Data Modeling with ERD
advertisement
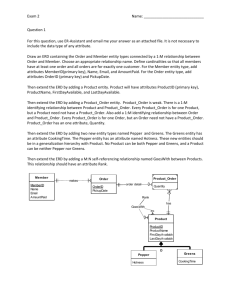
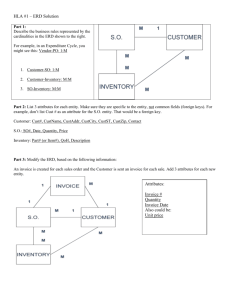
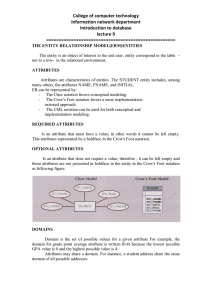
Data Modeling with ERD BUS 782 Entities • An entity is a person, place, object, event, or concept in the user environment about which the organization wishes to maintain data. – – – – – Person: Employee, Student, patient Place: Warehouse, Store Object: Product, Machine. Event: Registration, Sale, Renewal Concept: Account, Course • Physical existence: • Customer, student, product, etc. • Conceptual existence: • Bank accounts, sale Entity Type • A collection of entities that share common properties or characteristics. • An entity type represents a collection of entities. • A business environment may involve many entity types. – University: Faculty, Student, Course – Department, Employee, Dependent – Sales person, Customer, Order Relationship • Relationship: Interaction between entity types. – Faculty teach Course, Faculty advise Student – Customer open Account, Customer purchase Product. • Binary relationship: A relationship involves two entity types. • Three types of binary relationship: – 1:1, 1:M, M:M Entity-Relationship Diagram • ER modeling begins by identifying the entities and relationships between entities that must be represented in the model. • In an ERD, an entity type is represented by a rectangle labeled with a singular name. • A relationship has a verb phrase name: – Faculty teach Course, Faculty advise Student M:M Relationship Boy Girl Peter Mary Paul Linda John Nancy Woody Mia Alan Pia A boy may date 0, 1, or many girls. A girl may date 0, 1, or many boys. Note: “Many boys date many girls” is not a correct interpretation. 1:1 Relationship Man Woman Peter Mary Paul Linda John Nancy Woody Mia Alan Pia A man may marry 0 or 1 woman. A woman may marry 0 or 1 man. 1:M Relationship Father Child Peter Paul John Woody Alan A father has 1 or many children. A child has 1 father. Mary Brian Linda Aron Nancy Ronald Mia Pia Other Examples • 1:1 – State, State Governor – Order, Invoice • 1:M – Department, Employee – Customer, Order • M:M – Bank customer, Bank account – Student, Student organization ERD Notations 1 Student M M Advise Has 1 Account M Enroll 1 Faculty 1 Teach M Course Alternative Notations Student Has Account Enroll Advise Faculty Teach Course Attributes • Properties of an entity or a relationship. • Simple attributes vs Composite attributes – Address:Street address, City, State, ZipCode • Single-valued attributes vs multivalued attributes • Derived attributes • Primary key FullName SID Fname Lname DateOfBirth Age Student Major Domains of Attributes • The set of allowable values for one or more attributes. • Input validation • Examples: – Sex: F, M – EmpHourlyWage: Between 6 and 300 – EmpName: 50 charcters Introduction to Relational Database • Data is logically structured within relations. • Each relation is a table (file) with named columns (attributes, fields) and rows (records). Properties of a Relation • Simple attribute – No composite, no multivalued attribute • Each relation must have a primary key: – Simple or composite key – May have other keys (candidate keys) – Key cannot be null – Cannot be duplicated Relational Database Design • Create a table for each entity that includes all simple attributes • Relationship: – 1:1, 1:M • Relationship table • Foreign key – M:M: relationship table Database Design Example • University: – 1:1 Relationship: • Student and Account – What is Peter’s account balance – Find students that owe more than 2000 dollars. – 1:M Relationship • Faculty Advisor and student – Who is Peter’s advisor? – How many students advised by Chao? – M:M Relationship • Student and course – How many units Peter takes? – Find students that are taking 363. Database Design Example • Bank: – Customer, Account, bank employee Database Design Example • Order Processing: – Customer, Order, Product Aname Phone Attorney AID CID Phone M M Cname Case M Hours 1 M 1 Judge JID Jname Court CtID Room Advanced Topics • Composite key • Multivalued attribute – – – – Student’s Major attribute Faculty’s DegreeEarned attribute Vehicle’s Color attribute Others: PhoneNumber, EmailAddress • Create a table for each multi-valued attribute • Key + attribute • Attributes on a relation Online Shopping Cart CID Cname Customer Addr 1 Has CartID Date Phone M ShoppingCart M Has M Product Price PID Pname Order Form Online Shopping Cart CID Addr Cname Customer CartID Date Phone 1 Has M ShoppingCart M Qty Has M Product Price PID Pname Attributes on Relationship • Examples: – Student/Course: Grade – Order/Product: Quantity