EN2412 Mechanical Engineering Laboratory
advertisement

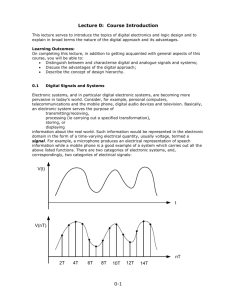
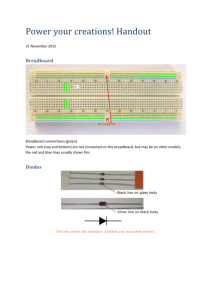
Principles to Computer Engineering ENG_4_532: Introduction Introduction Mr Ya Bao (Semester 1) Office Hours Room T-701, Tower Block email: baoyb@lsbu.ac.uk Tel: 020 7815 7588 Mondays 15:00 – 16:00 Lecture notes www.lsbu.ac.uk/vle, or from your mylsbu Text books (semester 1) Electric Circuits, Nilsson & Riedel, Prentice-Hall, 10E. 2015; ISBN:9781-292-06054-5 Digital Electronics, Roger L. Tokheim, Mcgraw hill, 8E, 2014; ISBN:978-1-259-06092-2 Overview Module Overview Assessment Methods Log books Good practice in labs Theory for Labs wk 2 Summary Learning Outcomes Develop an understanding of the principles of circuit theory and basic analogue electronics Introduce the concept of digital systems To develop your ability to manage and perform the successive steps involved in typical practical engineering experiments To develop your ability to work as a member of a team To develop your ability to communicate technical information (report writing) Assessment Methods Course split 50% Semester 1 & 50% Semester 2 Phase Test: 20% Formal report: 20% Scheduled for 16/Nov/15; Week 8 in BR-232 Due by Week 13, submit to School Office (T313) by 13th Jan 2016 Logbooks: 10% Submit with reports to School Office by 13th Jan 2016 Lab Schedule 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Introduction to Lab Equipment Voltage, Current, Power & Ohm’s Law Kirchoff’s Laws of Current and Voltage (*) Source Transformations Wheatstone Bridge Transformers and Rectifiers Basic TTL Logic Circuits Timing Circuits and Counters RULES: While you are in the lab No drinking No eating No smoking No dangerous activity Take care with electrical devices Switch off your mobile phone and ipod, distractions waste time Log Books (p7 of your lab manual) You MUST keep a log book! Do not use loose paper for intermediate recording before transfer to the log book. You must use the log book to document your procedure and results AS YOU GO ALONG Draw graphs only on graph paper, use pencil where needed Answer all questions from the script in your log Add ideas/points of interest too Conclude each experiment with the key points You MUST get your LOGBOOK stamped at the end of session You MUST leave your logbook in the lab Go to stores J205 or good stationers and buy a suitable book with lined paper and add graph paper as needed Best logbooks are Chartwell Laboratory Books A4-641C Page number Date Names of the group members Title of the experiment Brief description of the procedure Carefully record your results Do NOT use ‘Tipp-Ex’ Graphs should have a caption Make maximum use of the graph paper Choose an easy scale Label the axes Units Error margins/bars Error Margins You MUST estimate error margins for any reading you make You should propagate these errors for any calculations you make Common measurement devices Oscilloscope ±3% Digital Multimeter ±1% Analogue Meter ±5% The Breadboard Close-Up Vertically Connected Break Vertically Connected Horizontally Connected Break Error Margins Common components Example logbook notation E12 Resistor ±5% Electrolytic Capacitor ±20% Digital Timer ±0.001% 1.00kΩ ±5% 56.2 s ±0.3s Avoid quoting too many significant figures 3 is usually about right Resistor E series tables of values Finally Please keep your Laboratory Manual safe! Lab and lecture schedule on VLE All related materials will be posted on VLE – check often Please arrive promptly at 12:00 so we can start the lab on time Any questions? Principles of Computer Engineering: Experiment 1 Introduction to test equipment Experiment 1 Introduction to Breadboard Build simple electrical circuits Develop familiarity with Digital and Analogue Multimeters Introduction to Oscilloscopes and Signal Generators Building a Circuit on the Breadboard Push the component legs into suitably located sockets on breadboard with care Try to layout circuit neatly to look like that of the circuit diagram Double check circuit before connecting power (check polarity!) Use colour coded wires where possible; red = +V, black = 0V, blue = -V Example Circuits to be Built The Lamp Circuit Digital and Analogue Multimeters Can be used to accurately measure voltage and current in a circuit Have different characteristics – simple experiment to compare them DMM has an accuracy of around ±1% Analogue MM accurate to around ±5% Ideally have infinite internal resistance as acting as a voltmeter Digital and Analogue Multimeters Use 1MW resistors in series with both Voltmeters to estimate their input resistances 1 MW Resistor + PSU - + 1MW Analogue meter V IL Meter + + 5V Rx V m Figure 2 Analogue meter in high impedance 5 volt circuit Figure 4 Loading effects at 5 volts The Oscilloscope Used to display time varying waveforms Apply sinusoidal signal from generator at 1kHz (Alternating current) Measure frequency and voltage with ‘scope facilities Peak-to-Peak Voltage can be measured Vrms V pp 2 2 The Oscilloscope Summary Become familiar with use of a breadboard Build elementary circuits and test them Use standard test bench equipment and appreciate their accuracy Introduce the use of oscilloscopes