File - Crawford's Corner
advertisement

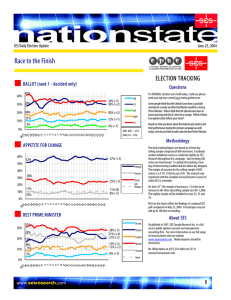
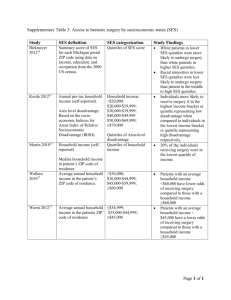
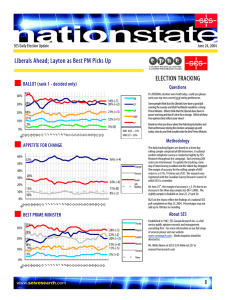
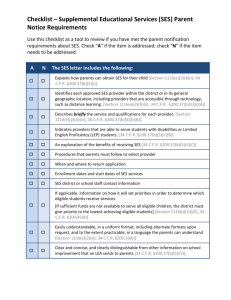
Intro to Teaching, Chapter 3 Stacy Crawford, BCHS I can describe changes in American families over the last 50 years. I can define socioeconomic status, and explain how different socioeconomic patterns influence school success. Describe societal changes and implications of these changes for education. Describe characteristics of at-risk students and how schools and teachers can help these students be successful. At your tables, brainstorm a list of ways that students are different now than they were a few decades back. Be ready to share. Fewer families are headed by married couples Most women with children are in the workplace Increase in divorce rate Nearly 1 in 4 children live only with their mothers Approximately 5% live only with their fathers About 4 % live with neither The incidence of poverty among single parent families is 10 times higher than among families with two parents. Why is quality childcare so important? While critics would contend that there is no substitute for a mother’s care during the early years of a child’s life, the reality for most families is that both parents work outside the home. Research shows a positive correlation between high quality childcare and children’s long-term cognitive and emotional development. Future earnings Drug use Delinquency Drop out rate Between 4 and 5 million children in America return home from school to empty houses until their parents get home from work. Lack of supervision Too much time playing games or watching television No help with homework The combination of family income, parents’ occupations, and level of parental education is one way to describe differences in family background. Researchers divide into 4 groups: Upper class--$170,000+ Middle Class—$80,000-$170,000(1/2); $40,00-80,000 (1/2) Working Class--$25,000-$40,000 Lower Class—Below $25,000 http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/poor-kids/ Low SES Transient/Homeless Divorced families Minority ESL Drug/Alcohol abuse in the home High Rate of Criminal Activity in the neighborhood Truancy Low grades Low participation in extracurricular Low motivation Misbehavior in class Low self-esteem Apathy toward school High suspension rates Retention in grade(s) Build a community of support Mental health issues Tutoring Family support assistance Positive relationships with adults to hold high moral and academic standards School climate is demanding and supportive Safe, orderly climate with clear rules and expectations Academic focus on mastery of content Sense of community Strong parental involvement Caring and demanding teachers who hold high expectations High level of structure and predictability Clear learning objectives High levels of interaction between teachers and students Frequent and thorough assessments Detailed feedback Emphasis on student responsibility Rewards/challenges of teaching What are the Praxis tests? National Board Certification is comprised of two areas: a content-specific test, and submission of evidence Compare/contrast traditional and alternative routes to teaching certification Making yourself marketable Merit Pay School Report Card Changes in American Families SES Be able to identify/evaluate pertinent information from a school report card Poverty and its implications for teachers— compare/contrast SES levels At-risk students—who are they? What behaviors might be present in the classroom? What can teachers/school staff do to help?