The Victorian Period 1832-1901 - Phoenix Union High School District
advertisement

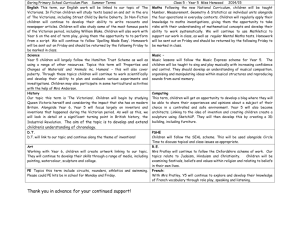
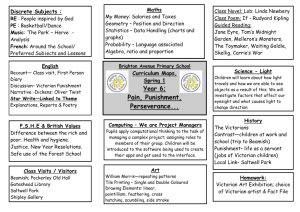
The Victorian Period 1832-1901 Important Events and Inventions 1844- first telegraph sent 1845- Irish potato famine 1859- Charles Darwin publishes the Origin of the Species 1861- U.S. Civil War begins 1869- Suez canal opens 1874- Alexander Bell invents telephone 1879- Edison invents the light bulb 1893- Ford makes first automobile 1893- New Zealand is first country to grant women suffrage 1895- Marconi invents first radio 1896- first modern Olympic games 1900- Sigmund Freud publishes dream interpretations The Era of Rapid Change During Queen Victoria’s reign, England transformed from Horse drawn carriages to cars From rule by aristocrats to votes for every man From farms to factories From confidence in progress to increased doubt Growth and Change “The sun never sets on the British Empire.” The British Empire included areas around the globe: Africa, India, Ireland, Hong Kong, New Zealand, Australia and Canada England was at the height of its power Dominated the world politically Modern Monarchy: Queen Victoria Became queen at age 18 Married her cousin, Prince Albert Ruled for over 63 years Hallmarks of her reign: Proper behavior Hard work and duty Support of Imperialism Changed the role of royalty by yielding control to the Prime Minister After the death of her husband in 1861she withdrew from politics and went into seclusion for the rest of her life. Progress, Problems, and Reforms Middle class Victorians enjoyed displaying their wealth in their dress, homes, furniture, etc. Refined manners was of the utmost importance Many were against these displays of materialism Progress, Problems and Reforms Cont. Conditions for the poor grew worse 16 hour work days 5 year olds worked in coal mines and in factories Potato blight/ famine caused 2 mill. Irish to emigrate to England’s over-crowded slums Reform and Uncertainty Parliament abolished slavery Restricted child labor Public schools established (1867) Working-class men given the right to vote Modern science threatened cherished beliefs Charles Darwin’s publication and theory Victorian Literature Early Victorian poets focused on “poetic” subjects At the time, works by writers such as Dickens, Emily and Charlotte Bronte, and George Eliot was seen as light entertainment, not serious literature Middle-class citizens wanted stories to have more realism. Captures elements of every day life Exposes social problems and pretentions Psychological realism Victorian Novels Novels were very long – divided into three books Novels were usually published serially in magazines several chapters at a time Readers might have to wait 2 years to find out how a story ended Introduction of Penny Dreadful: shocking serial stories with each section costing a penny Victorian Viewpoints Victorians read on all subjects They were curious about everything and would read non-fiction articles that only specialists might read today Uncertainty about religion, science, imperialism, and materialism permeated literature Pessimistic tone to many works New Writing Styles Naturalism an off-shoot of Realism Saw the universe as an uncaring force Focused on the harsh details of industrialized life No humor or happy ending Late Victorians began avoiding serious works Turned to adventure tales by Robert Louis Stevenson, H.G. Wells, and Oscar Wilde Children’s literature by Lewis Carroll and Rudyard Kipling Important Authors and Works Charles Dickens – A Tale of Two Cities Emily Bronte – Wuthering Heights Charlotte Bronte – Jane Eyre Rudyard Kipling – The Jungle Book Robert Louis Stevenson- Treasure Island Thomas Hardy – Tess of the D’Urbervilles Lewis Carroll- Alice in Wonderland George Eliot (Mary Evans)- Silas Marner Sir Arthur Conan Doyle- The Adventures of Sherlock Holmes Oscar Wilde- The Picture of Dorian Gray H.G. Wells – The Time Machine Focus Questions 1. What one invention from this time period? A: automobile, telegraph, radio, light bulb, and telephone Focus Question 2. What are two important world events from this time period? A: U.S. Civil War, Suez Canal, Irish potato famine, women suffrage in New Zealand, Charles Darwin’s publication, Prince Albert dies, English abolishment of slavery, Victoria crowned queen, first modern Olympics Focus Question 3. List three facts about Queen Victoria. A: ruled for over 63 years, became queen at 18, married her cousin, valued manners and imperialism, embraced constitutional law, mourned her husband’s death for the remainder of her life Focus Question 4. How would you describe middle-class Victorians? A: focused on manners and proper behavior displayed their wealth and materialism avid readers and curious about everything Deeply religious Embraced technology and science but were upset by what it showed them Focus Questions 5. How would you describe lower-class Victorians? A: Worked long hours in terrible conditions Lived in over-crowded slums Wanted to read realistic works Men gained the right to vote Able to attend public schools Focus Question 6. List three facts about Victorian literature. A: Long books published in serials Naturalism – focus on industrialized life and hardships Realism – focus on everyday life and social problems Early Victorian writing was serious, dark, and negative Late Victorian writing included children’s literature and adventure stories Focus Question 6. List three authors and their works from this time period. A: Charles Dickens – A Tale of Two Cities Emily Bronte – Wuthering Heights Charlotte Bronte – Jane Eyre Rudyard Kipling – The Jungle Book Robert Louis Stevenson- Treasure Island Thomas Hardy – Tess of the D’Urbervilles Lewis Carroll- Alice in Wonderland George Eliot (Mary Evans)- Silas Marner Sir Arthur Conan Doyle- The Adventures of Sherlock Holmes Oscar Wilde- The Picture of Dorian Gray H.G. Wells – The Time Machine