Introduction to Computer Graphics
advertisement
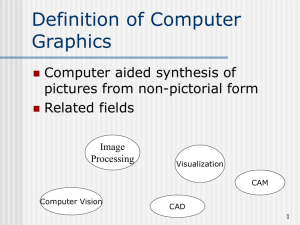
Introduction to Computer Graphics • • • • • Syllabus Handout Goal of Course Software - C/C++, OpenGL Hardware - Unix, Windows, NT, Mac Who you are and what you want from the course walters@buffalo.edu 480/580 Lecture 1 Slide 1 Definition of Computer Graphics • Computer aided synthesis of pictures from nonpictoral form • Subfields and related fields Symbols Structures walters@buffalo.edu Images Signals 480/580 Lecture 1 Slide 2 Reasons for CG 1. User can take in more information 1. Tables versus graphs 2. Easy to make changes 1. Circuit design 3. Can simulate 1. Auto design 2. Flight simulators - http://berkelium.com/OpenGL/flight.html • Can do the impossible – Not obey the laws of physics – ILM’s “Come Home” • http://www.ilmcp.com/home_index.html – Captain Kirk and USS Enterprise travel through spiral interior of DNA molecule walters@buffalo.edu 480/580 Lecture 1 Slide 3 Motivations for Development 1. Manufacturing industry • CAD/CAM http://www.cadsystems.com/profiles/0106_virtualplant.html • 777 design – http://www.boeing.com/commercial/777family/cdfacts.html • • Circuit design and layout - http://www.automationstudio.com/ Flight Simulators • Initial single biggest motivator for realism • • • Training – simulated crash vs. actual crash Simulate combat – 5 missions Realism – on ground simulators • • In plane goggles and runway 2000 feet up Low level flight – cactus spines walters@buffalo.edu 480/580 Lecture 1 Slide 4 More motivations 3. Motion Picture Industry – TRON, Star Wars, Twister, Perfect Storm, Jurassic Park III http://cgw.pennnet.com/Articles/Article_Display.cfm?Section=Articles& Subsection=Display&ARTICLE_ID=108471 – Amazingly difficult to produce • Toy Story – – • SGI hardware Pixar software and production techniques James and the Giant Peach – – walters@buffalo.edu 14.5 min of CG animation 9 months of work by Sony Pictures Image Works team 480/580 Lecture 1 Slide 5 More motivations 4. 5. Video Games - http://graphics.stanford.edu/ Music Videos • Morphing – transform one object into another http://graphics.stanford.edu/cgibin/alumni/tolis/personal/getpage.cgi?morph.html • Presentation Graphics • • • Videos, 35 mm slides, transparencies, reports Bar charts, line graphs, surface graphs, pie charts Computer Art • Paintbrush programs • • • • • Graphics tablet (digitizer) Stylus (brush shapes, sizes, colors) http://cgw.pennnet.com/Articles/Article_Display.cfm?Section=Artic les&Subsection=Display&ARTICLE_ID=108502 Commercial art Fine art walters@buffalo.edu 480/580 Lecture 1 Slide 6 More Motivations 8. Education and Training • • • • Computer generated models Simulators - http://www.virtual-u.org/ Virtual education - http://online.phoenix.edu/ Visualization • Business visualization • • View data sets Scientific visualization • • Genomics - http://www.neurophys.wisc.edu/~cozzi/2cb.html Computer vision http://www.vasc.ri.cmu.edu/demos/facedemo.html walters@buffalo.edu 480/580 Lecture 1 Slide 7 Why so Hard? • Computationally expensive • Still developing new algorithms for realism – Regular objects easy • Surface of revolution – Surface texture • Toys vs people • Orange vs ping pong ball • Texture mapping walters@buffalo.edu 480/580 Lecture 1 Slide 8 Why so Hard, cont. • Imperfections – Blemishes – woodwork in Toy Story • Reflectivity – Plastic versus rainbow – Matt surfaces versus specular surfaces • Motion – Model by hand – animators and key frames – Model by physical equations – Motion capture • http://cgw.pennnet.com/Articles/Article_Display.cfm?Section=Article s&Subsection=Display&ARTICLE_ID=108465 • Fur, Fire, Fern Fun – Dynamic systems http://cgw.pennnet.com/Articles/Article_Display.cfm?Section=Articles&S ubsection=Display&ARTICLE_ID=108473 – “grow” the processes – particle systems, etc walters@buffalo.edu 480/580 Lecture 1 Slide 9