Evolution of Man
advertisement

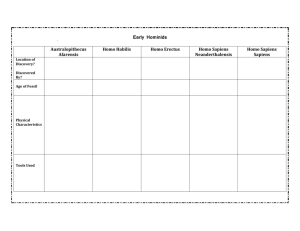
Definition of Evolution the process by which species arise and change over time. The idea that all organisms have descended from common ancestors Charles Darwin Origin of Species, 1859 Decent with Modification Natural Selection Sexual selection Fossil Record tells the story of evolution Taxonomy Classifying organisms into groups Comparative Anatomy Homologous structures Intermediate forms Vestigial structures Comparative Embryology Early embryos of vertebrates are alike Molecular Biology – DNA, proteins mtDNA An organism becomes a fossil only if it dies under the right conditions. Majority of dead plants and animals are consumed by other organisms and leave no trace. Dead organisms only leave a trace or imprint if they are quickly buried in a bog or at the bottom of a lake/ocean. Paleontologists find fossils Remains of humans were preserved in fossils Bog is a wetland low in nutrients, slightly acidic soil . Mossy Tollund Man. (Denmark) Europe Iron age 2,400 ya Buried in mud or at the bottom of a body of water, the remains of the dead are protected from scavengers, erosion and decay. Become buried deeply in successive layers of mud Over time pressure from all these layers of sediment turns the deepest layers into sedimentary rock After millions of years geologic forces raise the rock into mountains, canyons and reveal fossils Grand Canyon showing layers of rock. All organisms are grouped into hierarchies based on their relationships. Organisms of the same species can breed and produce viable offspring Major taxonomic levels - KPCOFGS Common Name: Human Chimpanzee Lion Kingdom Animalia Animalia Animalia Phylum Chordata Chordata Chordata Class Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia Order Primates Primates Carnivora Family Hominidae Hominidae Felidae Genus Homo Pan Panthera Species sapiens troglodytes leo Binomial nomenclature Genus and species Homo sapiens. Homo means “self” or “same”, meaning “the same as me” — which, for you, means “human”. Sapiens means “wise”. Homo sapiens means “Wise human”. Species descended from a common ancestor may evolve in different directions and still keep some of the same characteristics Evolutionary scientists compare the body structures of organisms to find clues. Homologous Structures – similar structures in two or more species that give evidence of a common ancestor. Similar structure Same origin Different in function Compare legs of Human and Ape Intermediate forms – successive changes in homologous bone structures provide evidence of evolution. Also called transitional forms https://handfacts.wordpress.com/tag/evolution / Comparing pelvis bones Vestigial Structures A part of an organism with little or no function that reflects evolutionary history Compare Embryo Development DNA, mtDNA, proteins 20 -20,000 genes in the Human Genome Molecular geneticists have compared DNA sequences of Humans and chimpanzees 98.8% identical Humans are more closely related to African apes than Asian apes (Immunological protein analysis) DNA sequence comparisons Mitochondrial DNA contains 37 genes Thirteen of these genes provide instructions for making enzymes involved in oxidative phosphorylation. Oxidative phosphorylation is a process that uses oxygen and simple sugars to create adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell's main energy source. The remaining genes provide instructions for making molecules called transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Mitochondrial DNA Passed from mother to all her children Points of mutations are a clear . Primatologists observe our closest living relatives, apes and chimpanzees Sahelanthropus tchadensis Discovered in the Sahara Desert in 2001 Between 6 – 7 million years old Considered oldest known hominid fossil Look up Rift Valley Explain where it is Explain why it is important to the study of Human Evolution. As we have evolved Humans have Larger brains Walk bipedally Sparse body hair Nonopposable toes and longer feet Grasping flexible thumb Unspecialized teeth Arching backs Australopithucus afarensis Lucy Found in Ethiopia in 1974 This the earliest species of Australopithecus, l ived in about 4 million and 3 million years ago. brain was about the same size as chimps 3 feet, 70 lbs The researchers also found that the model of locomotion produced in their simulations closely matched a set of fossilized footprints thought to have been left by A. afarensis in Laetoli, Tanzania, some 3.6 million years ago. They constructed the computer model using a fossilised A. afarensis skeleton known as "Lucy", recovered from Ethiopia in 1974. The researchers then added virtual muscle to their simulation and used genetic algorithms to "evolve" the optimal walking movement for the creature. Australopithicus africanus lived perhaps from 3 million to 1 million years ago, and probably evolved from A. afarensis had a rounder skull and slightly larger brain Tooth and jaw design suggest he chewed plant foods, but might also have scavenged meat from the remains of carnivores' kills. Neanderthal Man Fossils found in Germany Homo neanderthalensis More Neandertal skeletons have been found than any other ancient human species. They lived in Europe and Southwest Asia from at least 130,000 -28,000 years ago. May have evolved from Homo heidelbergensis in Southern Europe. protruding jaw, receding forehead, and weak chin. The average Neanderthal brain was slightly larger than that of modern humans, but this is probably correlated with larger body size in general. May have been a different species than Homo sapiens. Homo heidelbergensis (600,000 to 100,000 years ago) The skulls of this species share features with modern Homo sapiens. brain was smaller than most modern humans Homo sapiens sapiens Cro magnum man Earliest modern man Lived 35,000 ya The body heavy and solid , muscular. Straight forehead with slight browridges Cro-Magnons were the first humans to have a prominent chin. Neanderthal vs Cro-magnun Comparison of erectus, aferensis, neanderthal An evolutionary comparison (from left to right: Homo erectus, 1 million years old; Australopithecus afarensis, 2.5 million years old; Homo neanderthalensis, 100,000 – 32,000 years old)