Experiment 18:
advertisement

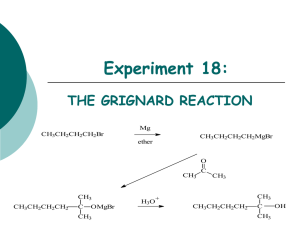
Experiment 18: THE GRIGNARD REACTION Mg CH3CH2CH2CH2Br CH3CH2CH2CH2MgBr ether O CH3 CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2 C OMgBr CH3 H3O C CH3 CH3 + CH3CH2CH2CH2 C CH3 OH Objectives: To synthesize a 3o alcohol from an alkyl halide and a ketone using a Grignard reaction. To purify product using a liquid extraction method. To determine purity using GC analysis. To characterize starting materials and products using IR, 1H-NMR, and 13C-NMR spectra. Before coming to lab… Review the following techniques: Extraction Drying organic solvents with MgSO4 Preparing GC samples You will be expected to perform these will little review, as you learned these techniques in the first semester lab. CHEMICAL EQUATION Mg CH3CH2CH2CH2Br CH3CH2CH2CH2MgBr ether O CH3 CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2 C OMgBr CH3 H3O C CH3 CH3 + CH3CH2CH2CH2 C CH3 OH MAKING THE GRIGNARD REAGENT Organic halides react with magnesium metal in ether or THF to yield an organomagnesium halide: RMgX ETHER R-X + Mg -------------> R-Mg-X or THF Where R= 1o, 2o, or 3o alkyl, aryl or alkenyl X= Cl, Br, I + MgX - C The C-Mg bond is a highly polar covalent bond. The carbon atom is both nucleophilic and basic making it very reactive with a wide variety of E+. WHEN THE GRIGNARD REAGENT MEETS WATER… Since the carbon atom of a Grignard reagent is so nucleophilic and basic, it reacts with proton donors (Brönsted acids) such as H2O, ROH, RCOOH, RNH2 to yield hydrocarbons. This makes it extremely important to keep the reaction flask and solvent completely dry of water. H + MgBr butyl magnesium bromide + O H butane HOMgBr MECHANISM CH3CH2CH2CH2Br + Mg n-BUTYL BROMIDE ether CH3CH2CH2CH2 MgBr Grignard reagent (butyl magnesium bromide) O O C CH3CH2CH2CH2 MgBr C H 3C CH3 MgBr H 3C H 3C CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2 O MgBr C CH3 CH2CH2CH2CH3 ACETONE 1. Lewis acid Mg2+ forms an acid-base complex with basic oxygen atom of acetone making the carbonyl group a better acceptor. 2. Nucleophilic addition of butyl group to acetone produces a tetrahedral intermediate… O H 3….which reacts with water when HCl is added, undergoing hydrolysis to form the product alcohol. H H 3C O H C CH3 CH2CH2CH2CH3 2-METHYL-2-HEXANOL + HOMgBr EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (Synthesis of Grignard reagent…) Place Mg turnings in 50mL flask and place a CaSO4 tube in the top IMMEDIATELY! Clamp flask to ring stand and set up remainder of reflux with addition apparatus. Start reaction with a small amount of nbutylbromide and ether by scratching Mg surface and stirring with glass rod. Add remaining n-butylbromide and ether to sep funnel. Add to reaction mixture dropwise. iron ring EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (Synthesis of alcohol product…) Add acetone/ether to sep funnel. Add to reaction mixture dropwise. Cool reaction flask in water bath. iron ring Transfer cooled liquid to 125 mL Erlenmeyer flask. Add an ice cube and NH4Cl. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (Purification…) Set up an extraction apparatus. Transfer the liquid from the flask to the funnel. Extract with 5%HCl, 10% NaHCO3, and Sat. NaCl. Transfer organic layer to a 50 mL flask and dry over MgSO4. Transfer dried organic liquid to a beaker. Submit a GC sample. Table 18.1 Compound GC Retention Times (min) Standard Adjusted Area % Sample methanol --- acetone n-butyl bromide 2-methyl-2-hexanol octane Record retention times for ALL peaks in standard chromatogram! The product is only pure if the sample chromatogram indicates presence of GC solvent and expected product ONLY. --- Record retention times for any peaks present in sample chromatogram! Calculate AA% for REACTANTS AND PRODUCT only! Product Analysis (IR Spectroscopy) Table 18.2 Functional Group Base Values acetone n-butyl bromide 2-methyl-2hexanol Frequency (cm-1) Frequency (cm-1) Frequency (cm-1) Frequency (cm-1) OH stretch 2500-3300 sp3 CH stretch 2800-3000 C=O stretch 1680-1740 C-O stretch 1000-1200 C-Br stretch 500-700 • IR spectra available on p. 155 of the lab manual! • In discussion, only refer to frequencies which indicate a CONVERSION to product! Product Analysis (1H-NMR Spectroscopy) Br CH2 1 CH2 2 CH2 CH3 3 4 1 OH H3C 2 C CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 3 CH3 1 4 5 6 Product Analysis (13C-NMR Spectroscopy) NMR solvent NMR solvent Table 18.3 1 OH H3C Br CH2 1 CH2 2 CH2 CH3 3 4 n-butylbromide (reactant) 2 C CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 3 CH3 1 4 5 6 2-methyl-2-hexanol (product) • Enter chemical shifts ONLY based on the spectra on page 154. • In discussion, only refer to frequencies which indicate a CONVERSION to product! SAFETY CONCERNS • Diethyl Ether is EXTREMELY flammable. Use extreme caution at all times! • Be sure to wear goggles at ALL times during this experiment! • GLOVES are available upon request! WASTE MANAGEMENT Unreacted magnesium should be rinsed with water and placed in “Recovered Magnesium (Grignard)” container. Aqueous extracts and washes: “Aqueous Waste (Grignard)” container. Crude Alcohol product: Transfer to bottle labeled “Grignard product (2methyl-2-hexanol, Student Prep”. CLEANING Rinse condenser and Claisen adapter with wash acetone only. Clean all other glassware with soap, water, brush, and rinse with wash acetone. Leave all ground glass jointware in lab hood for inspection. DO NOT place any in lab drawer. DO NOT return any glassware to lab drawer dirty or wet.