Civ 101-03 1-26-15 CLASS 3 *Prehistory and Early Cultures" & *The
advertisement

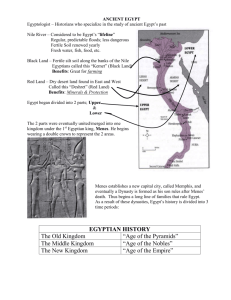
CIV 101-02 8-31-15 CLASS 3 “PREHISTORY AND EARLY CULTURES" & “THE RISE OF CIVILIZATION: MESOPOTAMIA” “The West” and the “other” parts that lead to it The Mesopotamian Parts (sort of) and the parts the lead to PRE-MESOPOTAMIA (PRE-3500BC) MAJOR CONTRIBUTIONS TO CIVILIZATION Speech Farming, esp. irrigation Boats Bricks Popular arts (weaving, dyeing, tanning, pottery) Lighting with oil lamps Tool use, stone then metal Writing (and all it brings) Construction methods Metal works Trade outside cohort From Timetables of History, Bernard Grun, Simon & Schuster, 1979, p. 2-3. PRE-MESOPOTAMIA MAJOR CONTRIBUTIONS TO WESTERN CIVILIZATION ? By 4000 BC, parts of Mesopotamia had the wheel. The wheel (and carts) didn’t get to Egypt right away, but eventually, get to the West. Later to China. The other innovations . . . Were . . . But other civilizations, esp. the Chinese also had many of them near the times of appearance in the West. AND, the south (Africa) took a lot from their close connections (Egypt) but ended up with different cultural outcomes. MESOPOTAMIA MAJOR CONTRIBUTIONS TO CIVILIZATION Oral epic literature (some that would eventually be written down) Code of Hammurabi & Law More and improved modes of writing (moving toward letters as we know them) Religious variety, with specificity, headed toward personification Headed toward Math Objects as adornments Wood and clay architecture Walled cities Ziggurats (“prepyramids” w/specific shapes, designs, executions, and towers) Reverse side of a pictographic tablet from Jamdat Nasr, near Kish, Iraq, ca. 3000 B.C.E., listing accounts involving animals and various commodities including bread and beer. Sumerian writing from pictographic script to cuneiform script To phonetic system. MESOPOTAMIA MAJOR CONTRIBUTIONS TO WESTERN CIVILIZATION ? Code of Hammurabi & Law More and improved modes of writing (moving toward letters as we know them) Religious variety, with specificity, headed toward personification “Urbanization” (city systems), some with fortifications tied to the politics TIMELINE REMINDER: Our book discusses Prehistory Then Mesopotamians Sumerian, Akkadian, Babylonian Then Egypt Then Heirs to Meso-Egypt Assyrians, Neo-Babylonians, Medes, Persians TIMELINE REMINDER: Remember: a lot of the Mesopotamians overlap with Egypt For example, Hammurabi’s Babylonian Laws (and the bronze) are presented on pages 1213. Egypt is covered from 15-26. But Hammurabi’s Laws (and the bronze) date to 1700 BC - - - pretty close to the MIDDLE of the 3,000 year period covered in the Egypt section . . . NOT before them, as the page numbering would suggest. EGYPT EGYPT: 3,000 YEARS Approximate dates, fully rounded EGYPT: 3,000 YEARS Old Kingdom: 2700-2185 BC First Intermediate: 2185-2050 BC Middle Kingdom:2050-1800 BC Second Intermediate: 1800-1552 BC New Kingdom: 1552-1079 BC Third Intermediate: 1079-732 BC Late Kingdom: 732-30 BC Dates with more precision OLD KINGDOM: 2700-2185 BC 3rd – 6th Dynasties The Great Pyramids were constructed in the 4th Dynasty within the Old Kingdom, (2613-2498 BC) The Great Sphinx. Ca. 2560 BCE. 65 ft high x 240 ft long. Great pyramids of Gizeh: from left to right, Menkure, ca. 2575 b.c.e., Khufu (Khefren), ca. 2650 b.c.e., Khafre, ca. 2600 b.c.e. Top height approx. 480 ft FIRST INTERMEDIATE: 2185-2050 BC War, famine, and fragmentation among the people. Conquest by Thebes: Montjuhotep I succeeded in subduing the entire country. MIDDLE KINGDOM: 2050-1800 BC 11th-14th Dynasties El Lahun, Pyramid of Senusret II SECOND INTERMEDIATE: 1800-1552 BC The original folks take (back over) from the foreigner Thebes but are also co-opted by the Hyksos NEW KINGDOM: 1552-1079 BC 18th-20th Dynasties Statue of Hatshepsut as Pharoah, 18th Dynasty, c. 1495 B.C.E. Granite, 7' 11" high. Roughly the time of Moses and the exodus.. Maybe around 1446 BC 1279-1213: The reign of Ramses II brings Egypt to the height of its power THIRD INTERMEDIATE: 1079-732 BC Civil wars and decline in the Imperial kingdom (abroad) Threats and Conquests by Assyrians Neo-Babylonians Persians LATE KINGDOM: 732-30 BC 25th Dynasty through Roman Rule Eventually, all roads lead to Rome