Lesson 4
advertisement

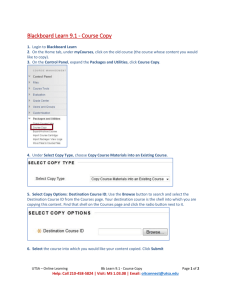
Lesson 4 Basics of Incident Detection Overview • Detection of Incidents • Basic IDS Theory • Types of IDSes UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response What is an Incident? Incident - an event in an information system/network Time based security: Protection time >> detection time + reaction time Some say its all about vulnerability management UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Detection of Incidents Company X IDS End Users Help Desk System Administrators Security Human Resources UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Indicators IDS Detection of remote attack Numerous Failed Logons Logins into Dormant or Default Accounts Activity During non-working hours New Accounts not created by SysAdmins Unfamiliar files or executable programs Unexplained escalation of privileges Altered web pages Gaps in logs files or erasure in log files Slower system performance System crash Receipt of extortion email Notification by upstream/downstream sites Pornography/Music files/Movies Detection of Incident Process Firewall Logs IDS Logs DETECT Suspicious user System Admin UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Begin IR Checklist Activate CIRT Are Firewalls Enough? • You have the world's best firewall, your Windows computers update their antivirus software regularly and your Information Security staffers enforce your policies with an iron fist. Does this mean you're safe? • Maybe not. In 1998, a news story asserted that the firewall for the New York Times was one of the best. Yet at 7:08 a.m. on Sunday, Sept. 13, 1998, someone on the paper's network e-mailed reporters: – ...COM3 V1S1T HTTP://WWW.NYTIMES.COM AND S33 0UR LAT3ST P13C3 0F ART. 1F 1T D0ESN'T L0AD, JUST H1T 'REL0AD' A F3W T1MES. CL3V3R ADMINZ HAD S0M3 W3IRD CR0NTABZ OR S0METHING. – 0H. W3 0WN YOU. Y0U JUST HAV3NT N0T1C3D US 0N Y3R N3TW0RK Y3T. UNT1L THE N3XT T1M3... • No one at the Times had noticed weeks worth of the Hacking for Girliez gang on their network. The intruders finally chose to go public by defacing the opening page of their Web site—on the day the Times expected millions of visitors to view the Monica Lewinsky transcripts. Instead, visitors encountered soft porn . . . UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Personal Firewall UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Firewall Traffic Monitor UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Firewall Configuration UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Firewall Settings UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Firewall Event Summary UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Hostile Event? UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Traceback Option UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Ranum on Intrusion Detection • “The real value of intrusion detection is diagnosing what is going on…never collect more data than you could conceivably want to look at. If you don’t know what to do with the data, it doesn’t matter how much you’ve got.” Marcus Ranum Network Flight Recorder UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Intrusion and Misuse Detection • Remember the operational model of security – protection = prevention + (detection + response) • Access controls and filters seek to prevent unauthorized or damaging activity. • Intrusion and misuse detection mechanisms aim to detect it at its outset or after the fact. • Has its roots in audit log files • Operate on the principle that it is neither practical nor feasible to prevent all attacks. UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Intrusion Detection • Can be manual (review of logs), automated, or a combination. • Closely related to monitoring. – Workplace monitoring used to • Ensure quality • Assess performance • Comply with regulations (e.g. ensure stockbrokers aren’t using high-pressure tactics in violation of stock exchange rules) UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Audit Trails • Early intrusion detection involved reviewing system log or audit files. • What events can be audited varies from system to system. • Examples of auditable events include – – – – – – Reading/opening of a file Writing to or modifying a file Creation or deletion of an object Logins and Logouts Other administrative actions Special operations (e.g. changing a password) UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Unix Logging • Several sources of log files in Unix – – – – syslog – the system log sulog – records actions to switch users (su) utmp – keeps track of users currently logged on wtmp – stores historical data on login, logout, shutdown, and restart events. – lastlog – tracks each user’s most recent login time and the point of origin of the user. Successful and unsuccessful logins can be tracked. • At login, this information (about the last login) is often displayed UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Windows NT/2K Auditing • By default security auditing is not enabled • NT: Start|Programs|Administrative Tools| User Manager – User Manager select Policies|Audit – Logs => C:\WINNT\System32\Config\*.evt • WIN2K: Administrative Tools| Local Security Policy – Logs => C:\WINNT\System32\Config\*.evt UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Win 10 Logging • By default auditing is enabled – Logs => C:\WINDOWS\System32\LOGFILES • Right click Windows LogoComputer Management|Event Viewer|Windows Logs UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Computer Management Logging • • • • • UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Application Logs Security Logs Setup Logs System Logs Forwarded Events The Use of Tools • “An apprentice carpenter may want only a hammer and a saw, but a master craftsman employs many precision tools. Computer programming likewise requires sophisticated tools to cope with the complexity of real applications, and only practice with these tools will build skill in their use.” Robert L. Kruse Data Structures and Program Design UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Windows 10 Logs UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Computer Management UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Computer Mgt Event Viewer Windows Logs UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Event Viewer UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Event Viewer Application Log UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Event Viewer Security Log UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Event Viewer System Log UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Schneier on Auditing • “ Audit is vital whereever security is taken seriously. Audit is there so that you can detect a successful attack, figure out what happened after the fact, and then prove it in court.” Bruce Schneier Secrets & Lies Digital Security in a Networked World UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Another Obvious Quick Look Tool • Your Anti-virus software – Check AV log to see when last scan conducted – Check Quarantine area – If only interested in root cause analysis – Execute the AV software to see what turns up UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Intrusion Detection Systems • Various types of activities that an IDS checks for – – – – – – – – Attempted/successful break-ins Masquerading Penetration by legitimate users Leakage by legitimate users Inference by legitimate users Trojan horses Viruses Denial-of-service UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Approaches to IDS • Attempt to define and detect abnormal behavior • Attempt to define and detect anomalous activity UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Methods to perform IDS • Four major methods attempted to perform intrusion detection: – – – – User Profiling Intruder Profiling Signature Analysis Action-based (attack “signatures”) UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response User Profiling • Basic Premise: the identity of any specific user can be described by a profile of commonly performed actions. • The user’s pattern of behavior is observed and established over a period of time. • Each user tends to – – – – use certain commands more than others, access the same files, login at certain times and at specific frequencies, and Execute the same programs. • A user profile can be established based on these activities and maintained through frequent updating. • A masquerading intruder will not match this profile. UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response User Profiling • Types of activity to record may include – – – – – – – – – CPU and I/O usage Connect time and time of connection as well as duration Location of use Command usage Mailer usage Editor and compiler usage Directories and files accessed/modified Errors Network activity • Initial profile takes time & can generate many alarms. • Weighted actions often used (more recent activities more important than activities accomplished in past) UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Intruder Profiling • Concept similar to criminal profiles used in the Law Enforcement community. • Attempt to define the actions that an intruder will take when unauthorized action is obtained. – For example: when an intruder first gains access the action often taken is to check to see who else is on, will examine files and directories, … • Can also apply to insiders gaining access to files they are not authorized to access. • Problem with this method is that it is hard to define all possible intruder profiles and often the actions of a new user will appear similar to the actions of an intruder. UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Signature Analysis • Just as an individual has a unique written signature which can be used for identification purposes, individuals also have a “typing signature”. • This characteristic first noticed in telegraph days. • The time it takes to type certain pairs or triplets of letters can be measured and the collection of these digraphs and trigraphs together form a unique collections used to characterize individuals. • This technique requires special equipment. • Variation on this is to watch for certain abbreviations for commands and common errors. UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Action Based • Also sometimes referred to as signature based. • Specific activities or actions (attack signatures) known to be indicative of intrusive activity are watched for. – E.g. attempts to exploit known security holes. • Can also be used to look for unauthorized activity by insiders. • Problem is that not all methods are known so new signatures are constantly being created and thus intrusion detection systems constantly need to be updated. UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response Summary • Detection of Incidents • Log File Analysis • Firewall Logs • Basic of IDS UTSA IS 3523 ID & Incident Response