Bone REVIEW
advertisement

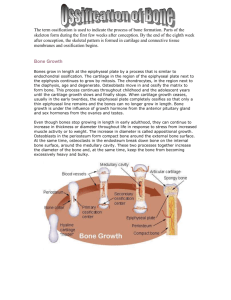
Chapter 7 REVIEW: Name: _____________________________________________ Date: _________________Class:______ 1. List and briefly describe the six main functions of the skeletal system. 2. Which of the following cell types is primarily responsible for breaking down osseous (bony) matrix? A) Osteoblast B) Osteocyte C) Chodroclast D) Osteoclast E) Chondrocyte 3. What is the basic unit of compact bone tissue? A) Osteon B) Stroma D) 4. 5. 6. Chromosome Spongy bone lacks A) Lamellae D) Osteons E) B) E) C) Lamellae Lacunae Lacunae Blood C) Which type of bone is the femur? A) Long bone B) Short bone D) Irregular bone E) Sesamoid bone C) Which type of bone is the scapula? A) Long bone B) Short bone D) Irregular bone E) Sesamoid bone C) Osteocytes Flat bone Flat bone 7. Which of the following bones originates from dense fibrous connective tissue? A) Sternum B) Temporal bone C) Femur D) cervical vertebrae E) Humerus 8. The epiphyseal plate of a long bone is made of which of these types of tissue? A) elastic cartilage B) hyaline cartilage C) fibrocartilage D) dense fibrous connective tissue E) loose areolar connective tissue 9. Osteoclast are stimulated by which of the following hormones? A) PTH B) Calcitonin C) Anti-diuretic hormone D) FSH E) Insulin E) Insulin 10. This is a structure of a long bone that stores nutrients. A) Diaphysis B) Epiphysis C) Metaphysis D) Periosteum E) Marrow Page 1 11. This is the region of a long bone that articulates with other bones. A) Diaphysis B) Epiphysis C) Metaphysis D) Endosteum E) Marrow 12. This is the shaft of a long bone. A) Diaphysis B) Epiphysis D) Endosteum E) Marrow C) Metaphysis 13. This is a layer of hyaline cartilage that reduces friction between bones involved in the joint. A) Periosteum B) Distal epiphysis C) Nutrient foramen D) Articular cartilage E) Epiphyseal plate 14. This is a layer of hyaline cartilage that allows the diaphysis to grow in length. A) Periosteum B) Distal epiphysis C) Nutrient foramen D) Articular cartilage E) Epiphyseal plate 15. This is the region in mature bone where the diaphysis and the epiphysis join. A) Endosteum B) Periosteum C) Metaphysis D) Diaphyseal line E) Diaphyseal plate 16. This tissue associated with bone promotes bone growth in width. A) Periosteum B) Endosteum C) Marrow D) Epiphysis E) Metaphysis 17. Put the bones cells in order of their maturation from unspecialized to specialized. A) Osteogenic, osteoblast, osteocytes B) Osteoblast, osteoclast, osteogenic, C) Osteogenic, osteocytes, osteoblast D) Osteoclast, Osteogenic, osteocytes E) None of the above are in the correct order 18. These are considered bone-building cells. A) Osteogenic B) Osteoclast D) Osteoblasts E) All of the above C) Oscteocyte These are considered bone-dissolving cells. A) Osteogenic B) Osteoclast D) Osteoblasts E) All of the above C) Oscteocyte 19. 20. Which of the following structures contains osteocytes? A) Central or haversian canals B) Perforating or Volkmann's canals C) Lamellae D) Lacunae E) Canaliculi 21. These are extensions of the lacunae and are filled with extracellular fluid. A) Perforating or Volkmann's canals B) Central or haversian canals C) Osteons D) Canaliculi E) Periosteum 22. Osteons in compact bone tissue are aligned: A) horizontal to the metaphysis. B) parallel to the epiphysis. C) along lines of stress. D) randomly between the epiphyseal plates. E) parallel to blood vessels. Page 2 23. Bone remodeling: A) occurs throughout life. B) involves bone resorption. C) involves bone deposition. D) occurs at different rates at different locations. E) all of the above. 24. The average renewal rate for compact bone tissue in a healthy individual is: A) 4% per year B) 15% per year C) 20% per year D) 25% per year E) There is no way to measure 25. Which of the following minerals is needed when bones are growing? A) Calcium B) Phosphorus C) Magnesium D) Fluoride E) All of the above 26. Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) Osseous tissue gets its “hardness” and ability to withstand compressive forces from the crystallized inorganic mineral salts located in the matrix. B) Spongy bone does not have osteons, nor does it have lamellae, lacunae, or an osteocyte population. C) Collagen fibers provide the ability to withstand tensile forces and are found in the osseous matrix, giving bone its flexibility. D) The periosteum is a tough sheet of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the bone's surface wherever it is not covered with articular cartilage. E) Compact bone is characterized by osteons, structures that consist of a central canal, concentric lamellae, lacunae, osteocytes and canaliculi. 27. The correct sequence of processes that occur during bone elongation at the epiphyseal plate are: A) B) C) D) E) 28. calcification, resting, proliferation, hypertrophication resting, proliferation, calcification, hypertrophication proliferation, resting, hypertrophication, calcification resting, proliferation, hypertrophication, calcification hypertrophication, calcification, proliferation, resting During adulthood, which of the following does NOT contribute to bone remodeling and growth? A) D) Calcium Sex hormones B) Vitamin E C) Vitamin K E) Weight bearing exercise 29. Bone resorption is promoted by which hormone? A) Calcitriol B) Calcitonin C) Human growth hormone D) Parathyroid E) Insulin 30. Which of the following statements is TRUE? A) The proximal and distal diaphyses are sites where red bone marrow can be found in adults. B) Articular cartilage is composed of elastic cartilage. C) The extracellular matrix of bone has no collagen fibers. D) Spongy bone is not characterized by the presence of osteons. E) Bony tissue gets its flexibility from mineral salts in the extracellular matrix. Page 3 31. Which of the following is best described as an irregular bone? A) a cervical vertebra B) femur C) humerus D) talus (a tarsal bone) E) sternum 32. Which of the following is best described as a flat bone? A) a cervical vertebra B) femur C) humerus D) talus (a tarsal bone) E) sternum 33. Which of the following is best described as a short bone? A) parietal bone B) femur C) humerus D) talus (a tarsal bone) E) sternum 34. Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) Osteogenic cells are found in the inner portion of the periosteum, in the endosteum, and in the canals within bones that house blood vessels. B) Calcification occurs when enough mineral salts are present to form crystals. C) Osteoclasts are large cells that release lysosomal enzymes and acids that digest the protein and mineral components of osseous matrix. D) Osteoblasts synthesize and secrete collagen fibers and initiate calcification. E) Osteocytes do not undergo cell division. 35. Which of the following is a TRUE statement? A) The patellae are the largest of what are called sesamoid bones, which develop within tendons. B) Bones are not classified according to their shape. C) Irregular bones include examples such as the bones of the cranium. D) Short bones include the bones of the forearm, the radius and ulna. E) Long bones are extremely straight so that they can absorb stress. 36. Blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves are found traveling through all of the following structures EXCEPT: A) Perforating or Volkmann's canals B) Central or haversian canals C) Nutrient foramina D) Canaliculi E) None of the above 37. Which of the following statements is CORRECT? A) The metaphysis is highly vascular. B) Spongy bone is characterized by osteons. C) Compact bone is characterized by trabeculae. D) The periosteum is made of loose areolar connective tissue. E) The endosteum is not an active site of bone resorption. 38. Which of the following structures are NOT parts of an osteon? A) Canaliculi B) Lamellae C) Osteocytes D) Lacunae E) Trabeculae 39. The skeletal system: A) provides attachment points for skeletal muscle. B) stores and releases minerals such as calcium. C) is a site of hematopoeisis (blood cell formation). D) stores triglycerides in yellow marrow. E) all of the above. Page 4 40. Which of the following is NOT made of dense irregular connective tissue? A) periosteum B) perichondrium C) fibrous portion of an articular capsule D) reticular layer of the dermis E) yellow marrow 41. Put the following steps of endochondral ossification in the correct order: 1) Formation of articular cartilage and epiphyseal plate 2) Development of cartilage model 3) Growth of cartilage model 4) Development of secondary ossification center 5) Development of medullary cavity 6) Development of primary ossification center A) 2, 3, 6, 5, 4, 1 B) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 C) 3, 2, 6, 4, 5, 1 D) 2, 6, 4, 3, 1, 5 E) 6, 1, 4, 5, 2, 3 42. The cranial bones undergo: A) Intramembranous ossification, where cartilage is replaced with bone B) Intramembranous ossification, where fibrous tissue is replaced with bone C) Endochondral ossification, where cartilage is replaced with bone D) Endochondral ossification, where fibrous tissue is replaced with bone E) None of the above 43. Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) The clavicle is the last bone to cease growth. B) If a bone fractures at the epiphyseal line, it may end up shorter than normal. C) Cartilage takes much longer to heal than bone. D) Bone is highly vascular. E) None of the above. 44. This is a bone located within ankles or wrists. A) Long bone B) Sutural bone D) Sesamoid bone E) Short bone 45. C) Irregular bone Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) The zone of hypertrophic cartilage consists of large, maturing chondrocytes arranged in columns. B) The zone of resting cartilage is the nearest to the epiphysis and consists of small, scattered chondrocytes. C) Growth in length requires growth of cartilage on the diaphyseal side of the epiphyseal plate, and the replacement of cartilage with bone on the epiphyseal side of the epiphyseal plate. D) The zone of proliferating cartilage contains chondrocytes arranged like stacks of coins. E) The zone of calcified cartilage is only a few cells thick and consists mostly of dead chondrocytes because the matrix has calcified. Page 5 Use the following to answer questions 46-50: 46. Where in the diagram is the distal epiphysis? 47. Where in the diagram can you find the medullary cavity? 48. Where in the diagram can you find red bone marrow in an adult? A) A and B B) B and D C) A and D D) C E) E 49. Where in the diagram is the growth plate? 50. Where in the diagram is the only place that does not have a periosteum? Use the following to answer questions 51-54 51. 52. 53. 54. In the diagram, where is the central or haversian canal? A) C B) A C) E D) F E) D In the diagram, where is the perforating or Volkmann's canal? A) A B) B C) C D) E In the diagram, where is the osteon? A) A B) B C) C In the diagram, where are the trabeculae? A) B B) C C) D D) D E) E D) E Page 6 E) F E) F Use the following to answer questions 55-58: 55. Which bone is the flat bone? 56. Which bone is the short bone? 57. Which bone is an irregular bone? 58. Which is a long bone? 59. Describe the major differences between compact and spongy bone. 60. Briefly describe the steps in endochondral ossification. Page 2 61. Briefly describe the steps in intramembranous ossification. 62. Briefly describe the steps in bone deposition. 63. Briefly describe the steps in bone resorption. 64. Describe the process by which bone increases in length and diameter. Page 3