Motherboards
advertisement

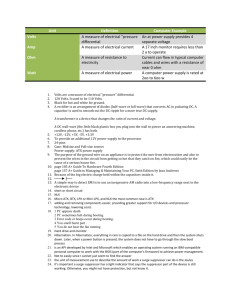
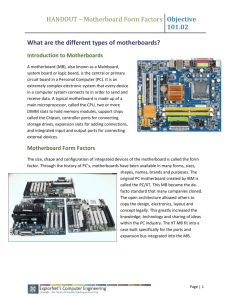
14. Motherboards Dezső Sima Fall 2006 D. Sima, 2006 Overview • 1 Predecessors • 2 Desktop motherboards • • • 2.1 Overview • 2.2 AT • 2.3 Baby AT • 2.4 LPX • 2.5 ATX • 2.6 NLX • 2.7 BTX 3 Server/workstation motherboards 4 Overview of the evolution of motherboards 1. Predecessors (1) AT Designation Type 5150 1 IBM/PC IBM/PC-XT 2 5160 Mod. 087 4.77 16 KB 3/83 8088 4.77 128 KB 64 KB Soldered+DIPP no 5 1/4 no 5 - 256 KB DIPP no 5 1/4 360 K 10 MB 8 - 8.5"*12" 216*305 5 1/4 1.2 M - 2 6 12"*13.8" 305*350 Type 1 MOB 360 K 20 MB 2 6 12"*13.8" 305*350 Type 1 MOB 1/2 6 256 KB 512 KB DIPP no 5170 Mod. 099 8/84 80286 6 512 KB 512 KB DIPP no 3 4 Mod. 339 IBM/PC XT-286 4 8088 4 5162 HD No. of ISA slots Motherboard size (standard) 8-bit 16-bit inches mm MB Chipset 80286 Mod. 319 3 8/81 Mhz FD (standard) Size KB Memory Type 8/84 Mod. 239 2 Proc. type 5170 Mod. 068 IBM/PC-AT 1 fc Memory size Min. Max. on-board on-board Date of intro. Remarks 10/85 80286 6 512 KB 512 KB DIPP no 3 720 K 30 MB 2 6 9.3"*13.8" 238*350 Type 2 MOB 4/86 80286 8 512 KB 512 KB DIPP no 3 1/2 1.44 M 30 MB 2 6 9.3"*13.8" 238*350 Type 2 MOB 4/86 80286 8 512 KB 512 KB DIPP no 3 1/2 5 1/4 1.44 M 30 MB 2 6 9.3"*13.8" 238*350 Type 2 MOB 5 8.6"*13" 218*330 9/86 80286 6 640 KB 640 KB DIPP+SIMM/30 no 1.2 M 20 MB 3 BASIC compiler in PROM, up to two optional5 1/4FD with 160 KB/diskette, the max. on-board memory was increased to 256 KB in 3/83. Several further models followed with enhanced features. Baby AT 84-Key keyboard. 101-Key keyboard. Figure 1.1: Main features of early IBM/PCs 1. Predecessors (2) ROM RAM 16-64 kbyte or 64-256 kbyte 5x ISA/16 Casette Keyboard DMA vezérlő Parallel Intel 8088 I/O CPU PC 8087 arithm. proc. socket Figure 1.2: The motherboard of the IBM PC Source: http://www.tomh.net/museum/mobo/pccassif.html 1. Predecessors (3) 1 8-bit 16-bit Inches no 5 - yes 5 - 372*180 8 - 332*333 yes 3 5 8.6"*13" 330*218 DIPP yes 3 2 8.6"*13" 330*218 DIPP yes ~12"*10" 302*256 Compaq Portable 1 11/82 8088 4.77 128 KB 256 KB Compaq Portable Plus 10/83 8088 4.77 128 KB 640 KB Compaq Deskpro 6/84 80286 8 128 KB 640 KB DIPP Compaq Desktop 286 4/85 80286 8 256 KB 2125 KB DIPP Compaq Portable 286 4/85 80286 8 256 KB 640 KB Compaq Portable II 2/86 80286 8 128 KB 640 KB Compaq Deskpro 386 9/86 80386 16 Mhz Memory size Min. Max. on-board on-board Motherboard size Proc. type Designation fc No. of ISA slots Date of intro. Memory Type Chipset Soldered no IDE Remarks mm The Compaq Portable delivered 3/83 was the first 100x compalible IBM/PC clone. Baby AT Figure 1.3: Main features of early COMPAQ PCs 2. Main types of motherboards 2.1. Overview (1) AT 8/84 LPX 2 Enhanced version 1987 Chipsets ATX w/riser 5 NLX4 11/96 12/99 Slim boxes Baby AT 1 ATX3 Enhanced version ~1985 BTX7 Efficient cooling 8/95 Value oriented microBTX 7 microATX 6 1/98 Value oriented picoBTX7 9/03 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 1 Baby AT: Smaller board size through higher integrated components (chip sets) 2 Non-standardized slimline design with a central mounted riser card allowing 2-3 expansion slots 3 Through better component arrangement reduced cost and EMI emission, integrated AGP (from version 2.02 on) 4 Standardized, improved slimline design with an edge mounted riser card, integrated AGP 5 Low cost slimline ATX design by using a riser card with 2-3 expansion slots 6 Reduced size low cost ATX design with up to four expansion slots In-line core layout to improve system cooling with scalable board dimensions 7 01 02 03 04 05 Figure 2.1: Genealogy of major form factors 2.1. Overview (2) PCI AT 8/84 LPX 2 ATX w/riser 5 NLX4 1987 11/96 12/99 ATX3 Baby AT ~1985 BTX7 8/95 microBTX 7 microATX 6 1/98 picoBTX7 9/03 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 Figure 2.2: Introducing new types of system architectures 99 00 01 02 03 04 05 ISA EISA 8.33 MHz 8/16-bit 8.33 MHz 32-bit 1987 88 89 PCI PCI v.2 PCI v.2.11 33 MHz 33 MHz 32-bit 64-bit 90 91 92 93 33/66 MHz 32/64-bit 94 Figure 2.3: Introducing the PCI bus 1995 2.1. Overview (2) PCI AT HUB architecture 8/84 LPX ATX w/riser NLX 1987 11/96 Baby AT 12/99 ATX ~1985 BTX 8/95 microBTX microATX 1/98 picoBTX 9/03 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 Figure 2.2: Introducing new types of system architectures 99 00 01 02 03 04 05 PCI architecture HUB architecture P P System contr. MCH PCI Perif. contr. ICH ISA Figure 2.4: Contrasting the PCI and the HUB architectures PCI 2.1. Overview (3) SIMM/72 AT DIMM/168 8/84 LPX ATX w/riser NLX 1987 11/96 Baby AT 12/99 ATX ~1985 BTX 8/95 microBTX microATX 1/98 picoBTX 9/03 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 Figure 2.5: Introducing new types of memory modules 00 01 02 03 04 05 2.1. Overview (4) PCI AT ATA AGP USB LPC 8/84 LPX AC ‘97 ATX w/riser NLX 1987 11/96 Baby AT PCI-E SATA 12/99 ATX ~1985 BTX 8/95 microBTX microATX 1/98 picoBTX 9/03 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 Figure 2.6: Introducing new types of buses 99 00 01 02 03 04 05 2.1. Overview (5) Date of intro. AT Type of strandard Typ. nr. of I/O-slots 8/84 Quasi-standard 8 Baby AT ~1985 Quasi-standard LPX (Western Digital) ~1987 NLX Typical board measures (W*D) inches mm Case 12"*13.8" 305*350 Full AT, Full Tower 7/8 8.6"*13" (~9"-13") 218*330 (~229-330) Baby AT Quasi-standard 3/4 9"*13" (~9"-13") 229*330 (~229-330) Slimline 11/96 Standard 3/4 (8"-9")*(10"-13.6") (203-229)*(254-345) Slimline ATX 8/95 Standard 7 12"*9.6" (~7"-9.6") 305*244 (~178-244) ATX MicroATX 1/98 Standard 4 9.6"*9.6" 244*244 MicroATX ATX with riser 12/99 Standard 2/3 12"*9.6" (~7"-9.6") 305*244 (~178-244) Slimline MicroATX with riser 12/99 Standard 2/3 9.6"*9.6" 244*244 Slimline BTX 9/03 Standard 7 12.8"*10.5" 325*267 BTX MicroBTX 9/03 Standard 4 10.4"*10.5" 264*267 MicroBTX PicoBTX 9/03 Standard 1 8"*10.5" 203*267 PicoBTX W: Maximum allowable width D: Maximum allowable depth Figure 2.7: Salient features of major form factors 2.2. AT (1) 8/16-bit ISA slots 305 DIPP CPU (286) KBD KBD PC 350 Figure 2.8: Layout of an AT-motherboard 2.2. AT (2) DRAM 512 Kbyte 2x 8 bit/ 5x 16 bit ISA 8087 arithm. proc. socket Keyboard PC Intel 8088 CPU Figure 2.9: The motherboard of the IBM PC/AT Source:http://library.thinkquest.org/18268/photos.htm 2.2. AT (3) This is a Western Digital Disk Drive Interface Card. This is a Case Interface, both parallel and serial. Figure 2.10: Adapter cards of the IBM PC/AT Source:http://library.thinkquest.org/18268/photos.htm 2.3. Baby AT (1) KBD Power connectorPC 244 SIMM/30 8/16-bit ISA slots L2 cache DIPP CPU (386) 218 Figure 2.11: Layout of an early Baby AT-motherboard 2.3. Baby AT (2) KBD FD HD 230 PC PCI/32 slots SIMM/72 ISA/16 slots CPU (Pentium) L2 cache 218 Figure 2.12: Layout of a late Baby AT-motherboard 2.3. Baby AT (3) 3x PCI/32 PC System contr. 4x SIMM/72 3x ISA/16 FD L2 CPU Periph. contr. IDE Figure 2.13: Example: A Pentium-based late Baby AT-motherboard 2.4. LPX (1) PCI/32 ISA/16 I/O connector s PC 330 Riser card HD FD RAM SIMM/72 DIPP L2 cache 229 Figure 2.14: Layout of an LPX-motherboard 2.4. LPX (2) Figure 2.15: Example: A Pentium-based LPX-motherboard (The PB680 from Packard Bell) source: http://www.geocities.com/anotherpackardbellsite/en_pb_carte680.htm#1 2.5. ATX (1) 1 Double-high expandable I/O Figure 2.16: Layout principles of an ATX case Source: ATX Specification v. 2.01, Source: http://www.berkprod.com/docs/atx_201.pdf MIDI/Game port MIDI/Game port USB VGA Line Out COM1 Line In Mic In Figure 2.17: Double height connectors of an ATX motherboard Source: ABIT SL6 Users’s Manual http://www.abit.com.tw PS/2 Mouse PS/2 Keyb. 2.5. ATX (1) 1 Double-high expandable I/O 2 One chassis fan 3 7 Six full-length slots 6 4 Processor located near power supply One power connector 5 Connectors close to peripheral bays Easy to access system memory Figure 2.18: Layout principles of an ATX case Source: ATX Specification v. 2.01, Source: http://www.berkprod.com/docs/atx_201.pdf 2.5. ATX (2) ATX Baby AT AT Figure 2.19: Placement of the mounting holes on the AT, Baby AT, and ATX motherboards Source: ATX Specification v. 2.01, Source: http://www.berkprod.com/docs/atx_201.pdf 2.5. ATX (3) Main types of ATX motherboards Early PCI-based Late PCI-based Early port-based Mature port-based Serial port-based Chipset 430 440 81x/82x 84x/86x 915 Processor Pentium PentiumII/ PentiumIII (slot 1) PentiumIII Pentium4 Pentium4 Prescott Typ. Memory I/O SIMM/72 DIMM/168 IDE/ATA USB AGP PCI-E Example Example Example Example 2.5. ATX (4) Early port based Serial port based Mature port based Late PCI based AT 8/84 LPX 2 1987 11/96 Baby AT 1 85 12/99 ATX3 ~1985 84 ATX w/riser 5 NLX4 8/95 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 Figure 2.20: Main types of ATX motherboards 00 01 02 03 04 05 2.5. ATX (5) USB I/O connector PC PC 186 Slot1 (Pentium II/III) PCI/32 AGP DIMM/168 ISA/16 HD FD 305 Figure 2.21: Layout of a late PCI-based ATX-motherboard 2.5. ATX (6) 3x ISA/16 4x PCI/32 AGP ATX connectors CPU (Slot1) System contr. PC 4x DIMM/168 BIOS Peripherial contr. Battery FD IDE Figure 2.22: A late PCI-based motherboard for PentiumIIs (MSI’s MS-6111) (Based on Intel’s 440LX chipset for slot 1 processors (1997) Source: http://www.msi.com.tw/program/support/download 2.5. ATX (7) USB I/O connector CPU (Pentium III) PC PC 186 PCI/32 AGP DIMM/168 ISA/16 HD FD 305 Figure 2.23: Layout of an early port based ATX-motherboard for Pentium III/Pentium4 processors. 2.5. ATX (8) CNR 5x PCI/32 ATX connectors AGP PC MCH CPU Battery 3x DIMM BIOS ICH IDE FD Figure 2.24: Early, port based ATX motherboard for Pentium IIIs (Abit’s SL6) (based on Intel’s 815 chipset) Source: http://www.abit-usa.com/products/mb 2.5. ATX (9) 4x PCI/32 AGP ATX connectors Battery CPU (P4) BIOS 4x DIMM/168 ICH FD MCH PC IDE Fgure 2.25: Mature port-based ATX motherboard for Pentium4 processors (Intel’s D865PERL) Source: http://www.intel.com/products/motherboard/d865perl/index.htm 2.5. ATX (10) I/O connector PCI E. x1 244 PCI/32 CPU (Pentium 4) PCI E. x16 HD DIMM/168 SATA PC FD 305 Figure 2.26: Layout of a serial-port based ATX-motherboard for Pentium4 Prescott processors. 2.5. ATX (11) PCI Ex16 BIOS 2x PCI Ex1 MCH (915P/G) 3x PCI/32 P4 Prescott Bat IDE RAID c. (VIA 6410) IHC6/6R 4x DIMM 2x USB Syst. monitoring 2xIDE 4x SATA IDE PS FD Figure 2.27: Serial port-based ATX-motherboard for Pentium4 Prescotts (MSI’s 915G Combo) http://www.pricegrabber.com/search_getprod.php/masterid=3191326 2.6. NLX (1) PCI/32 HD FD I/O connectors PC ISA/16 AGP Riser card 330 Slot1 (Pentium II/III) SIMM/168 229 Figure 2.28: Layout of an NLX-motherboard 2.6. NLX (2) Figure 2.29: View of an NLX-motherboard Source: Intel Corporation, Intel NLX Form Factor http://www.intel.com 2.7. BTX (1) Figure 2.30: Overview of BTX-motherboard sizes Source: Shimpi A.L., „Balanced Technology eXtended (BTX) Form Factor” Sept. 2003 http://www.anandtech.com/ 2.7. BTX (2) I/O connector PCI E. x1 SATA HD PCI/32 267 PCI E. x16 MCH FD DIPP/168 CPU (Pentium4) PC 325 Figure 2.31: Layout of a micro BTX-motherboard 2.7. BTX (3) ATX connectors PC PCI-X/64 ICH PCI IDE 4x DIMM/168 MCH FD CPU Figure 2.32: A micro BTX-motherboard (Intel’s D915GMH) http://www.intel.com/design/motherbd/mh 2.7. BTX (4) Figure 2.33: Temperature distribution in the example motherboard Source: Shimpi A.L., „Balanced Technology eXtended (BTX) Form Factor” Sept. 2003 http://www.anandtech.com/ 3. Server/workstation motherboards (1) Figure 3.1: Block diagram of a pserial port-based entry level server motherboard ( P8SCT) Source:http://www.supermicro.com/products/motherboard/P4/E7221/P8SCT.cfm 3. Server/workstation motherboards (2) IDE PCI-X 64bit 4x DIMM 2x GbE ATX connectors PCI MCH E7221 ICH IPMI CPU IDE Figure 3.2: Example: A P4-based ATX-board for entry-level servers (The P8SCT from Supermicro) Source:http://www.supermicro.com/products/motherboard/P4/E7221/P8SCT.cfm 3. Server/workstation motherboards (3) IPMI: Intelligent Platform Management Interface (Intel, HP, DELL, NEC) • Set of common hardware and firmware interfaces to manage the system remotely • Operates independently of the OS • Operates even in the absence of the OS or if the monitored system is not powered on • Alerts can be sent out via a serial or LAN connection to a remote client (from v. 1.5 on) • It allows to query platform status, to review hardware logs, etc. IPMI consists of a main controller, called BMC (Baseboard Management Controller) and other satellite controllers. 3. Server/workstation motherboards (4) Remote Mgmt. Card MODEM / Serial LAN ICMB Bridge Controller “sideband” IPMB (I2C) RS-232 Mgmt Netwk Ctrlr Baseboard NV Store SMBus/PCI Mgmt. Bus SDR, Mgmt. SEL, Controller FRU I2C/SMBus (BMC) PCI Baseboard SENSORs & control circuitry System Interface System Bus IPMI Messages Figure 3.2: IPMI Architecture Source:http://www.intel.com/design/servers/ipmi Satellite Mgmt. Controller sensors & control circuitry I2C / SMBus Aux. IPMB FRU SEEPROM Chassis 3. Server/workstation motherboards (5) Figure 3.3:Blockdiagram of a serial port based DP-server (Intel’s SE7525GP2) Source: http://www.intel.com/products/server/motherboard 3. Server/workstation motherboards (6) ICH HW management PCI-X 64-bit IDE PRO/1000 server adapter PCI Expr. x8 PCI PCI Expr. x16 MCH (I7525) Registered ECC DDR Dual Processor ATX connectors Figure 3.4: Serial port based DP-server board of ATX style (Intel’s SE7525GP2) Source: http://www.intel.com/products/server/motherboard 4. Overview of the evolution of motherboards (1) On card 1 On-board 2 By the chipset Examples: VGA controller IDE/ATA controller 1 2 On an ISA/PCI adapter card By dedicated controller chips on the motherboard Figure 4.1: Evolution of the implementation of I/O controllers 4. Overview of the evolution of motherboards (2) ATX w/riser ~2000 NLX ~1997 Form factors of announced motherboards LPX ~1987 AT ATX 8/84 ~1996 Baby AT ~1985 microATX ~1998 BTX microBTX picoBTX ˇ~2004 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 01 02 Figure 4.2: Estimated use of form factors in announced motherboards 03 04 05 4. Overview of the evolution of motherboards (3) ATX w/rise r ~2000 NLX ~1997 Formfactors of announced motherboards LPX ~1987 AT ATX 8/84 ~1996 Baby AT ~1985 m icroATX ~1998 BTX m icroBTX picoBTX ˇ~2004 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 01 02 03 8088 6/79 286 2/82 386 10/85 486 4/89 Processors used in the motherboards Pe n tiu m 3/93 Pe n tiu m Pro 11/95 Pe n tiu m II 5/97 Pe n tiu m III 3/99 Pe n tiu m 4 11/00 Figure 4.3: Estimated use of supported processor types in announced motherboards 04 05 4. Overview of the evolution of motherboards (4) ATX w/rise r ~2000 NLX ~1997 LPX ~1987 AT Formfactors of announced motherboards ATX 8/84 ~1996 Baby AT ~1985 m icroATX ~1998 BTX m icroBTX picoBTX ˇ~2004 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 01 02 03 04 05 DRAM 1981 FPM ~1987 EDO DRAM technology and packaging 1995 S DRAM ~1996 DIPP 1981 RDRAM 2000 S IPP/30 ~1983 S IMM/30 ~1984 S IMM/72 ~1989 DIMM/168 1995 Figure 4.4: Estimated use of DRAM technology and packaging style in announced motherboards 4. Overview of the evolution of motherboards (5) ATX w/ri se r ~2000 NLX ~1997 LPX ~1987 AT Formfactors of announced motherboards ATX 8/84 ~1996 Baby AT ~1985 m i croATX ~1998 BTX m i croBTX pi coBTX ˇ~2004 79 80 81 82 83 84 8 16 1981 1984 IS A 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 PC I 1992 93 94 95 96 97 98 v2.0 v2.1 v2.2 1993 1995 1998 99 00 01 02 03 04 v2.3 2002 PC I-X 2004 2000 US B PC I-E 1.0 2.0 1996 2002 2004 LPC Supported I/O 1997 2x 4x 8x 1997 1999 2002 AGP SCSI ~1991 ATA 1991? ATA-2 1995 ATA/33 ATA/66 ATA/100 1999 1997 2000 1.0 S ATA Implemented on-board Implemented on-chipset 2003 MbE 1991? GbE 2002 AC /97 1999 2000 2001 Figure 4.5: Estimated I/O-support in announced motherboards 05