Classification of plants - Varga
advertisement

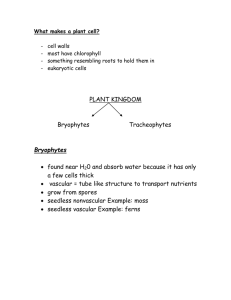
Three Types of Plants That We Will Discuss... Seedless, non-vascular plants Seedless, vascular plants Seed-bearing plants – all of them are vascular. Seedless, Non-vascular Plants Also known as BRYOPHYTES Bryophytes (non-vascular) Bryophytes are non-vascular plants, which means that they do not have xylem and phloem. Because they do not have a vascular system, bryophytes require an external source of water in order to survive, such as dew or rain. Bryophytes usually grow in damp, dark environments to provide and retain moisture. MOSS is an example of a bryophyte Despite the fact that they require an external source of water, bryophytes can often grow where other organisms can not, such as the harsh desert. They do this by entering a state of dormancy until a water source is available. This ability of mosses makes them critical in colonizing dry, inhabitable lands and beginning the soil-making process. Properties of Mosses Mosses do not have true leaves. They have structures that look like leaves, but they are only one cell thick. Some mosses have cuticles, and most of them have stomata. Mosses anchor themselves to surfaces using rhizoids. Make Some Assumptions About Bryophytes for These Questions... How tall do you think a bryophyte can grow, and why do you think this? What are some challenges that bryophytes might have reproducing? If you were a plant, do you think you would want to be a bryophyte? Why or why not? Seedless, Vascular Plants Club Mosses and Ferns are seedless, vascular plants. A TYPE OF FERN CLUB MOSS Seedless, Vascular Plants Club mosses, which are not true mosses, belong to the oldest living group of vascular plants. 300 million years ago, shallow swamps were home to enormous seedless, vascular plants, which got wiped out. Their remains, however, got pressed and heated underground, forming coal. This is why coal is called a FOSSIL FUEL. Club Mosses and Ferns Some club mosses look like mini pine trees, and are sometimes called “ground pines.” Ferns are the most successful survivors of the carboniferous period, with about 12,000 currently living species that existed back then. Some tree ferns can grow over three stories tall. Make Some Assumptions About Bryophytes for These Questions... Why can club mosses and ferns grow taller than a bryophyte? Although they are able to grow taller, club mosses and ferns still have some evolutionary disadvantages. What are they? Would you rather be a seedless, vascular plant or a bryophyte? Why or why not? Seed-bearing, Vascular Plants These include Flowering Plants! Seed Plants Have 3 HUGE Evolutionary Advantages... 1. Seed plants can reproduce without free-standing water. - - Unlike the seedless plants, seed plants do not depend on water to transport their sperm to the eggs. Seed plants produce pollen. Pollination occurs when pollen meets female reproductive parts of the same plant species. Seed Plants Have 3 HUGE Evolutionary Advantages... 2. Seeds nourish and protect plant embryos - - - Remember that a seed is a protective outer layer that contains a food source and a plant embryo. Seeds can survive for many months or years in a dormant state, and they can survive harsh conditions that would kill an adult plant. The plant embryo will begin to grow when conditions are favourable for the plant. Seed Plants Have 3 HUGE Evolutionary Advantages... 3. Seeds allow plants to disperse to new places - - Wind, water, or animals can carry seeds to new places far from where the individual plant produced them. Many seed plants have dispersal mechanisms, such as “wings” for their seeds. It is thought that seed plants may have evolved when earth’s climate shifted from warm and moist to hot and dry. Seed Plants Can Be Grouped Into Two Categories Gymnosperm • • Angiosperm A seed plant whose seeds are not enclosed in a fruit. • A seed plant that has seeds enclosed in some type of fruit Most are cone-bearing and evergreen • Angiosperms belong to a phylum of their own, and are called flowering plants. Flowering Plants A flower is the reproductive structure of a flowering plant. Flowers protect a plant’s gametes and fertilized eggs, the way woody cones do for gymnosperms. A fruit is the mature ovary of a flower, and contains the seeds of the plant.