You should be working on your “Taking it to the Next Level” Column.
advertisement

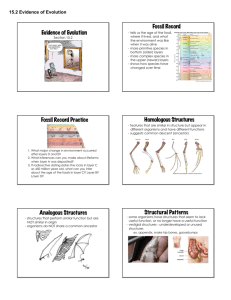
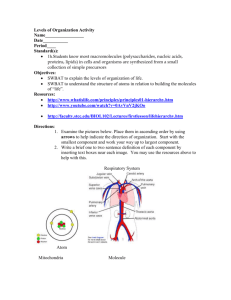
Focus Lesson: You should be working on your “Taking it to the Next Level” Column. If this was a test question could you answer it? The EOC is only 83 days away! Remember our procedures! Grab your group’s pencil box. Have your id out. Daily Objective • Explain the theories proposed on the origin of life. • Compare contradictory theories, such as the Cell Theory and the Theory of Life. • Describe the observations used to support the Theory of Evolution. How will we get there? Last Class • Notes: Hominid Evolution Pg 27 • Revisting Darwin Pg 26 • Origin of Life timeline Pg 28 Today’s Class • Origin of life notes Pg 29 • I.P. Origin of Life Pg 31 – Pg 387: 4,17,19,27 (EC18,20) • Contradicting Theories Pg 30 • Gallery Walk: Evolution Pg 32 • Home Learning – Flashcards – Page 35 WHAT WAS EARTH LIKE BILLIONS OF YEARS AGO? Violent and hot So hot that it was likely in a molten state! Air was made of ammonia, water vapor, methane and CO2 VERY little Oxygen As Earth began to cool the water vapor fell to the earth creating vast oceans. ORGANIC MOLECULE HYPOTHESIS MILLER-UREY EXPERIMENT (1953) Scientists recreated the inorganic atmosphere of early Earth Simulated lightning to demonstrate how electrical current could create organic molecules from a mixture of gases. Organic molecules created included amino acids. Why is this monomer so important to life? REVIEW Organic compounds contain what TWO atoms? Carbon Hydrogen Organic Molecules must be formed before life can exist WHAT WAS THE FIRST LIFE LIKE? Anaerobic organisms…why? Single celled prokaryotes Asexual Reproduction Heterotrophs…why? WHAT CAME NEXT? • Autotrophs…why? • Endosymbiosis The creation of the Eukaryotic cell. Smaller free-living bacteria were enclosed within a larger cell becoming what we know today as organelles • Multicellular organisms • Sexual Reproduction--how would this influence evolution? • HUMANS WHICH ONES ARE BIOTIC? ABIOTIC? PAGE 31- INDEPENDENT PRACTICE Volume level zero Using the textbook answer questions 4, 17, 19, 27 from page 387 If you complete earlier than time is called complete extra credit questions 18 20 Make me Proud! PAGE 30 In your notebook: Compare and Contrast the Theory of the Origin of Life with the cell theory proposed by Francisco Redi? Recall that Francisco Redi disproved spontaneous generation in the 17th century. HOME LEARNING Create flashcards for any new vocabulary. #YOLO Remember to keep an open mind when discussing theories. It is not a fact It is not something that has to be proven It is one attempt to answer questions raised by observation. (EX AMPL E: HAV I N G A LON GER NECK WOULD BE A FAVORAB L E T RAI T B EC AUS E T H E Y C A N E AT M O R E F O O D ! ) OBJECTIVES SWBAT explain why fossil records are evidence for the theory of evolution. SWBAT explain how geographic isolation and environmental differences leads to speciation. SWBAT describe how homologous structures and similar embryology demonstrate common ancestry. SWBAT define the concept of coevolution. INTRODUCTION Evolutionary biology's rarely get all of the pieces of what they are studying. So what do they do?? Make inferences!! GALLERY WALK: PAGE 32 Each group will travel to different stations around the room to view different pictures. At each picture the group must answer the prompts. REFLECT Debrief: What inferences did you make at these pictures? What type of evidence might paleontologists (people that study fossils) find that would allow them to see the big picture of a species’ evolutionary past? A B C D E F BIG QUESTION Before fancy technology, how did people figure out what evolved from what? FOSSIL RECORDS Mineralized material (ex. bone). Records changes in a species over time. Can see possible common ancestry between 2 species. FOSSILS AND STRATIGRAPHY How do scientist’s know how old fossils are? STRATIGRAPHY- the order of rock and dirt layers in the soil. Science was pioneered by Charles Lyell. Law of Superposition states that new material will accumulate ABOVE older material. A homo ergaster is found below a homo erectus. What conclusion can you draw based on Lyell’s law? ANATOMY Homologous Structures: body parts on different species that are similar and most likely evolved from a common ancestor. MISCONCEPTION You may see the words analogous structures on the EOC This is NOT the SAME!!! Analogous Structures: Two UNRELATED organisms have similar functions Similar Problem= Similar Solution EMBRYOLOGY Similar features of embryos (unborn offspring) in different organisms suggest evolution from a common ancestor. VESTIGIAL STRUCTURES Structures that had a function in an early ancestor but are no longer useful VESTIGIAL STRUCTURES CONTINUED Organisms that share these structures share a common ancestor. Shrink because they no longer have a function Other examples include: eyebrows, male nipples BIOGEOGRAPHY Geographic isolation and environmental differences could lead to speciation. Speciation= formation of new species. COEVOLUTION Coevolution: process in which 2+ species evolve in response to changes in each other. “An arms race between interacting species” Example: Bat vs. Moth http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O8psKvn0_3w BACK TO OUR BIG QUESTION… Before fancy technology, how did people figure out what evolved from what? WE DO! This picture describes the process of ___________ This picture describes the process of ___________ This picture describes the process of ___________ This picture is an example of ____________________ WHAT ARE 5 METHODS WE CAN USE TO PROVE COMMON ANCESTRY BETWEEN TWO SPECIES? Embryology Fossil Records Homologous structures Vestigial Structures Biogeography HOME LEARNING: PAGE 35 Apply your knowledge on this worksheet. You will have a quiz next class that covers: Darwin and Natural Selection Hominid Evolution Origin of Life Evidence of Evolution THIS IS A BIG QUIZ! PREPARE YOURSELF WITH THIS PRACTICE, FLASHCARDS AND REVIEW!