Area Border Router (ABR)
advertisement

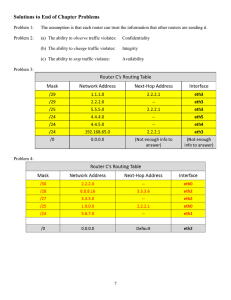
CO5023 Multi Area OSPF Limitations of single area OSPF • When networks become large, single area OSPF develops problems • Routing table becomes large • Link state database becomes large also as it stores the topology of the entire network • Frequent SPF calculations • The larger the network the more frequent the changes in topology. • The solution to this is multi area OSPF: where we divide the network into multiple areas. Each router computes the topology for the areas it is attached to • The scheme is hierarchical, we have a backbone area (area 0) which all other regular areas must connect to. Multi-area rules and terminology Rules… 1. All inter area traffic must cross the backbone area 2. An area should have no more than 50 routers 3. A router should not be in more than 3 areas 4. A single router should not have more than 60 neighbours Terminology • An Internal router is one which belongs to a single non-backbone areas • A Backbone router has all interfaces in the backbone area • An Area Border Router (ABR) has interfaces in more than one area • An Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR) has a connection to an external internetwork LSA Types 1. Lists directly connected network and prefix types 2. For multi-access networks, generated by Designated Router. 3. Used by ABRs to advertise networks in other areas. Summarised where possible 4. Used by the ABR to identify the ASBR and provide a route to it 5. Used by ASBR to describe routes to external networks Multi-area routing table O - Router (type 1) and network (type 2) LSAs describe the details within an area (intra-area). O IA - When an ABR receives summary LSAs, it adds them to its LSDB and regenerates them into the local area. Summary LSAs appear in the routing table as IA (inter-area routes). O E1 or O E2 - External LSAs appear in the routing table marked as external type 1 (E1) or external type 2 (E2) routes. The SPF calculation starts with intra-area routes, then inter-area, then external. Multi area configuration… OSPF Route Summarisation Configure Route Summarisation