Incorporating a research module into an introductory Geology lab
advertisement

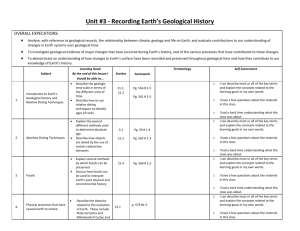
Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Incorporating a research module into an introductory geology lab: Successes and challenges Elizabeth Moss and Cinzia Cervato November 7th, 2012 Acknowledgements • • • Bill Simpkins, Kristie Franz, Chris Rehman, Jake Smokovitz, Craig Ogilvie Josh O’Brien, Sarah Feiner, Jake Smokovitz, Maddie Mette, Sarah Day, Ning Zhang Funding from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Iowa Math and Science Education Program, Iowa State University Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Outline • • • • Geology 100L overview Student project overview Research question Results Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Geology 100L • • • • • Introductory physical geology lab 2/3 of students are non-STEM majors 3-4 sections of up to 25 students Weekly for 2 hours Taught by graduate student TAs Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Curriculum reform to improve student engagement • • Develop an authentic research project Design inquiry-based labs Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Geology 100L: Before and after Before After Week 1 Introduction to Earth processes Introduction + NOS tubes activity Week 2 Plate Tectonics Introductory Field Activity Week 3 Earthquakes Streams and Groundwater (practice investigation) Week 4 Mineral Identification Streams and Groundwater (practice investigation) Week 5 Mineral Identification Mineral Identification Week 6 The Rock Cycle +Igneous Rocks Rock Identification Week 7 Sedimentary Rocks Rock Identification Week 8 Metamorphic Rocks Rock Cycle Week 9 Geologic Time Field Day Week 10 Stream Processes Plate Tectonics Week 11 Groundwater Processes Pangea Week 12 Geologic Structures and Maps Research Day Week 13 Topographic Maps Topographic Maps Week 14 Glacial Processes and Climate Change Poster Presentations + Virtual Volcano Activity Week 15 Quiz Geologic Time + Capstone Activity Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences What is an authentic research project? Modeled after CASPiE (Center for Authentic Science Practice in Education) modules for chemistry (Weaver et al. 2008) • Students design procedure or project • Students do not know the results beforehand • Students contribute to real research • Unlike chemistry, geoscience research is often non-experimental Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Research project • • • Students design a research project that investigates local groundwater and surface water issues Projects and questions are open-ended Student data contribute to a growing database of water quality measurements Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Geology 100L: Now Week 1 Introduction + NOS tubes activity Week 2 Introductory Field Activity Learn how to use equipment Week 3 Streams and Groundwater (practice investigation) Week 4 Streams and Groundwater (practice investigation) Practice writing a research proposal Week 5 Mineral Identification Week 6 Rock Identification Week 7 Rock Identification Week 8 Rock Cycle Week 9 Field Day Iterate proposal with TA Collect data Methods submitted to TA Week 10 Plate Tectonics Week 11 Pangea Abstract Peer Review and past poster evaluation Week 12 Research Day Week 13 Topographic Maps Week 14 Poster Presentations + Virtual Volcano Activity Week 15 Geologic Time Activity Evening poster session with faculty judges Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Equipment Item Water-level tape Handheld pH meter Pocket colorimeter Nitrate reagents Phosphate reagents Bailer (PVC pipe) Well key Wells--not outfitted Wells--outfitted with continuous pH, temperature and conductivity probes Stream gauges Quantity Available 2 2 2 As needed As needed 4 3 4 4 2 (1 USGS, 1 ours) Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Students’ research questions “How will precipitation affect phosphorus levels in the stream and the wells?” • “How does temperature affect nitrate and phosphorus levels?” • “How do river discharge and depth to water in wells correspond?” • “How do chemical levels vary midstream and at the confluence of Squaw Creek and Skunk River?” • “Does an Iowa State football game at Jack Trice Stadium, in addition to commuter traffic, parking, and tailgating, have a short term effect on specific pollutant levels of nearby Squaw Creek?” • Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Our research hypothesis • An authentic research project will be an effective tool in increasing students’ understanding of the nature of science and selfefficacy toward science Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Nature of science Nature of science: • What science is, how it works, what scientists are like, how society influences science (McComas et al., 1998) • Scientific knowledge is tentative, observations are influenced by theories, science requires creativity • Misconceptions about nature of science can prevent students from entering STEM fields (Tobias, 1990) • Modified version of the Student Understanding of Science and Scientific Inquiry (SUSSI) (Liang et al., 2005; Clough, 2010) Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Self-efficacy • • • • Belief in one’s ability to successfully complete a task (Bandura, 1977) Can be increased by “performance accomplishments” (successfully doing a task) (Campbell and Hackett, 1986) Influences career decisions (Luzzo et al., 1999) Used a modified vocational self-efficacy survey (Riggs et al., 1994) Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Results: Nature of Science • • Positive normalized changes each semester Pre-test and post-test means not statistically different Spring 11 Fall 11 Spring 12 Pre 114.2 116.6 117.2 Post Normalized change 118.4 117.7 117.6 11.5% 8.6% 7.3% Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Results: Nature of Science • Non-STEM students impacted more than STEM students One-way ANOVA analysis of normalized changes of Non-STEM majors versus STEM majors. A: Spring 2011, n=47, p=0.037 B: Fall 2011, n=46 C: Spring 2012, n=50, p=0.029 Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Results: Self-efficacy • • • Positive normalized changes Spring 2011 and 2012 Slight loss Fall 2011 semester Pre-test and post-test means not statistically different Spring 11 Fall 11 Pre Post Normalized change Spring 12 63 64.5 68.3 66.1 62.2 67.2 11.8% -0.9% 5.9% Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Results: Self-efficacy • STEM students impacted more positively than Non-STEM students S11 F11 S12 Non-STEM 11.1% -1.9% 2.8% STEM 1.5% 10.6% 13.4% Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Conclusions • • • An authentic research project is not sufficient to increase overall students’ understanding of the nature of science and their self-efficacy Improvement in understanding of the nature of science is significantly higher in Non-STEM students Improvements in science self-efficacy are higher in STEM students than Non-STEM students Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences Questions? Bandura, A. 1977. Social Learning Theory. New Jersey: Prentice Hall. Campbell, N. K., and Hackett, G. 1986. The effects of mathematics task performance on math self-efficacy and task interest. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 28: 149-162. Clough, M. P., Herman, B. C. and Smith, J. A. R. 2010. Seamlessly teaching science content and the nature of science: Impact of historical short stories on post-secondary biology students. Association for Science Teacher Education (ASTE) National Conference, Sacramento, CA, January 14-16. Liang, L. L., Chen, S., Chen, X., Kaya, O. N., Adams, A. D., Macklin, M., and Ebenezer, J. 2005. Student understanding of science and scientific inquiry (SUSSI): Development and validation of an assessment instrument. Paper presented at the International History and Philosophy of Science Teaching Conference. Leeds, UK. Luzzo, D.A., Hasper, P., Albert, K.A., Bibby, M.A., and Martinelli, E.A. Jr. 1999. Effects of Self-Efficacy-Enhancing Interventions on the Math/Science Self-Efficacy and Career Interests, Goals, and Actions of Career Undecided College Students. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 46: 233-243. McComas, W.F., Clough, M.P., and Almaroza, H. 1998. The role and character of the nature of science in science education. In McComas, W.F. ed, The Nature of Science in Science Education. Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers, p. 3-39. Riggs, M., Warka, J., Babasa, B., Betancourt, R., and Hooker, S. 1994. Development and validation of selfefficacy and outcome expectancy scales for job-related applications. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 54: 793-802. Tobias, S. 1990. They're Not Dumb, They're Different: Stalking the Second Tier. Tucson, AZ: Research Corporation. Weaver, G., Wink, D., Varma-Nelson, P., Lytle, F., Morris, R., Fornes, W., Russell, C., and Boone, W. 2006. Developing a New Model to Provide First and Second-Year Undergraduates with Chemistry Research Experience: Early Findings of the Center for Authentic Science Practice in Education (CASPiE). The Chemical Educator, 11: 125-129 Department of Geological and Atmospheric Sciences