prokaryotes began to do photosynthesis Which of the following molecules were not likely present on early Earth? A. Oxygen gas B. Hydrogen gas C. Methane gas D. Ammonia After an ice age, many new species began to rapidly evolve and diversify. What pattern of evolution best describes this? A. Divergent evolution B. Convergent evolution C. Gradualism D. Punctuated Equilibrium What is the difference between an autotroph and heterotroph? A. Autotrophs make their own food using photosynthesis while heterotrophs eat other organisms for food B. Autotrophs eat other organisms for food while heterotrophs make their own food using photosynthesis C. Autotrophs eat plants while heterotrophs eat meat D. Heterotrophs can do photosynthesis while autotrophs cannot How does embryology provide evidence for evolution? A. Each animal develops in the same way from early embryo to late embryo. B. The early embryos have different characteristics. C. The embryos of animals look different as they age. D. The early embryos of animals are very similar Scientists compared a short segment of DNA from 5 different organisms. Which organism most likely shares the most recent common ancestor with humans? Organism Organism 1 Organism 2 Organism 3 Organism 4 Human A. B. C. D. Organism 1 Organism 2 Organism 3 Organism 4 DNA Sequence TGTTATCGC GCGTATCCT CAGGTTACT CAATGTGGT CAGTGTACT Evolutionary Biologist In your notebook create a subtitle: Evolutionary Biologist– center and underline On the next slide – there is a description of the job of a evolutionary biologist. In ten words or less – explain what a evolutionary biologist does. What do they study? Evolutionary Biologists study the evolution of organisms. They use data collected from a variety of different sciences to contribute to our knowledge of history and explain the diversity of species. How does that contribute to evidence for evolution? They present a complete picture for how organisms have evolved over time. Using homologous and vestigial structures they illustrate relationships between organisms. What is anatomy? What is comparative anatomy? Close Read of Modern Life: Evidence for Evolutionary Change As you read: • Underline important words or phrases • Circle words or phrases you don’t understand • Write notes in the margin. • After each paragraph, write a summary/paraphrase of what you read. • In your summary include an explanation of how that relates to evidence for evolution. Exit Slip 1. The shark fin and dolphin flipper are both used for swimming, but have different bone structures. Analogous or homologous? 2. The bat wing and cat leg have different functions, but similar bone structure. Analogous or homologous? 3. How do vestigial structures provide evidence for evolution? How did you do? Rate yourself! We will investigate how comparative anatomy is used as evidence for evolution I can define and give examples of homologous, analogous and vestigial structures Evolutionary Biology Bell Bell Ringer Ringer – 09/09 1. What is the difference between analogous and homologous structures? 2. How do homologous structures provide evidence for evolution? Voice Level 0 Learning Target: We will investigate how comparative anatomy is used as evidence for evolution. Closure task: I can complete a CER on comparative anatomy. Agenda Bell Ringer 1.Comparative anatomy reading 2.Flash cards 3.Comparative anatomy CER Homework!! Due: Friday 09/11/15 Close Read of Modern Life: Evidence for Evolutionary Change As you read: • Underline important words or phrases • Circle words or phrases you don’t understand • Write notes in the margin. • After each paragraph, write a summary/paraphrase of what you read. • In your summary include an explanation of how that relates to evidence for evolution. Homologus Structures Similar in structure to other species' comparative parts. Evidence that life on Earth has a common ancient ancestor that the diverse species have evolved from over time. Homologus Structures The more closely the organisms are related, the more similar the homologous structures between organisms. Analogous Structures Structures in different species that have the same appearance, structure or function but have evolved separately → No common ancestor → Example of Convergent Evolution! Vestigial Structures Are remnants of structures that served important functions in a common ancestor Smaller, useless versions of previously important structures Comparative anatomy coloring handout Color the homologous bones for extra credit! On the back of your coloring sheet, answer the following questions: 1) Are the structures on the sheet homologous, analogous, or vestigial? Why do you think so? 2) Name 2 homologous structures that are shared between all three organisms. 3) What do the homologous structures suggest about these organisms? Comparative Anatomy Reflection 1. What does comparative anatomy suggest about the relationship between two animals? 2. What is the difference between homologous, vestigial and analogous structures? 3. What is the value in these structures as evidence for evolution? 4. Create a simile or a metaphor for vestigial, homologous and analogous structures. ExitBellSlip Ringer ◉ What are two things you clearly understand. ◉ What are two things you do not understand? How did you do? Rate yourself! We will investigate how comparative anatomy is used as evidence for evolution I can complete a CER on comparative anatomy. Voice Level 0 Bell Bell Ringer Ringer – 09/10 1. What are vestigial structures? 2. What are two examples of vestigial structures? Learning Target: We will review the forms of evidence for evolution. Closure task: I can create a foldable that describes the various pieces of evidence for evolution. Agenda Bell Ringer 1.Comparative anatomy CER 2.Evidence for evolution foldable Comparative Anatomy CER ◉ SIDE TWO! ◉ What are the qualities of a 3 or 4 CER? ◉ Be SURE to answer all of the questions that are listed in the prompts in your final product – paragraph. Flash cards! Homologous structures Analogous structures Vestigial structures Gradualism Punctuated Equilibrium Foldable: Evidence for Evolution Follow along as I demonstrate how to set up your foldable. On the inside of each flap, you must answer the question: How does this provide evidence for evolution? Homology, Analogy or Vestigial? Homologous = Analogous = Vestigial = 1. Similar forelimb structure between human, whale and bird 2. Fins of a penguin and a fish 3. The appendix in humans 4. Wings in a butterfly, bird and fly 5. Hind limbs in snakes Time for Review! Remember… Class website: Southernbio.weebly.com Homework due tomorrow! Topics on the test: 1.Miller & Urey experiment 2.History of the Earth 3.Heterotroph vs. Autotroph 4.Gradualism vs. Punctuated Equilibrium 5.Evidence for evolution 6.Homologous, analogous, & vestigial structures ExitBellSlip Ringer ◉ What will you do today to study for tomorrow’s exam? How did you do? Rate yourself! We will analyze fossil evidence and describe methods for determining the age of fossils. I can describe how the fossil record provides evidence for natural selection Evolution Test Bell Bell Ringer Ringer – 09/11 Voice Level 0 1. What are the four pieces of evidence for evolution? 2. What was the Miller & Urey experiment? Learning Target: We will review the topics on the evolution test!. Closure task: I can complete the evolution test. Agenda Bell Ringer 1.Review for test 2.Evolution test! Video!! Evidence for Evolution: • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lIEoO5KdPvg Kahoot! You may use your cell phones ONLY to play the game. If you do not have a cell phone, partner up with somebody that does. Summary What is the main importance of Lucy? • Walks on two legs! • This makes Lucy an evolutionary link between the apes and humans! Earth’s History timeline BIRTH OF A PLANET 4.6 Billion Years Ago FIRST ORGANISMS 3.5 Billion Years Ago PHOTOSYNTHESIS 3.4 Billion Years Ago BREATHABLE AIR 2.4 Billion Years Ago THE OZONE LAYER COMPLEX CELLS 2.1 Billion Years Ago 2 Billion Years Ago PLANTS COLONIZE THE LAND 460 Million Years Ago FISH THAT WALK ON LAND 400 Million Years Ago FIRST MAMMALS 220 Million Years Ago FIRST PRIMATES EVOLVE 55 Million Years Ago 3.5 Billion Years Ago FIRST ORGANISMS The oldest confirmed fossils of singled celled microorganisms. Life may have begun in warm alkaline vents on the seabed, or in open water, or on land. 3.4 Billion Years Ago PHOTOSYNTHESIS All life needs energy to survive, and the biggest source of energy for life on Earth is the Sun. Some of the early microorganisms evolved a way to use the energy from sunlight to make sugars out of simpler molecules. But unlike green plants today, the first photosynthesizing organisms did not release oxygen as a water product, so there was no oxygen in the air. 2.4 Billion Years Ago BREATHABLE AIR Some bacteria began harnessing sunlight to make sugar from carbon dioxide and water, just like plants today. These microbes pumped out oxygen as waster product, creating the oxygen-rich atmosphere we have today. 2.1 Billion Years ago THE OZONE LAYER Significant amounts of oxygen had collected in the atmosphere of the Earth and created a layer of ozone (O3). This layer of ozone blocked out the UV rays from the sun. 2 Billion Years Ago COMPLEX CELLS The first organisms were simple cells like modern bacteria, but some of them became much more internally complex. These “eukaryotes” developed lots of specialized equipment within their cells. They also had a new source of energy, objects called mitochondria that were once free living bacteria but were absorbed in a process called endosymbiosis. Endosymbiosis Prokaryote Endosymbiosis Eukaryote 460 Million Years Ago PLANTS COLONIZE THE LAND Some animals ventured onto land briefly, perhaps to lay eggs in a place without predators. Plants were the first to take up permanent residence on land. The first land plants were relatives of green algae, but they rapidly diversified. 220 Million Years Ago FIRST MAMMALS At the same time the dinosaurs were spreading and diversifying, the first mammals evolved. Early mammals such as Morganucodon were small and shrew-like, and probably only active at night. This may have spurred them to evolve warmbloodness: the ability to keep their body temperature constant. Review Timeline ◉ ◉ ◉ ◉ Important Events – Cause and Effect Bacteria gain the ability to do photosynthesis Creates oxygen and the ozone layer Allows life on land ◉ Meteor Impact ◉ Extinction of Dinosaurs ◉ Mammals and other complex animals are able to evolve ◉ Humans! Creating of the first living organisms How did the first life evolve? ◉ Small organic molecules to larger ones ◉ Chemical reactions start to make systems (ex: photosynthesis) ◉ Formation of DNA, which can self-replicate ◉ Not in video—enclosure of systems of chemical reactions by a membrane—primitive membranes can self-assemble How do we know? ◉ Miller-Urey experiment proved that complex organic molecules can form from simple, non-organic molecules. http://www.sciencechannel.com/tvshows/greatest-discoveries/videos/100greatest-discoveries-origin-of-life/ Modes of evolution Change over Time Add these terms to your notes: ◉ Catastrophism – Change only happens when Earth has been affected by sudden, short-lived, violent events – possibly worldwide. (not plausible) ◉ Gradualism – Large changes are made slowly and continuously. ◉ Punctuated Equilibrium – a period of very little change (stasis/static) then a few rapid, significant changes. Homologous, Analogous, and Vestigial structures Time for the test! ExitBellSlip Ringer ◉ How did you feel about the exam? ◉ Which topics did you struggle on? How did you do? Rate yourself! We will review the topics on the Evolution Exam. I can complete the Evolution Exam.