Orange Earth - Bonneville High School
advertisement

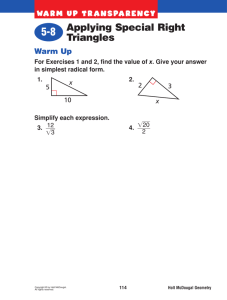
The Economic Way of Thinking Dr. T. D. Mitchell Bonneville High School, Idaho Falls, Idaho Scarcity: The Basic Economic Problem • Principle 1 People Have Wants • Principle 2 Scarcity Affects Everyone • Goods • Services • Consumer • Producer Economics: Concepts and Choices, 2011. Holt McDougal Scarcity: The Basic Economic Problem • Scarcity Leads to Three Economic Questions • What will be produced? • How will it be produced? • For whom it will be produced? Economics: Concepts and Choices, 2011. Holt McDougal The Factors of Production Land Labor Capital Entrepreneurship Economics: Concepts and Choices, 2011. Holt McDougal Economic Choices: Opportunity Cost • Making Choices • Incentives • Utility • Economize • Factors that help you make an economic choice: 1. Motivations for choice 2. No Free Lunch Economics: Concepts and Choices, 2011. Holt McDougal Trade-Offs and Opportunity Cost • Making Trade-Offs • Counting the Opportunity Costs • Analyzing Choices • Marginal Cost • Marginal Benefits Economics: Concepts and Choices, 2011. Holt McDougal Analyzing Production Possibilities • Economic Models • Production Possibilities Curve (Frontier) • Assumption • Resources are fixed • All resources are fully employed • Technology is fixed Economics: Concepts and Choices, 2011. Holt McDougal Review: Production Possibilities Curve Economics: Concepts and Choices, 2011. Holt McDougal What We Learn from PPCs • Efficiency • Underutilization • Law of increasing opportunities costs • Guns and Butter Economics: Concepts and Choices, 2011. Holt McDougal Changing Production Possibilities Production Possibilities Curve 7 6 Refrigerators 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 Cars Economics: Concepts and Choices, 2011. Holt McDougal 12 14 More on the PPC Economics: Concepts and Choices, 2011. Holt McDougal Economists Toolbox • Statistics • Using economic models • Charts and tables Chart Title 6 4 2 0 Category 1 Category 2 Series 1 Category 3 Series 2 Category 4 Series 3 • Using Graphs 6 4 2 Series 1 0 Category 1 Series 2 Category 2 Series 3 Category 3 Category 4 Economics: Concepts and Choices, 2011. Holt McDougal Economists Study Macroeconomics The study of the whole economy Microeconomics The study of the individual consumer Units of Study Units of Study Economic Growth Economic Stability International Trade Topics of interest Money, Banking, finance Government Taxing and Spending Policies Employment and unemployment Inflation Consumer Markets Business Markets Labor Markets Topics of Interest Markets, prices, costs, profits, Competition, Government Regulations Consumer Behavior Business Behavior Economics: Concepts and Choices, 2011. Holt McDougal Positive and Normative Economics Positive Economics • A way of describing and explaining economics as it is, not as it should be. • Involves verifiable facts, not value judgments. Normative Economics • A way of describing and explaining what economic behavior ought to be, not what it actually is. • Does not involve value judgments because it seeks to make recommendations for action. Economics: Concepts and Choices, 2011. Holt McDougal Adam Smith: Founder of Modern Economics 250 Years ago, economics did not exist as an academic discipline. In 1776, Adam Smith changed all this. Born in Scotland, studied literature, logic, and moral philosophy. Wrote Wealth of Nations in 1776. ‐ ‐ ‐ Economic self-interest The invisible hand Became the foundation of modern economics Economics: Concepts and Choices, 2011. Holt McDougal