Nurs1510/oxygenation unit
advertisement

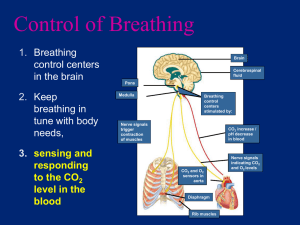
Basic human need O2 is classified as a drug Must have MD order for rate and route Nose and nasal cavities: mm, ciliated, vascular Pharynx: posterior to nasal & oral cavity Nasopharynx=air passage way, eustachian tubes from middle ears Trachea: 4-5in tube from larynx to bronchi. Ciliated Bronchial tree: air passage ways within lungs Lungs: lobes 3=R 2=L Gases move in and out due to pressure in atmosphere. Lungs stay inflated due to pressure around them which is less than pressure within them. Alveolar level: sacs exchange CO2 and O2 Surfactant must be present for alveoli to function correctly Diaphragm: does 80% of the work of breathing Intercostals Accessory Involuntary control of breathing: Medulla oblongata Voluntary control of breathing: Cerebral cortex Process of moving air in & out of the lungs: ◦ Compliance ◦ Surfactant ◦ Airway resistance Perfusion: moving blood to & from alveolarcapillary membrane for gas exchange ◦ Pulmonary circulation ◦ Distribution Diffusion: > to < concentration Heart=pump 4 chambers-R atrium-tricuspid valve-R ventricle-pulmonic valve-pulmonary arterylungs Return via pulmonary veins to L atriumbicuspid valve-L ventricle-aortic valve out to aorta Electrical conductive system Impulse begins in SA node located in R atrium (pacemaker) Travels thru both atrium ( A=contracts) Thru mid heart called AV node To the Bundle of His Down the R and L bundles To purkinje fibers which stimulate the V to contract Cerebral cortex: voluntary Medulla oblongata: involuntary Chemical: is based on the amount of CO2, hydrogen, and O2 present in blood at any given moment. Chemoreceptors in aortic arch and carotids sense the chemical content and adjusts rate and depth of respirations to meet needs. Decreased hemoglobin: will > HR & RR Decreased inspiration: will > HR Hypovolemia: will > HR & RR Increased metablolism: will > HR & RR Chest wall movements: can decrease ventilation yet may see > RR but more shallow Pregnancy Obesity Musculoskeletal abnormalities ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Trauma Muscle or musculoskeletal disease: scoliosis CNS diseases: ALS (Lou Gehrings) COPD, other pulmonary disorders Age: premature, children, elderly Nutrition: obesity & malnutrition Exercise: with CV fitness enhances O2 exchange Smoking: increases HR and RR Substance Abuse: depresses resp centers Anxiety: increases metabolic=>>02 demand Environmental—Smog, hi altitude, dust,etc Hyperventilation: ventilation in excess of that required to maintain normal CO2 levels in tissues. CO2 is expired in greater amounts Hypoventilation: depressed resp rate causing retention of CO2=hypercapnia Hypoxia: state of inadequate oxygenation from deficient delivery or utilization of O2 at the cellular level. Rate, Rhythm, Work of breathing Dyspnea: deals with work of breathing Wheezing: narrowed air passages, hi-pitched Pain: evaluate, onset, location, duration, radiation, effects on respirations Cough: Secretions+characteristics of Lung sounds: bilateral chest assessment Risk factors:family Hx of lung CA, pulmonary ds, smoking Medical history of respiratory infections, smoking Maintain lung expansion ◦ Positioning Semi-fowlers, Fowlers, orthopneic Change position frequently ◦ Breathing exercises Pursed lip Diaphragmatic breathing Incentive spirometry Mobilization of pulmonary secretions: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ TCDB every 2 hours Hydration to thin secretions Humidify environment to moisten mm Postural drainage & chest precussions to mobilize secretions Vital signs: pulse rate, respiratory rate Color: cyanosis, pink, dusky, ruddy Dyspnea: the difficulty and work of breathing Restlessness/anxiousness Retractions O2 saturation/ABG’s Mental alertness/awareness Room air=21% Nasal 1L=21%-24% 2L=24%-28% 3L=28%-32% 4L=32%-36% 6L=40%-44% = max O2 level for Nasal O2 5-6 L = 40% O2 6-7 L = 50% O2 7-10 L= 60% O2 Simple mask: 40% to 60% (varies) Venturi mask: 24%=50% with O2 flow rate of 4L to 10L (more exact) Non-rebreathing mask: up to 80%-90% Partial rebreathing mask: 60-90% Gauge pressure(psi) X cylinder factor (0.28)/liter flow per minute Example: 900 X 0.28/3 liters per min =84 min O2 in cylinder will last 84 min Correct liter flow System on then to patient Correct positioning of cannula or mask No smoking-signs and remove ashtrays Avoid use of electrical equipment-avoid sparks, razors, electric hand held games Must keep airway patent Inner cannula cleaned per protocol Suction no greater 10 seconds Sterile technique O2 setting per respiratory care/orders Care of trach ties, trach dressing