Unit IV Factor Market
advertisement

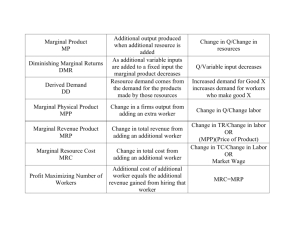
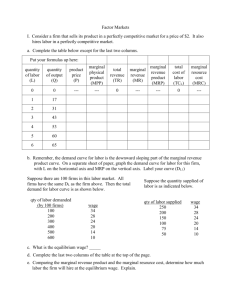
Factor Market Quiz 1 The Demand for Resources Factor Market and Firm Graphs Which of the following statements best illustrates the concept of derived demand? 1. 2. 3. 4. A decline in the price of margarine will reduce the demand for butter. A decline in the demand for shoes will cause the demand for leather to decline. As income goes up the demand for farm products will increase by a smaller relative amount. When the price of gasoline goes up, the demand for motor oil will decline. 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 T he demand for labor is derived from: 1. 3. the demands for other variable inputs. consumer demand for the product or service it is helping to produce. the cost-minimization rule. 4. the supply of related inputs. 2. 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Fastest Responders Seconds Participant Seconds Participant Marginal revenue product measures the: 1. 2. 3. 4. amount by which the extra production of one more worker increases a firm's total revenue. decline in product price that a firm must accept to sell the extra output of one more worker. increase in total resource cost resulting from the hire of one extra unit of a resource. increase in total revenue resulting from the production of one more unit of a product 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The purely competitive employer of resource A will maximize the profits from A by equating the: 1. 2. 3. 4. price of A with the MRC of A. marginal productivity of A with the MRC of A. marginal productivity of A with the price of A. price of A with the MRP of A. 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The MRP curve for labor: 1. intersects the firm's labor 25% 25% 25% 2 3 25% demand curve from above. 2. is the firm's labor demand curve. 3. lies below the firm's labor demand curve. lies above the firm's labor demand curve. 4. 1 4 Fastest Responders Seconds Participant Seconds Participant Marginal product is: 1. 2. 3. the output of the least skilled worker. a worker's output multiplied by the price at which each unit can be sold. the amount any given worker contributes to the firm's total 25% 25% 25% 2 3 25% revenue. 4. the amount an additional worker adds to the firm's total output. 1 4 If one worker can pick $30 worth of grapes and two workers together can pick $50 worth of grapes, the: 1. 2. 3. marginal revenue product of each worker is $25. marginal revenue product of the first worker is $20. marginal revenue product of the 25% 25% 25% 2 3 25% second worker is $20. 4. data given do not permit the determination of the marginal revenue product of either worker. 1 4 Fastest Responders Seconds Participant Seconds Participant A competitive employer should hire additional labor as long as: 25% 1. 2. 3. the MRP exceeds the wage rate. the wage rate is less than MP. average product exceeds MP. 4. average product exceeds MP. 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 A firm will find it profitable to hire workers up to the point at which their: 1. 2. 3. 4. marginal resource cost equals their wage rate. wage rate equals product price. MP is equal to their MRP. marginal resource cost is equal to their MRP. 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The MRP curve is the resource demand curve for: 1. 2. 3. 4. neither the purely competitive nor the imperfectly competitive seller. the imperfectly competitive seller, but not the purely competitive seller. the purely competitive seller, but not the imperfectly competitive seller. both the purely competitive and imperfectly competitive seller. 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Fastest Responders Seconds Participant Seconds Participant Employers will hire more units of a resource if: 1. 2. 3. 4. the price of the resource increases. the productivity of the resource increases. the price of the good being produced declines. the price of a complementary resource rises. 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 If a firm is hiring a certain type of labor under purely competitive conditions: 1. 2. 3. 4. its labor demand curve will be perfectly elastic at the marketdetermined wage rate. the labor supply curve will lie above the marginal labor cost curve. the labor supply and marginal labor (resource) cost curves will coincide and be upsloping. the labor supply and marginal labor (resource) cost curves will coincide and be perfectly elastic. 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Fastest Responders Seconds Participant Seconds Participant Which of the following describes a purely competitive labor market? 1. 2. 3. 4. MRP = Wage Rate. MRP > Wage Rate. Wage Rate > MRC. Wage Rate < MRC. 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 The labor supply curve facing a purely competitive employer is __________ whereas the labor supply curve facing a monopsonist is ___________. 25% 1. 2. 3. 4. 25% 25% 2 3 25% upward sloping; horizontal downward sloping; vertical vertical; upward sloping horizontal; upward sloping 1 4 The economic term for a sole employer in a nonunion community is: 25% 1. 2. 3. 4. 25% 25% 2 3 25% monopsonist. monopolist. bilateral competitor. bilateral monopolist. 1 4 Fastest Responders Seconds Participant Seconds Participant Which of the following is most likely to be an example of monopsony? 25% 1. 2. 3. 4. the market for fast-food workers in a large summer resort town the market for card dealers in Las Vegas. the market for major league baseball umpires. the market for retail sales clerks in a major city. 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 A monopsonist: 1. 2. 3. 4. boosts the wage rate above the competitive level to attract more workers. reduces the number of workers it employs so that it can pay each worker a lower wage rate. is a "wage taker." pays a wage rate equal to MR 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 "Player drafts" of professional athletes: 1. 2. 3. 4. increase the competitiveness of the labor market for professional athletes. reduce the profitability of professional sports franchises. promote monopsony in the hire of professional athletes. increase salaries of professional athletes. 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Fastest Responders Seconds Participant Seconds Participant If the diagram to the left was relevant to an individual firm, we could conclude that the firm is: 25% 1. 2. 3. 4. a pure competitor in the hire of labor. a monopsonist in the hire of labor. selling its product in an imperfectly competitive market. selling its product in a purely competitive market. 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 25% 25% 25% 2 3 25% Refer to the above diagrams. The firm: 1. 2. 3. 4. is a monopsonist in the hire of labor. must be selling its product in an imperfectly competitive market. is a "wage taker." must pay a higher marginal resource cost for each successive worker. 1 4 Participant Leaders Points Participant Points Participant