Computer Architecture Test: Memory & Cache
advertisement
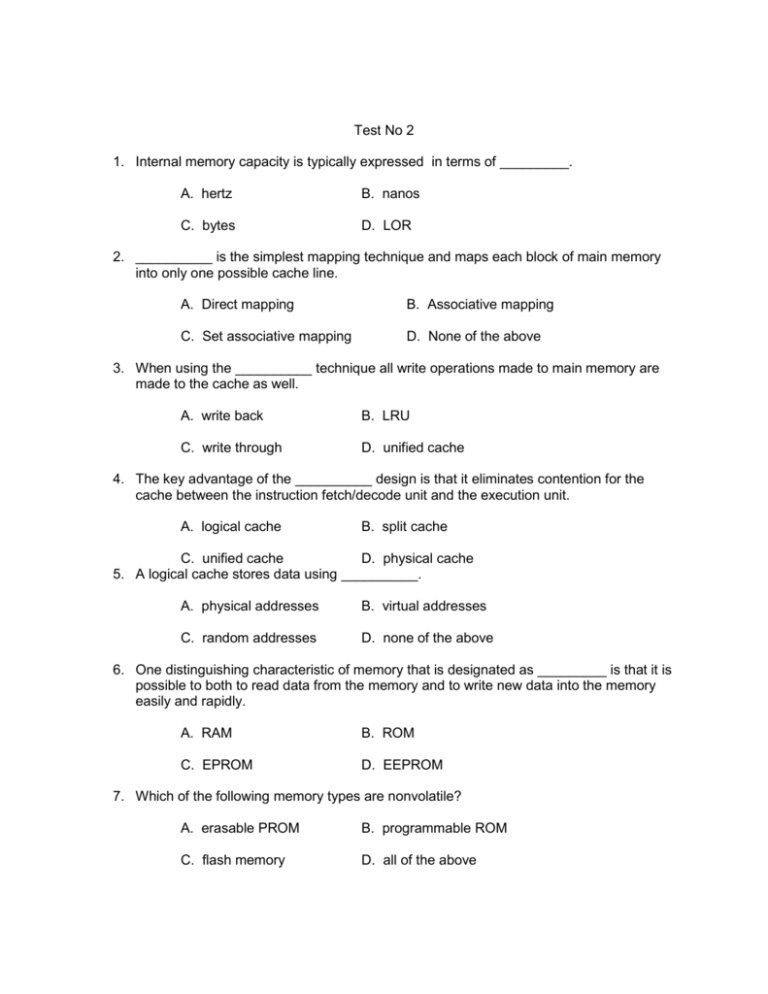
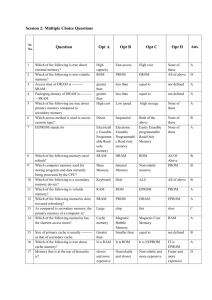
Test No 2 1. Internal memory capacity is typically expressed in terms of _________. A. hertz B. nanos C. bytes D. LOR 2. __________ is the simplest mapping technique and maps each block of main memory into only one possible cache line. A. Direct mapping B. Associative mapping C. Set associative mapping D. None of the above 3. When using the __________ technique all write operations made to main memory are made to the cache as well. A. write back B. LRU C. write through D. unified cache 4. The key advantage of the __________ design is that it eliminates contention for the cache between the instruction fetch/decode unit and the execution unit. A. logical cache B. split cache C. unified cache D. physical cache 5. A logical cache stores data using __________. A. physical addresses B. virtual addresses C. random addresses D. none of the above 6. One distinguishing characteristic of memory that is designated as _________ is that it is possible to both to read data from the memory and to write new data into the memory easily and rapidly. A. RAM B. ROM C. EPROM D. EEPROM 7. Which of the following memory types are nonvolatile? A. erasable PROM B. programmable ROM C. flash memory D. all of the above 8. In a _________, binary values are stored using traditional flip-flop logic-gate configurations. A. ROM B. SRAM C. DRAM D. RAM 9. A __________ contains a permanent pattern of data that cannot be changed, is nonvolatile, and cannot have new data written into it. A. RAM B. SRAM C. ROM D. flash memory C. DRAM D. EEPROM 10. The _________ exchanges data with the processor synchronized to an external clock signal and running at the full speed of the processor/memory bus without imposing wait states. A. DDR-DRAM C. CDRAM SHORT ANSWER B. SDRAM D. none of the above 1. RAM, ROM, PROM, EPROM, EEPROM, and flash memory are all examples of __________ memory types. 2. A _________ RAM is made with cells that store data as charge on capacitors. 3. A __________ RAM is a digital device that uses the same logic elements used in the processor. 4. Three common forms of read-mostly memory are: EPROM, EEPROM, and _________. 5. One of the most widely used forms of DRAM is the _________ DRAM. 6. __________ memory is a facility that allows programs to address memory from a logical point of view, without regard to the amount of main memory physically available. 7. For set-associative mapping the cache control logic interprets a memory address as three fields: Set, Word, and __________. 8. The Pentium 4 processor core consists of four major components: fetch/decode unit, outof-order execution logic, memory subsystem, and __________. 9. One byte equals __________ bits. 10. From a user’s point of view the two most important characteristics of memory are capacity and _____________.