FirstLecture
advertisement
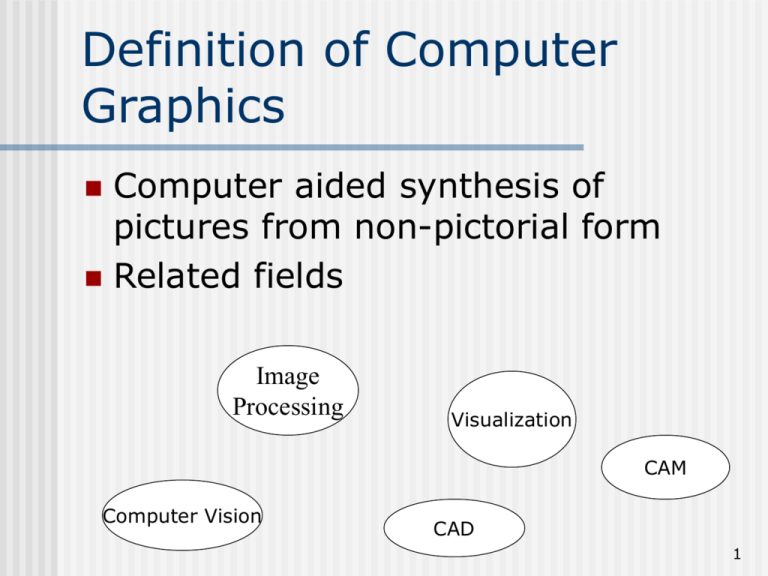
Definition of Computer Graphics Computer aided synthesis of pictures from non-pictorial form Related fields Image Processing Visualization CAM Computer Vision CAD 1 Computer Graphics Goals Realism Interactivity Real-time image generation Sometimes these goals are mutually exclusive (more realism = more calculations = less possibility of realtime image creation) 2 Distinctiveness of CG Dynamic environment – real-time image support Interactive environment for The creator The consumer Simulation environment Provides an environment for visualizing large quantities of data. 3 Computer Graphics “Operations Modeling Coordinates of the ‘corners’ of objects Primitives (2 & 3D geometric objects) Equations that define the 2 & 3D shape of objects Attributes (color, surface texture, etc.) 4 Computer Graphics “Operations” Storing (first in memory), then on disk Manipulating Change shape Change position Change characteristics Rendering– create a picture by applying an algorithmic version of the physics of the real world to create the artificial image. 5 Computer Graphics “Operations” Viewing – display scene from various viewpoints 6 Major application areas Business graphics Much of the profit of CG comes from this area Low quality (and simple) bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, presentation graphics systems Much effort spent on hardware development (overhead display panels, film recorders) & software (charting & presentation graphics) to support this area 7 Major application areas Computer-aided design & computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) Virtual Plant design - http://www.cadsystems.com/archiv e/0003f03.html 777 design – http://www.boeing.com/commercia l/777family/background.html Circuit design and layout http://www.automationstudio.com/ 8 Major application areas Data plotting & visualization “see” the structure of massive data sets Genomics - Computer vision - http://www.neurophys.wisc.edu/~cozzi /2cb.html http://www.ri.cmu.edu/project_lists/ind ex.html 9 Major application areas Entertainment Film makingToy Story, TRON, Star Wars, Twister, Perfect Storm, Jurassic Park III - http://cgw.pennnet.com/Articles/Article_Display.cfm?S ection=Articles&Subsection=Display&ARTICLE_ID=108 471 Video Games Music Videos http://graphics.stanford.edu/ • Morphing – transform one object into another http://www.cs.clemson.edu/~rmg/homepage.html 10 Major application areas Computer Art Paintbrush programs • Graphics tablet (digitizer) • Stylus (brush shapes, sizes, colors) • http://cgw.pennnet.co m/Articles/Article_Disp lay.cfm?Section=Articl es&Subsection=Displa y&ARTICLE_ID=10850 2 11 Reasons for using of CG User can take in more information Tables versus graphs Easy to make changes Circuit design Can simulate Auto design Flight simulators - http://berkelium.com/OpenGL/flight.html Can do the impossible Not obey the laws of physics • Captain Kirk and USS Enterprise travel through spiral interior of DNA molecule 12 Why is CG hard? Computationally expensive Still developing new algorithms for realism Regular objects easy • Surface of revolution Surface texture • Toys vs people • Texture mapping 13 Why so Hard, cont. Imperfections Reflectivity Matt surfaces versus specular surfaces 14 Why so hard continued Motion Model by hand – animators and key frames Model by physical equations Motion capture • http://cgw.pennnet.com/Articles/Article_Display.cfm?Secti on=Articles&Subsection=Display&ARTICLE_ID=108465 Fur, Fire, Fern Fun Dynamic systems - http://cgw.pennnet.com/Articles/Article_Display.cfm?Section =Articles&Subsection=Display&ARTICLE_ID=108473 “grow” the processes – particle systems, etc 15