Reproductive System Test

Reproductive System Test
_____ 1. How do the reproductive cells of males and females differ in terms of production and storage ability?
A. mature sperm are stored for long periods in the reproductive tract while the eggs of the female are not mature when they are stored
B. the male system produces fewer gametes thatn the female system does
C. more of the structures of the female reproductive system are external than those of the male repductive system
D. the female system produces gametes for more of the individual’s lifespan than the male system does
_____ 2. Accessory organs of the male reproductive system include all of the following except:
A. seminal vesicles
B. prostate glands
C. the scrotum
D. bulbourethral gland
_____ 3. Which of the following are not components of the male reproductive system:
A. ureters
B. accessory glands and organs that secrete fluid into the ducts of the reproductive system
C. ducts that receive and transport the gametes
D. the external genitalia
_____ 4. The pathway of the spermatozoa from the testes to the exterior of the body through tubules in the correct order is:
A. epididymis, ductus deferens, urethra, ejaculatory duct, and seminal vesicles
B. epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory duct, and the urethra
C. seminal vesicles, ejaculatory duct, urethra and epididymis
D. ductus deferens, ejaculatory duct, and the urethra
_____ 5. The main function of the uterus is to provide a site for fertilization, nourish and protect the growing fetus, and provide a pathway to the exterior for the female gametes.
A. true B. false
_____ 6. Components of the female reproductive system include all of the following except:
A. the ovaries
B. the vagina
C. the uterine tubes
D. the bulbourethral glands
_____ 7. The rete testis:
A. is connected to the epididymis by fifteen to twenty efferent ducts
B. form the septa of the testis
C. contains interstial cells
D. is contained in the seminiferous tubules
_____ 8. Which of the following is not a function of the testosterone?
A. determination of the secondary sexual characteristics
B. stimulation of spermatogenesis
C. promotion of physical and functional maturation of spermatozoa
D. none of the above is an exception; all of the above are functions of testosterone
_____ 9. The process whereby sperm cells are produced is:
A. spermatogenesis
_____ 10. In the testis, the first step in the process of meiosis is:
A. production of 4 primary spermatocytes
B. spermiogensis
C. production of interstitial cells in response to a surge in the production of LH
D. division of a primary spermatocyte to produce a pair of secondary spermatocytes
_____ 11. The lining of the uterus is called the:
A. endometrium
_____ 12. Which of the following is not a uterine function?
A. mechanical protection of the developing embryo
B. site of fertilization
C. waste removal for the developing embryo
D. nutritional support of the growing embryo
_____ 13. The phases of the menstrual cycle, in correct order, are listed in which of the following choices?
A. menses, oogenesis and proliferative phase
B. menses, proliferative phases, and secretory phase
C. proliferative phase, atresia, oogenesis, secretory phase and menses
D. menses, secretory phase, oogenesis, atresia and proliferative phase
_____ 14. The rising levels of estrogen as the point of ovulation nears triggers a massive release of _________ from the anterior pituitary:
A. LH B. inhibin
_____ 15. The function of the placenta is to:
C. GH D. FSH
A. produce hormones and facilitate gas and nutrient exchange between the fetus and mother
B. store gases and nutrients for later delievery to the fetus
C. allow direct exchange of blood between the mother and fetus for nutrition
D. support the weight of the developing fetus in the uterus
_____ 16. Menopause:
A. does not always occur in females
B. is a time of peak fertility for a woman
C. occurs monthly as a normal part of a woman’s cycle
D. occurs because of a shortage of primordial follicles and causes menstruation and ovulation to cease
_____ 17. The reproductive organs that produce gametes and hormones are the:
A. accessory glands
B. gonads
C. vagina and penis
D. all of the above
_____ 18. Which of the following statements about the bulbourethral glands is true?
A. they are located at the base of the penis
B. they contribute less that 5 percent of the semen volume
C. they secrete an alkaline mucous
D. all of the above
_____ 19. In the process of spermatogenesis, the developmental sequence is:
A. spermatocytes, spermatogonia, spermatids, spermatozoa
B. spermatogonia, spermatocytes, spermatids, spermatozoa
C. spermatogonia, spermatids, spermatocytes, spermatozoa
D. spermatids, spermatozoa, spermatogonia, spermatocytes
_____ 20. Starting at the superior end, the uterus in the femae is divided into:
A. fundus, body, cervix
B. body, cervix, fundus
C. cervix, body, fundus
D. body, fundus, cervix
_____ 21. The proper sequence that describes the ovarian cycle involves the formation of:
A. primary follicles, secondary follicles, corpus, luteum and ovulation
B. corpus luteum, primary follicles, secondary follicles and ovulation
C. ovulation, corpus luteum, secondary follicle and primary follicle
D. primary follicles, secondary follicles, ovulation, corpus luteum
_____ 22. Th e prostate, seminal vesicle and bulbourethral glands do not:
A. provide chemicals to make the female’s vagina more acidic
B. activate spermatozoa
C. provide nutrients spermatozoa needed for motility
D. cleanse the urethra
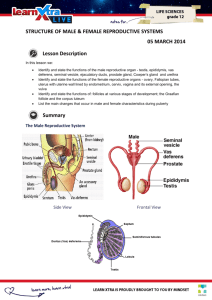
Male Reproductive System Matching:
_____ 23. Coiled tube where sperm mature
_____ 24. Produces testosterone
_____ 25. Holds the enzymes needed to enter the egg
_____ 26. The capsule that surround each testis
_____ 27. Moves the sperm by peristalsis from the
epididymis to the ejaculatory duct
_____ 28. Contains the ductus deferens, blood vessels, and nerves in a connective tissue sheath
_____ 29. Cutting of the ductus deferens at the level of the testes to prevent transportation of sperm
_____ 30. Produces a thick secretion that makes up 60% of semen and provides fructose for the sperm
_____ 31. A gland that surrounds the upper part of the urethra and secretes a milky fluid that helps activate the sperm
_____ 32. A gland that produces a thick mucus to cleanse the urethra of acidic urine
_____ 33. The stem cell of spermatogenesis
A. acrosome
B. bulbourethral gland
C. epididymus
D. prostate gland
E. seminal vesicles
F. spermatic cord
G. spermatogonia
H. tunica albuginea
I. vas deferens
J. vasectomy
Female Reproductive System Matching:
_____ 33. The principle hormone that prepares the uterus for pregnancy is:
_____ 34. The rupture of the follicular wall and ovulation
are caused by:
_____ 35. When the egg is mature the follicle ruptures
_____ 36. A hollow organ that receives, retains, and nourishes a fertilized egg
_____ 37. The inner layer of the uterus that allows for implantation or sloughs of if not pregnant
_____ 38. The female stem cells found in a developing fetus
_____ 39. The developmental stage that begins with 16 cells through the ninth week
_____ 40. Hormone that is secreted by the blastocyst and stimulates
the corpus luteum to continue producing hormones
_____ 41. Projection of the blastocyst that cooperate with cells of the uterus to form the placenta
_____ 42. The result of the fusion of DNA from sperm and egg
_____ 43. The serous layer on the outer portion of the uterus
_____ 44. The narrowing portion of the uterus
TRUE or FALSE:
_____ 45. Females are born with their total supply of eggs
_____ 46. The secondary oocyte is completely mature at ovulation
_____ 47. Functional layer of the endometrium is sloughed
_____ 48. On average the oocyte is viable for 48 hours
_____ 49. The ovary is directly attached to the fallopian tubes
_____ 50. The embryo attaches to the fallopian tube and begins it maturation process
A. cervix
B. chorionic villi
C. embryo
D. endometrium
E. hCG
F. luteinizing hormone
G. oogonia
H. ovulation
I. progesterone
J. uterus
K. visceral peritoneum
L. zygote