Cells Cell Structure & Function Cells & Energy Cell Growth & Division
advertisement

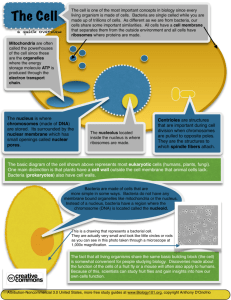
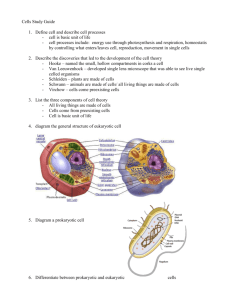
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ow0j H2Eg8v4 What are the eight characteristics of living things? What are the four major macromolecules? 1. Made up of cells 2. Reproduce 3. Maintain Homeostasis 4. Metabolism 5. Evolution /Adapt 6. Respond to Stimuli 7. Grow and Develop 8. DNA Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, and Nucleic Acids Arises by evolutionary change leading to the present biodiversity we see. Divided into Three Domains: 1. Bacteria- single celled prokaryotes (no nucleus) 2. Archaea- single celled prokaryotes (no nucleus) 3. Eukarya- Plants and Animals, complex organelles and multicellular DOMAINS Bacteria Archaea Eukarya KINGDOMS Eubacteria Archaea AnimaliaAnimals Plantae- Plants Fungi- Fungus Protista- animal like and plant like True bacteria, mostly heterotrophic, live in all sorts of environments Largest groups of organisms on Earth Only a small amount are disease causing Most have very important roles: Photoautotrophs such as cyanobacteria Saprophytes- decomposers that break down dead material. Symbionts- they have a relationship with other organisms Most recent domain, 1970’s Live in extreme environments with high temperatures and some produce methane. Vast difference in genetic and biochemical make-up from other bacterium. Microscopically similar in looks so it is likely that it has been around for a long time but we just missed it. Live in extreme environments Hot springs, hydrothermal vents, extremely acidic or alkaline water, anoxic mud swamps, petroleum deposits, and the digestive tracts of cows, termites, and marine life where they produce methane. Has a pigment that makes it purple called bacteriorhodopsin, which also helps it synthesize ATP. San Francisco Bay http://www.newscientist.com/article/dn 20577-hidden-ecologies-salt-ponds-andentombed-marshes.html#.VB97I1eKVEM Eukarytotes= have a nucleus, are unicellular and multicellular 4 Kingdoms 1. Kingdom Protista: unicellular eukaryotes, multicellular algae (dinoflagellates, diatoms, etc) 2. Kingdom Plantae: have cells walls, cellulose, and obtain energy through photosynthesis. 3. Kingdom Fungi: Cell walls are made of chitin, obtain energy by secreting enzymes and absorb the products they release. 4. Kingdom Animalia- no cell walls, obtain energy by ingesting other organisms. Carl Linnaeus (1707-1778) He came up with a means of naming organisms that was simple and universal. Problem- before this people were naming organisms multiple names that were really long, and there wasn’t any consistency. Taxonomy- science of classifying organisms and assigning each organism a universally accepted name. Linnaeus came up with binomial nomenclature-> two word naming system Genus, species Always in italics Genus is capitalized and species lowercased Ex- Homo sapiens Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Dear King Phillip Came Over From Great Spain!!!! Cyto= cell Iso= Equal Kary= Kernel Hyper= Above Endo= Within Hypo= Below Exo= Out of First to identify cells by observing cork from the bark of an oak tree. 1665 Described living things and observed them in greater detail. Called them “animalcules” 1674 Found that plants are made of cells 1838 All living things are made of cells 1839 Proposed that cells come from preexisting cells 1855 1. All organisms are made of cells 2.All existing cells come from preexisting cells 3. Cells are the basic unit of life. http://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-wacky-historyof-cell-theory#watch The way they are shaped directly relates to their job or function. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u54b RpbSOgs 1. Long, thin nerve cells transmit sensory info from your brain to the rest of your body. 2. Short, blocky skin cells that cover and protect the body. Nerve Cells http://www.pinterest.com/pin/32088216071181270/ White blood cell engulfing a bacteria cell and spewing out the remnants http://www.nature.com/naturejobs/2013 /130815/images/nj7462-367a-i1.0.jpg http://io9.com/photos-of-the-amazingand-gruesome-world-under-a-micros1291328130 Inside the chloroplast of a plant cell Eyelashes! http://www.ebaumsworld.com/pictures/view/83877873/ Bacteria on the tongue http://www.ebaumsworld.com/pictures/ view/83877873/ Artery and blood cells http://www.ebaumsworld.com/pictures/ view/83877873/ Clump of sperm tails in the testes http://www.ebaumsworld.com/pictures/ view/83877873/ Staphylococcus bacteria in the trachea http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/12 812/enlarge Liver cell http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/31 0232/enlarge Lung Cells http://images.sciencesource.com/preview /14917208/SQ7335.html http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HNP1EA YLhOs&feature=fvwrel http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rpj0emE GShQ&feature=related 1. Prokaryotic 2. Eukaryotic No nucleus or membrane bound organelles DNA is suspended in the cytoplasm and circular Single celled Cell Walls Evolved 3.5 bya Ex- Bacteria or Archaea Divided into groups based on their need for oxygen: Obligate anaerobes- cannot survive in the presence of oxygen. Obligate aerobe- needs oxygen to survive Facultative aerobe- can survive whether or not oxygen is present. Cytoplasm Cell membrane Pili Cell Wall www.biologyjunction.com DNA Ribosomes Flagella Pili- help prokaryotes stick to the surfaces Flagellum- tail like structure used for movement. Plasmid- small piece of DNA that replicates separately from the main chromosome. DNA- shaped in a loop or circle and is located in the cytoplasm. Cytoplasm- jellylike substance that surrounds molecules and organelles in a cell Cell wall- structural support Cell membrane- controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell. Provide nutrients to humans and animals, especially in digestion. Bacteria have a symbiotic relationship called mutualism where both the host and bacteria benefit. The bacteria has a home and obtains food from the host while at the same time the bacteria helps the host by breaking down foods and helping them absorb nutrients and vitamins. Important in the ecosystem- some produce oxygen while others help cycle carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and phosphorus through the environment. Bioremediation- using living things to break down pollutants. Some bacteria can digest oil= clean up oil spills. Can attack the cells in tissues. Tuberculosis / TB, is caused by a bacteria that invades the lungs and uses the tissues for nutrients Can make poisons called toxins Blood carries it to other parts of the body. Food poisoning E. coli bacteria on a lettuce leaf http://io9.com/photos-of-the-amazing-and-gruesome-world-under-amicros-1291328130 Antibiotics are used to fight bacterial disease Chemicals that kill or slow the growth of bacteria Work by stopping the cell wall from developing, animal cells don’t have cell walls, viruses also lack cell walls When you take antibiotics it can kill the good bacteria= illness Antibiotic Resistance: Overuse of the antibiotics has caused certain strains of bacteria to become resistant to medications, which allows the bacteria to survive and reproduce and pass the genetics on. Has a nucleus with membrane bound organelles Nucleus store the genetic material and is linear Multicellular or unicellular Larger, more complex Plants and animals Evolved 1.5 mya * Microscopic in size * Composed of similar building blocks * Cell Membrane * Cytoplasm * Have DNA * Loaded with ribosome's Ranges from smallest to largest Level Cell Organelle Cell Tissue Function Example Tiny organelles that each have specific functions. Mitochondria Basic unit of life. Plant or Animal Cell A group of similar cells that work together. Muscle Tissue Organ Collection of tissues joined together Lungs Organ System Organism Collection of organs that work together for a similar goal. Respiratory System A living thing Human Defined- Process where a generic cell develops into a specific type of cell. Example-> zygote -> embryo Allows germ cells, stem cells, and somatic cells to develop and mature. Crucial for embryonic development, plays a role in the functioning of many organisms throughout their lives. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rAB KB5aS2Zg&feature=related Description- Thin covering, protects cells, made up of two layers- hydrophobic fatty acid tails and hydrophilic glycerol / phosphate heads Function- Controls the passage into and out of the cell, semi-permeable= some things come in and some things go out. Description- Jellylike substance throughout the cell Function- Cushions organelles, transports proteins, nucleic acids, minerals, and ions Description- Network of proteins that is constantly changing to meet the needs of a cell. Function- Protects, structural support and shape 1. Microtubules= long hollow tubes. Give cells its shape and acts as “tracks” for organelle movement. 2. Intermediate filaments- give a cell its strength 3. Microfilaments- tiny threads that allow the cell to move and divide. Help the muscle contract and relax. Description- Plants only, made up of cellulose, rigid, tough Function- Protects, supports, and shapes the cell. Process- Turgor Pressure Description- Fluid filled sacs Function- Full of water, nutrients, and waste that is on its way out. Process- Storage Description- Large fluid filled sac in plants only Function- Used for storage of materials needed by the cell such as water, food, enzymes, and inorganic molecules. Process- Storage Description- Plants only, green structure with chlorophyll Function- Carry out photosynthesis by capturing and converting solar energy. Process- Photosynthesis Description-Small sacs that divide some materials from the cytoplasm Function- transport materials from place to place in a cell through the cytoplasm Process- Exocytosis and Endocytosis Description- In the nucleus, made of DNA and protein, contains genes Function- To package DNA into a smaller volume so that it can fit into a cell. Process- Cell Division Description- Dense, ball shaped structure, contains DNA, Storehouse of the DNA Function- Protein synthesis occurs here, control center of the cell Process-Processes DNA and Protein Synthesis Description- Dense region in the middle of the nucleus, dark ball Function- Ribosome's are made here Process- Protein Synthesis Description- Double membrane around the nucleus Function- Protects the nucleus and has pores around it for molecules to pass in and out Description- little holes around the membrane of the nucleus Function- Allows things to move in and out of the nucleus. Description- No ribosomes, Lots of folds, inner membrane= lumen Functions- Makes proteins and lipids, controls calcium levels in muscles, breaks down drugs and alcohol Process- Detoxification, Synthesis of Carbs and Lipids Description- Covered in ribosomes and attached to the nucleus Function- Produces, transports enzymes and proteins throughout the cell. Process- Processing Proteins Description- tiny little balls throughout the cell. Function- Makes proteins and RNA, tiny balls that link amino acids together to form proteins, site of protein synthesis Process- Protein Synthesis Description- Small region of cytoplasm that produces microtubules, contains centrioles. Function- During mitosis this divides and the two parts move to opposite sides of the cell. Process- Cell Division Description- Small bags with tubes connecting them and contains enzymes Function- Processes, sorts, packages, and delivers proteins and carbohydrates into vesicles for export out of the cell. Process- Processes Proteins Description- kidney bean shaped organelle Function- Supplies energy to the cell, converts food into energy (glucose into ATP), have their own ribosomes and DNA Process- Cellular Respiration Description- small cylinders Function- Helps divide DNA during cell division Process- Mitosis / Meiosis Description- Small, round structures that contain enzymes Function- Contains digestive enzymes, nutrients and old cells are broken down and digested, and defend a cell from invading bacteria and viruses. Process- Digestion, Phagocytosis Description- flagella = tail-like, cilia= hair-like Function- Help the cell move Process- Movement http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LP7xAr2 FDFU&feature=related http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.h tm