ppt - Spatial Database Group

English Sentence Structure and
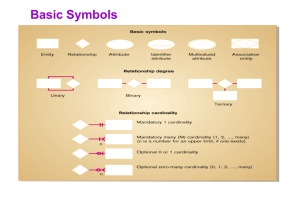
Entity-Relationship Diagrams
Jian Liu and Bo Xue
Csci 5707: Introduction to Databases, Fall 2013
Relationship to Course:
-Textbook Chapters 7 -10 on Conceptual Data Model
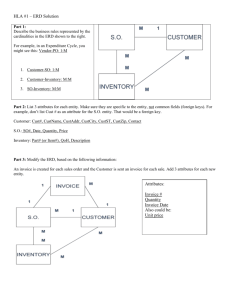
- Lab 2 Part III - Building conceptual data model from document
Reference: Peter P. Chen, “ Entity-Relationship Diagrams and English Sentence
Structure ”, Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on the Entity-Relationship
Approach to Systems Analysis and Design, p.13-14, January 1980, http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=726196
Motivation
•
Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD) Promise:
– easy to understand
•
ERD Challenge:
– Old Approach: DB designer study old system documents
– Difficult to translate requirements documents into DB schemas
•
Proposed Approach:
– 11 translation rules
– More like hints and guidelines than strict rules!
First 4 Rules
• 1: common noun => an entity type
• 2: transitive verb => a relationship type
• 3: adjective => an attribute of an entity
• 4: adverb => an attribute of a relationship
• Example:
– A 40-year-old person works on a project with project number 2175 for 20% of his time .
– ERD
Next 4 Rules
• 5: Convert “There are … X in Y,” into the equivalent form “Y has … X”
• Leading Question for Rules 6 and 7: Convert following to ERD
(6): The father of James Smith is Robert Smith
(7): The color of the desk is blue
• 6,7: “The X of Y is Z ”
– 6. if Z is a proper noun, we may treat X as a relationship between Y and Z
– 7. if Z is NOT a proper noun, we may treat X as an attribute of Y
– and Z represents a value of X .
• 8: objects of algebraic or numeric operations => attributes
– Note: can be derived from Rule 7.
– Ex: “The average salary is $20,000.”
= “The average salary of employee is $20,000.”
Rule 9
• 9: A gerund => a relationship-converted entity type
• Example: “Products are shipped to customers, and the shipping is performed by clerks”
• Note: Chen’s notation is different from Textbook notation.
PRODUCT Ship CUSTOMER
CLERK
Rules 10, 11
• 10: A clause in English is a high-level entity type abstracted from a group of interconnected low-level entity and relationship types in ERD
• 11: A sentence in English corresponds to one or more entity types connected by a relationship type, in which each entity type can be decomposed into low-level entity types interconnected by relationship types
• Example: “The manager decides which machine is assigned to which employee”
• Leading Question? Is this model allowed by Textbook ?
Hint: It has a relationship involving another relationship!
Exercise
Develop ERD in Textbook notation for
“The manager decides which machine is assigned to which employee”
Do not show cardinality & participation constraints.
Do not show sub-type super-type.
Decide
ASSIGNMENT
MACHINE
Compare possible model for
• Ability to detail employee, machine, …
• ERD to Table conversion rules
• Redundancy for
MANAGER
EMPLOYEE
MACHINE
MANAGER
Assign EMPLOYEE
MACHINE
MANAGER
Assign EMPLOYEE
Decide
MACHINE
ASSIGNMENT
Assign
MANAGER
EMPLOYEE
Decide
ASSIGNMENT to for
MANAGER
EMPLOYEE
MACHINE