unit 4
advertisement

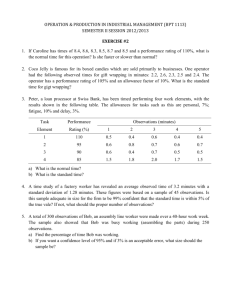
UNIT 2 WORK STUDY, INCENTIVES AND SAFETY Work study It is the systematic examination of the methods of carrying on activities so as to improve the effective use of resources and to set up standards of performance for activities being carried out. Total work content = basic work content + work content added due to poor product design or improper utilization of the materials + work content added by inefficient methods of manufacture + ineffective time due to inefficient human resources. Why work study? It improves the not just production but also productivity It is systematic It is the most accurate method It improves the safety and work conditions at the work It can be applied anywhere Techniques of work study 1. Method study: It is the systematic recording and critical examination of ways of doing things in order to make improvements. 2. Work measurement: It is the application of techniques designed to establish the time for a qualified worker to carry out a task at a defined rate of working. Method study The basic steps of method study are: 1. SELECT 2. RECORD 3. EXAMINE 4. DEVELOP 5. EVALUATE 6. DEFINE 7. INSTALL 8. MAINTAIN Charts and diagrams Charts and diagram are used to record the activities. Commonly used charts are 1. Outline process chart 2. Flow process chart – material type, men type, equipment type 3. Two handed process chart 4. Multiple activity chart 5. Simo chart Commonly used diagrams are 1. Flow diagram 2. String diagram 3. Cycle graphs 4. Chrono cyclegraphs 5. Travel chart Process chart symbols 1. Operation 2. Inspection 3. Transport 4. Delay or temporary storage 5. Permanent storage Principles of motion economy These principles are concerned with economy of movements that are developed over years of experience, which can be grouped into three categories 1. Use of human body 2. Arrangement of the workplace 3. Design of tools and equipments Use of human body 1. Two hands should begin and complete their movements at the same time 2. Two hands should not be idle at the same time except during period of rest 3. Motions of arms should be symmetrical and in opposite directions and should be made simultaneously 4. Rhythm is essential for the smooth and automatic performance of a repetitive operation 5. Work should be arranged so that the eye movements are confined to a comfortable area. 6. Free swinging movements are faster, accurate and easier than restricted movements Arrangement of the workplace 1. Definite and fixed stations must be provided 2. Tools and materials must be pre positioned to reduce searching 3. Gravity feed, bins and containers should be used to deliver the materials 4. Tools, materials and controls should be located within the maximum working area 5. Drop deliveries and ejector pins must be used wherever possible 6. Color of the workplace must be contrast with that of the work Design of tools and equipments 1. The hands should be relieved of all work of ‘holding’ the work piece 2. Two or more tools must be combined wherever possible 3. The load should be evenly distributed in accordance with inherent capabilities Ex: Typewriter 4. Handles of the tools must be so designed as to make maximum surface of the hand is in contact with the handle Work measurements The basic procedure is: SELECT RECORD EXAMINE MEASURE COMPILE DEFINE Standard time It is the total time in which a job should be completed at standard performance Standard performance is the rate of output which qualified worker will naturally achieve without over-exertion as an average over the working day or shift, provided that they know and adhere to the specified method and provided that they are motivated to apply themselves to their work. This is regarded as 100% on performance scales. Qualified worker is the one who has acquired the skill, knowledge and other attributes to carry out the work in hand to satisfactory standards of quantity, quality and safety. Standard time Standard time = basic time + allowances BT= Observed time X observed rating/standard rating Rating is the assessment of workers rate of working relative to the observers concept of the rate corresponding to the standard pace. Job evaluation Job evaluation systems are developed to fix the salary. The following principles have to be used 1. Rate the job not man 2. Select minimum elements but cover all job requirements 3. The rating plan must be easily understandable 4. Foreman or supervisors must be involved. 5. Employees must be allowed to participate Types of job evaluation 1. Ranking method – involves responsibility, amount of work, difficulty, supervision required 2. Classification method – graded based on equal levels of skill difficulty and responsibility 3. Factor comparison – mental requirement, physical requirement, skill requirement, responsibility, working conditions. 4. Point rating – job factors will be subdivided into sub factors, each sub factor will be given weightage Ex: Skill – education, experience, initiative. Incentive plans 1. Piece rate system 2. Cent per Cent premium – any early completion of the job will attract more salary 3. Halsey premium plan – daily wage is fixed, in addition the extra wage is give at the rate of 33.33% of the basic W=R*T + (P/100)*(S-T)*R 4. Bedaux premium plan – here the extra wage rate is 75%, W=R*T+(Ns-Nt/60)*0.75*R 5. Rowan premium plan – W=R*T + (S-T/S)*R*T Training and development Objectives: 1. Increase productivity 2. Make employees more effective 3. To bring more cordial relationship 4. To increase the morale 5. To increase the co-operation 6. To develop the individual 7. To increase the knowledge Training methods 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. on the job training Training center training Demonstration Apprenticeship Programmed instruction Films/slides Simulation exercises Industrial safety Due to unsafe working conditions two types of losses occur 1. Direct losses – which can be compensated 2. Indirect losses – time of worker, decrease in morale, loss to machine, reduction in efficiency, etc. Reasons for accidents 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Age Experience Improper layout of machines Moving objects Unsafe working conditions Electrical causes Personal reasons Exposure to harmful substances Preventive measures 1. 2. 3. 4. Safe workplace and working conditions Safe material handling Personal protection devices Good housekeeping