MENSTRUATION
Euphemisms for Menstrual Period
all anal sex week
aunt Rose (Ruby, May, etc.) is visiting
bitchy witchy week
Bloody Mary
blow job week
crimson tide, crimson wave
the Curse
closed for maintenance
code red
MENSTRUATION
Euphemisms for Menstrual Period (Cont’d)
Dracula’s tea bag
red flag
leak week
Little Red Riding Hood in the woods
monthly visitor
Mother Nature’s gift
Mother Nature’s curse
oil change
Old Faithful
MENSTRUATION
Euphemisms for Menstrual Period (Cont’d)
the rag
rag time
raining down South
riding the cotton cowboy
scarlet letter
shark bait
TOM (time of the month)
trolling for vampires
wound of Eve
MENSTRUATION
Menses: latin plural of ‘month’: mensis
Onset:
Menarche – mean age: 12.6
1900:
Mean age 16
Diet
changes, body fat
Lasts until Age 45-55
MENSTRUATION
Historically menses rare event:
This Century:
Pregnant or lactating
38 years x 12 months = 456 periods subtract two kids:
24 months = 432 periods vs. about 40 before.
More estrogen circulating = reproductive cancers?
Is there a comparable event or process in
males?
First ejaculation: spermarche (with or without
orgasm) around age 13-14, usually does not
contain mature sperm until 1-2 years later.
Nocturnal emissions or wet dreams.
MENSTRUATION
PSYCHO-SOCIO-CULTURAL CONTEXT
Ancient views:
power, bleed but don’t die!
Ceremonies:
red ochre, many cultures
associated with the moon, “moon blood”
goddesses of ancient religions associated with the
moon, fertility
calendars based on the moon
blood seen as cleansing and with magic powers
Patriarchal societies:
dangerous
evil, dirty
ruins crops, food
isolation
MENSTRUATION
PSYCHO-SOCIO-CULTURAL CONTEXT (CONT’D)
Contemporary
view:
disease model
• pain
• disability
• mood swings
• bloating, discomfort
• shameful
• curtail activities
• no sex
• PMS
MENSTRUATION
PSYCHO-SOCIO-CULTURAL CONTEXT (CONT’D)
to hormonal fluctuations – no
scientific data
Men’s hormones fluctuate in 24 hrs. many
times
Social contagion
Attributed
MENSTRUATION
PSYCHO-SOCIO-CULTURAL CONTEXT (CONT’D)
Amenorrhea
primary
secondary (medications, weight loss,
pregnancy, etc.)
Dysmenorrhea:
pain – prostaglandins
MENSTRUATION
Role
of Pharmaceutical Industry
Very negative expectations anxiety
physical symptoms
Unhealthy diet, no exercise, smoking
Endometriosis
Diane Ruble’s research
Katharina Dalton (England) murder
acquittals due to PMS
MENSTRUATION
Feminine
role:
sweet
soft
pliable
never angry
PMS:
allowed to rage
Severe PMS: PREMENSTRUAL DYSPHORIC DISORDER
(DSM) very contested, not evidence based
MENSTRUATION
Medicalization:
50’s Valium
90’s Prozac (Sarafem)
PMS
not universal
studies failed to show a decrement
or fluctuation in physical (sports) or
intellectual performances in the
LUTEAL or premenstrual phase
MENSTRUATION
Sex
During Menstruation:
cultural, religious taboos
up to people involved
no medical contraindication
orgasm relieves cramps
MENSTRUATION
Sex Drive and Cycle:
3 Reported Peaks:
1. at ovulation:
•
•
increase in testosterone causes more
interest in sex
increase in estrogen makes women
sexier, more attractive to men
2. just before/during menses
3. just after menses
MENSTRUATION
Why not have sex during menses?
dirty, unhygienic
2. told not to
3. might catch disease
4. uncomfortable
5. embarrassing
Almost 100% no oral sex
Masturbation increases
1.
70+% avoid it, give these reasons:
MENSTRUATION
Hormonal
Interplay:
Hypothalamus:
• GNRH: gonadotrophin-releasing hormone
Uterine Phases:
•
•
•
•
menstrual (days 1-5)
proliferative (days 6-13)
ovulatory (day 14)
secretory (rest of cycle)
MENSTRUATION
Hormonal Interplay (Cont’d):
Ovarian Phases:
• follicular (days 1-12)
• ovulatory (days 12-15)
• luteal (days 16-28)
Pituitary:
FSH
LH
Ovarian Follicle:
Estrogens and Progesterone
MENSTRUATION
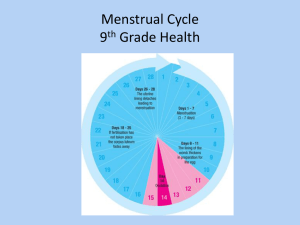
MENSTRUAL
CYCLE:
28 days
Days 1-5:
• low estrogen in blood signals the pituitary to
secrete lots of FSH, which stimulates the follicles
in the ovary (one each cycle). An egg ripens.
Endometrium grows. Estrogen increases.
Days 10-14:
• Ovum continues to grow and bursts free of follicle
on day 14: ovulation. Endometrium at its thickest,
in preparation for possible pregnancy. High levels
of estrogen signal the pituitary to decrease FSH
and also signal the hypothalamus to produce
GNRH. GNRH signals the pituitary to produce LH.
MENSTRUATION
MENSTRUAL
CYCLE:
28 days
Days 15-28:
• The follicle turns into the corpus luteum (yellow
body), which makes lots of progesterone (to
maintain pregnancy). High levels of progesterone
signal the pituitary to stop LH production, and the
corpus luteum degenerates toward day 26. This
leads to a sharp decrease in estrogen and
progesterone and the cycle starts anew.
All
these feed-back loops go through the
hypothalamus, as only the hypothalamus
can influence the pituitary.
MENSTRUATION
Ovulation:
Mittelschmerz (pain of the middle of the
month)
Anovulatory cycles (esp. adolescents and
climacteric)
Basal body temperature fluctuations
There is an OTC kit that analyzes saliva and
pinpoints ovulation
• saliva ferns at ovulation just like ovulatory mucus
MENSTRUATION
Ovulation
(Cont’d):
Changes in cervical mucus during
cycle:
• Regular functions of non-ovulatory
mucus:
lubrication
bacteriostatic
pH regulation (acid)
It is cloudy, whitish, thick, most of
cycle
MENSTRUATION
Ovulation
(Cont’d):
Ovulatory cervical mucus:
• days 12-16 of cycle duration varies, some women
only hours. It is transparent, very stretchy, like raw
egg white
Functions:
•
•
•
•
To help sperm
regulating pH (normal to alkaline)
sugars
conveyor (fern pattern)
CHANGES IN BASAL BODY TEMPERATURE
TEMP.
MENSTRUATION
New
Pill Suppresses Menstruation
What might the consequences be?
Benefits
MENSTRUATION
Warning:
Menstrual products can be hazardous to your health!
• Presence of staphilococcus aureus, particularly
when using tampons, can lead to toxic shock
syndrome (TSS), can be fatal.
• Absorbent fibers also absorb normal vaginal
secretions, leading to drying and, occasionally,
ulceration, painful intercourse.
• Bleaching chemicals: dioxin – used in “sanitary”
products:
powerful carcinogen
can affect hormones
immunosuppressant
endometriosis
Environmental Damage
Disposable
sanitary products contaminate
water sources, both at factory sites and
when disposed.
Dioxin affects fish, birds, etc.
If incinerated, toxic gases released (acid
rain, global warming)
Alternative products are available!