Cellular basis of reproduction and inheritance Prokaryotes
advertisement
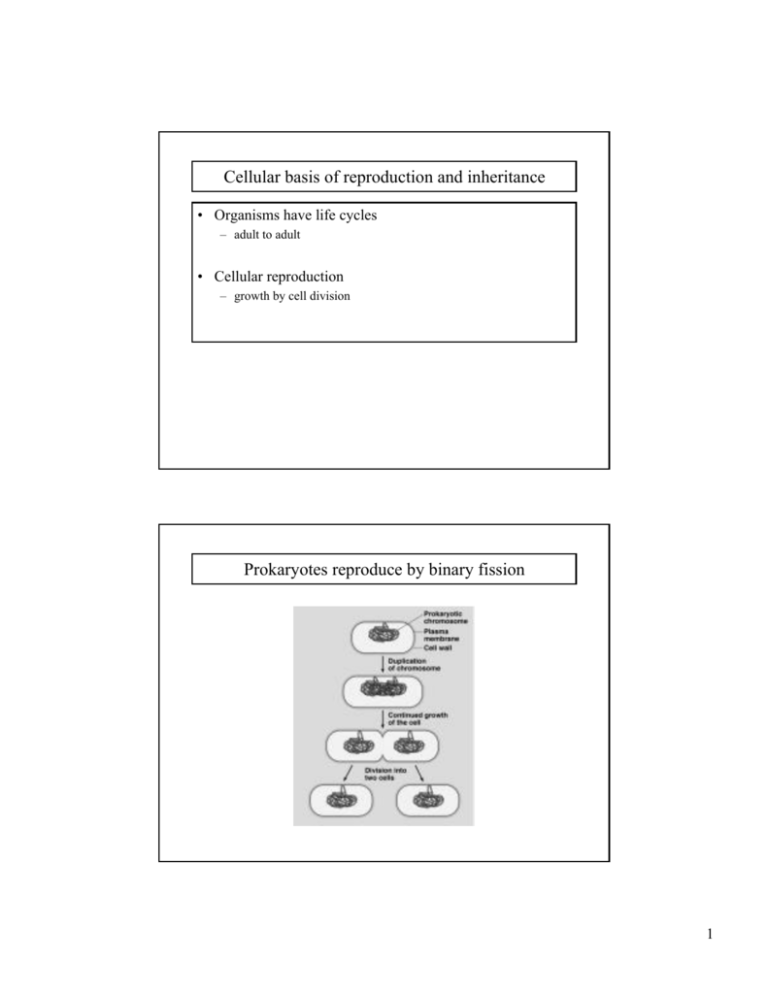
Cellular basis of reproduction and inheritance • Organisms have life cycles – adult to adult • Cellular reproduction – growth by cell division Prokaryotes reproduce by binary fission 1 Eukaryotic cell cycle and mitosis • More complex • Large amounts of DNA arranged in chromosomes – chromosomes visible only during cell division – chromosomes exist as a diffuse mass called chromatin at other times • Number of chromosomes differ between species – 46 in humans, 4 in fruit fly. Chromosomes duplicate with each cell division • Duplicated sister chromatids attached at centromere 2 The cell cycle Mitosis and cytokinesis 3 Mitosis and cytokinesis (cont’d) Cytokinesis differs for plant and animal cells 4 Factors affecting cell division • anchorage dependence – need to be in contact with a surface • density dependent inhibition – form single layer in cell culture • growth factor portein stimulates cell division Density dependent inhibition growth factors 5 Growth factors signal the cellcycle control system Cancer as a result of improper functioning of the cell-cycle control system • Tumors – benign and malignant • Metastasis of cancer cells • Cancers named according to the originating organ – Carcinomas – external or internal linings (skin and intestine) – Sarcomas – supporting tissues (bone and muscle) – Leukemias and Lymphomas – blood forming tissues • Cancers cells not affected by density dependent inhibition • Treatments target cell division – radiation and chemotherapy 6 Meiosis Meiosis with crossing over 7 Independent orientation of chromosomes and random fertilization lead to much variation 2n 8