Microeconomics AP Syllabus-2014-15 MWHS
advertisement

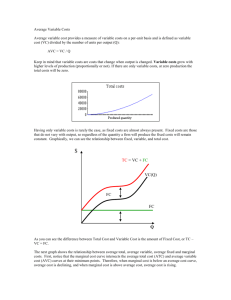
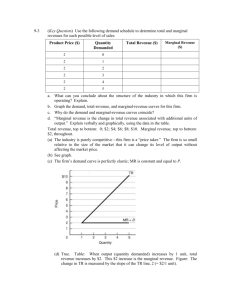
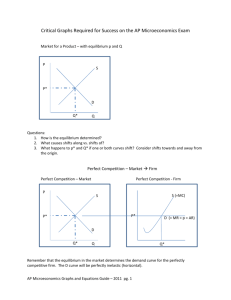
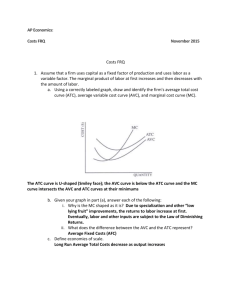
ADVANCED PLACEMENT MICROECONOMICS Magnolia West High school-2014-2015 Jeremy Day-281-252-2550 (jday@magnoliaisd.org) WELCOME TO AP Microeconomics! Microeconomics is the study of how individuals, households, businesses, and government make economic decisions in the context of different types of markets and economic circumstances. AP Microeconomics will prepare students to take the corresponding Advanced Placement Exam in May. PURPOSES The course goals are: 1. To give students an understanding of microeconomic concepts and theories. 2. To enable students to use these concepts to analyze current economic problems and issues. 3. To give students practical experience in communicating their understanding of various economic issues through both written and oral means. 4. To develop in students the “economic way of thinking”—the economist’s systematic use of analytical decision-making skills to discuss and solve problems. TEXT Principles of Microeconomics by N. Gregory Mankiw EXPECTATIONS Class preparation and participation are extremely important. The classroom is a place of mutual respect with learning as our goal. Students are expected to model such respect and encouragement. Incomplete or late assignments will be severely penalized. If a student is absent on the day an assignment is due, that assignment is due upon the student’s return to class. If a student is absent from class, it is his/her responsibility to obtain all make-up work from the teacher and fellow students and to arrange any necessary make-up assessments. The reading for this course is both exciting and rigorous. It is the student’s responsibility to set aside time to thoroughly read each section of the assigned material. Mastery of this material will prove invaluable during class discussions, activities, lectures, and on the AP exam itself. All other policies stated in the MWHS Student Handbook are in effect in the classroom setting. For grading guidelines please see the schools website. EXAMS AND QUIZZES Quizzes and Exams will be given throughout the semester in order to assess understanding of course material and to prepare students for the AP Microeconomics Exam. These assessments will model the actual AP exam in terms of both time and structure so that students become continually more comfortable with both aspects of AP testing. I will give surprise quizzes randomly to make sure you are understanding the material. I will average your quiz grades and that will count as one of your summative grades. AP EXAM Students are strongly encouraged to take the AP exam in May. If they make a 3 or higher on the test, most colleges will grant them a 3 hour credit for economics. This is a tremendous opportunity for the student to gain credit while in high school at a minimal cost. Tutoring I am available most days before school in my room or by appointment after school. Students are encouraged to stop by for questions, review, and extra help. Closer to the actual exam date, after-school review sessions will also be scheduled. My phone number and email address can also be found at the top of the syllabus. Please feel free to contact me with any questions or concerns throughout the semester. Things Needed for Class 1 Box of Dry Erase Markers 1 Ream of 8x11 Computer Paper 1 3 ring Binder 1 Cracking the AP Economics Macro & Micro Exams, 2010 Edition Bring your AP Packets everyday( I will give these to you) Complete and return to Mr. DAY I have read and understand the requirements, expectations, and grading procedures for Advanced Placement Microeconomics. Student Name ______________________________________ Date ____________ Student signature________________________________________Date____________ Parent Signature ________________________________________ Date ___________ Unit 1 Scarcity, choice, and opportunity cost Production possibilities curve Comparative advantage, specialization, and trade(Hatfields and McCoys) Economic systems(Traditional, Command, and Market) Property rights and the role of incentives-Free Enterprise System Marginal analysis-Equations for Margins-MC, MR, MU, and MP Circular Flow Model Accountants vs Economist Implicit/Explicit Cost Unit 2 Demand-Reading the Graph Quantity Demanded Law of Demand Inferior and Normal Goods Change in Demand Curve Supply-Reading the Graph Quantity Supplied Law Supply Change in Supply Curve The Date-Equilibrium Price Floors and Ceilings Shortages/Surpluses-Ticket Scalpers are good Consumer Surplus Producer Surplus Elastic/Inelastic-Determinants Perfectly Elastic/Inelastic Midpoint Formula/Total Revenue Formula Taxes Deadweight Loss Total Revenue from Tax Import and Exports Unit 3 Utility and Production Utility-Total and Margin Equation-MU Utility Maximization-How many Hamburgers to Buy Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility Reading the Graph-Relate to Demand Curve Production of Cookies-How many workers is too many Total Production Marginal Production Equation for Marginal Production Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns-Too many cooks in the Kitchen Average Production-Equation and what does it mean? AP and MP relationship Unit 4 Cost Curves Fixed Cost-Definition and Reading the Curve Variable Cost-Definition and Reading the Curve Total Cost-Definition Relationship with VC and FC Total cost versus Unit Cost Average Costs-Definition Average Fixed Cost-Definition and Reading the Graph Average Variable Cost-LODMR Relation Average Total Cost-Relationship with AFC and AVC Short-run Atc curves Long-run Atc-Economies of Scale, Diseconomies of Scale and Constant Returns Marginal Cost-Equation, LODMR, and relationship with AVC and ATC Unit 5 Perfect Competition Firm Characteristics of Firm Market Sets Price Marginal Revenue-Equation Average Revenue-Equation Marginal Revenue=Marginal Cost Marginal Revenue, Price, Average Revenue, and Price Magic Q-How many to Produce Profit Maximization Point=Magic Q Calculating Profits and Losses Normal Profits or Zero Economic Gain Short-run FC-Sunk AVC=Open/Closed ATC=Open/Shutdown Supply Curve-Mc>AVC Short-run Supply Curve-Mc>ATC Long-run MC/AVC/ATC/MR-Moving up or down Long-run always at Zeg Allocative Efficiency and Productivly Efficient Unit 6 Monopolies Characteristics How they Form Government Laws Stopping them Reason MR is always less then Price Profit Maximization Point-Magic Q Finding the Price Calculating Profits and Losses Deadweight Losses Inefficiency of Monopolies-AE and PE Price Discrimination Perfect Price Discrimination Natural Monopolies Regulated Versus Unregulated Monopolies Social Optimum Unit 7 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Characteristics of Monopolistic Competition Reading the Graph Finding Profit Maximization and Magic Q Long-run Zero Economic Gain Efficiency Oligopolies Characteristics Collusion/Cartels Game Theory Follow the Leader Tendencies Kinked Demand Curve Model Efficiency Unit 8 Labor/Resource Market/Wages Calculating Marginal Revenue Products MRP=MRC MRPL Labor/Capital and MRP Wage Market and Firm Pure Competition Labor Market Monosony Labor Market Unit 9 Market Failures Understanding Society versus Firm MSC and MPC MSB and MPB Positive and Negative Externalities Taxes and Subsidies Public goods versus private goods Free Rider antitrust policy Regulation Income distribution Equity Sources of income inequality