meiosis - Doral Academy Preparatory
advertisement

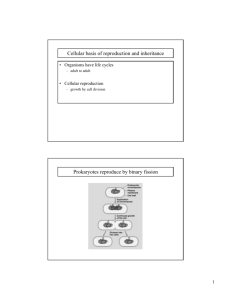
Mitosis & Meiosis CHAPTER8 CHROMOSOMES Chromosome: DNA in a Eukaryotic cell that is tightly coiled and compacted in the cell nucleus Histones: Proteins in Which DNA is Tightly wrapped Around that Help maintain The shape of The chromosomes Chromosome Structure: Chromosome numbers: Chromosomes are categorized as either sex chromosomes or autosomes Sex chromosomes: chromosomes that determine the sex of an organism Autosomes: all other chromosomes in an organism Homologous chromosomes: one copy of each autosome from each parent. The two copies of each autosome are called homologous chromosomes Diploid: cells having 2 sets Of chromosomes (2n) Haploid: cells which contain only one set of chromosomes (1n) Karyotype: photomicrograph of the chromosomes in a cell Cell division in prokaryotes: Binary fission Cell Division in Eukaryotes • Cell Cycle – The cell cycle is the repeating set of events in the life of a cell. – The cell cycle consists of cell division and interphase. – Cell division in eukaryotes includes nuclear division, called mitosis, and the division of cytoplasm, called cytokinesis. Mitosis: If a cell wants to make a duplicate of itself, it first must copy its DNA (part of a chromosome). The copies then must be separated & sorted into two sides of the cell. The cell then splits in two. Part of each parent is carried to the two new cells. Results in cells such as internal organs, skin, bones, blood, etc. Mitosis Mitosis animations: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VlN7K1-9QB0 http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter 2/animation__mitosis_and_cytokinesis.html Interphase occurs just before Mitosis begins: Cells spend most of the cell cycle in interphase During g1 – offspring cells grow to mature size During S phasecells DNA is copied During g2 phase- cell prepares for cell division (mitosis) http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/1110Lab/notes/notes1/lab6.htm G0 phase Cells can sometimes exit the cell cycle usually from the g1 phase and enters state called g0 During g0, cells do not copy their DNA and do not prepare for cell division. Many cells in the human body are in the g0 phase Interphase Animal cell Plant cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm st 1 step in Mitosis: Prophase (preparation phase) The DNA recoils, and the chromosomes condense; the nuclear membrane disappears, and the mitotic spindles begin to form. http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/1110Lab/notes/notes1/lab6.htm Mitosis Prophase Animal cell Plant cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm 2nd step in Mitosis: metaphase The chromosomes line up the middle of the cell with the help of spindle fibers attached to the centromere of each replicated chromosome. http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/1110Lab/notes/notes1/lab6.htm Mitosis Metaphase Animal cell Plant cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm rd 3 step in Mitosis: Anaphase (separation phase) The chromosomes split in the middle and the sister chromatids are pulled by the spindle fibers to opposite poles of the cell. http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/1110Lab/notes/notes1/lab6.htm Mitosis Anaphase Animal cell Plant cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm th 4 step in Mitosis: Telophase spindle fibers disassemble, and the chromosomes return to a less condensed chromatin state. A nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes and a nucleolus forms in each of the newly formed cells. http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/1110Lab/notes/notes1/lab6.htm Mitosis Telophase Animal cell Plant cell Photographs from: http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm After Mitosis: Cytokinesis The actual splitting of the daughter cells into two separate cells is called cytokinesis and occurs differently in both plant and animal Cells. Beginning of cytokinesis in a plant: a plate forms along the midline of the dividing cell Beginning of cytokinesis in an animal: cell membrane pinches in at the middle of the dividing cell(this is called a cleavage furrow) Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis IPMATC http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L0kenzoeOM Julie Camp’s mitosis power point - http://sciencespot.net/Pages/classbio.html#Anchor-mitosis Meiosis: As in mitosis, if a cell wants to make a duplicate of itself, it first must copy its DNA (part of a chromosome). Results in reproductive cells (sperm, eggs, etc). Part of each parent is carried to the four new cells. Meiosis Interphase The cell grows and copies its DNA, and the chromatin begins to condense into chromosomes. http://morgan.rutgers.edu/MorganWebFrames/Level1/Page7/meiosis1.html Meiosis Prophase I -DNA coils tightly into chromosomes and spindle fibers appear -In meiosis the homologous chromosomes pair with one another to form tetrads - Portions of chromatids may break off and attach to adjacent chromatids, this process is called crossing over (When portions of homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material) .Crossing over leads to genetic recombination. http://morgan.rutgers.edu/MorganWebFrames/Level1/Page7/meiosis1.html Meiosis Metaphase I - The tetrads line up randomly along the midline of the cell -Spindle fibers attach to the centromeres of each homologous chromosome http://morgan.rutgers.edu/MorganWebFrames/Level1/Page7/meiosis1.html Meiosis Anaphase I -The chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell. - The random separation of the homologous chromosomes is called independent assortment http://morgan.rutgers.edu/MorganWebFrames/Level1/Page7/meiosis1.html Meiosis Telophase I & Cytokinesis The cell begins to divide into two daughter cells. It is important to understand that each daughter cell can get any combination of maternal and paternal chromosomes. http://morgan.rutgers.edu/MorganWebFrames/Level1/Page7/meiosis1.html Meiosis Prophase II Spindle fibers form and begin moving chromosomes toward the middle of the cell http://morgan.rutgers.edu/MorganWebFrames/Level1/Page7/meiosis1.html Meiosis Metaphase II As in Meiosis I, the chromosomes line up on the spindle fibers at the midline of the cell. http://morgan.rutgers.edu/MorganWebFrames/Level1/Page7/meiosis1.html Meiosis Anaphase II The two cells each begin to divide. As in Meiosis I, the chromosomes move to opposite ends of each cell. http://morgan.rutgers.edu/MorganWebFrames/Level1/Page7/meiosis1.html Telophase II & Cytokinesis - - - a nuclear membrane forms around the chromosomes in each of the four new cells. Cytokinesis II then occurs. - each new cell contains half the original cells number of chromosomes http://morgan.rutgers.edu/MorganWebFrames/Level1/Page7/meiosis1.html Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis 2 daughter cells Diploid (2n) Genetically identical Meiosis 4 daughter cells Haploid (1n) Not genetically identical http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zGVBAH AsjJM&feature=g-vrec http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qCLmR9 -YY7o