Teaching Pyramid Observation Tool (TPOT) Why and
Data? –TPOT’s and BIR’s
Why? How Do I Use It?
Annette Hahn
Teaching Pyramid
Consultant/Coach,
Trainer vahahn1@yahoo.com
Objectives
Understand purposes for use of the
Teaching Pyramid Observation Tool
(TPOT)
Assess how well teachers are implementing the Teaching Pyramid model through use of the TPOT
Summarize and evaluate the results of the TPOT on the TPOT Summary
Objectives
Understand challenging behavior has meaning for the child.
Know children use behavior to access something or someone (obtain/request) or avoid something or someone
(escape/protest).
Use Behavior Incident Reports behavior.
to determine the function or purpose of challenging
TPOT
What is it?
Used as a way to determine how well teachers are implementing the pyramid
Meant to be an ongoing tool, not a one time event
Can be a pre/post measure
Can supplement other tools (e.g., ECERS…)
The Teaching Pyramid
Individualized
Intensive
Interventions
Social Emotional
Teaching Strategies
Designing Supportive Environments
Building Positive Relationships
CSEFEL
TPOT
Benchmarks of Quality
Program-wide adoption of fidelity tool
Identifies strengths and areas for implementation
Captures growth in fidelity of implementation
Galena am Pre TPOT 9-16-08
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
En vi ro nm en t (
1-
7)
#8 #9
#10 #11 #12 #13 #14 #15 #16 #17 #18 #19 #20 #21 #22
R ed
F la gs
Series1
Series2
Galena pm Pre TPOT 9-16-08
6
5
4
3
8
7
2
1
0
En vi ro nme nt
(1
-7
)
#8 #9
#1
0
#1
1
#1
2
#1
3
#1
4
#1
5
#1
6
#1
7
#1
8
#1
9
#2
0
#2
1
#2
2
R ed
F la gs
Series1
Series2
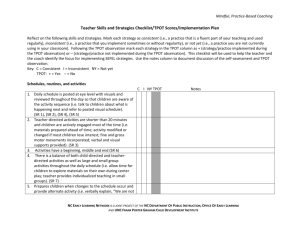
Using the TPOT
Observations
Conducted for a minimum of 2 hours
Must observe centers or free play and at least one teacher-directed activity
Focus on observation is lead teacher’s behavior
Interviews
For those practices that cannot be observed in a 2-hour observation
Format of the TPOT
Three types of items
Environmental items (items 1-7) – yes/no based on observation
Ratings of practices (items 8-22) – ratings based on observation and/or teacher report
Red Flags (items 23-38) – yes/no based on observation
Environmental Arrangement
Items
Clear boundaries
Move easily around room
Lack of large open spaces
Adequate number of centers
Materials support play
Preparation of centers
Classroom rules
Items based on observations and/or teacher report
Schedules
Transitions
Conversations
Promoting Engagement
Behavior Expectations
Providing Directions
Social Skills
Expressing Emotions
Problem Solving
Friendship Skills
Persistent Problem Behavior
Communication with Families
Involving Families
Relationships with Adults
Items are scored based on teacher report
Supporting children with persistent problem behavior
Communication with families to promote involvement
Involving families to support social emotional development and addressing problem behavior
Strategies to build collaborative teaching with other adults
Red Flag items 23-38
Represents issues related to teacher training, support, or program practices
Indicated areas for immediate training
Scored as yes/no
TPOT Practice Activity
TPOT Practice Activity
TPOT Table Activity
Summarize Results
Use Teaching Pyramid Observation Tool
(TPOT) Summary
Strengths
Emerging Skills
Professional Development needs
Challenging Behavior
Basic Assumptions
Challenging behavior usually has a message- I am bored, I am sad, you hurt my feelings, I need some attention.
Children often use challenging behavior when they don’t have the social or communication skills they need to engage in more appropriate interactions.
Behavior that persists over time is usually working for the child.
We need to focus on teaching children what to do in place of the challenging behavior.
Tom Herner (NASDE President,
Counterpoint 1998, p.2)
“If a child doesn’t know how to read,
“If a child doesn’t know how to swim,
“If a child doesn’t know how to multiply,
“If a child doesn’t know how to drive,
“If a child doesn’t know how to behave,
……….teach? ………punish?” we teach .” we teach .” we teach .” we teach.” we…….....
“Why can’t we finish the last sentence as automatically as we do the others?”
Children who are identified as hard to manage at ages 3 and 4 have a high probability (50:50) of continuing to have difficulties into adolescence (Campbell &
Ewing, 1990; Egeland et al., 1990; Fischer,
Rolf, Hasazi, & Cummings, 1984).
Changing Our View
Take the problem away from the
child and ask:
Why is this behavior happening?
What changes can I make to
prevent the problem from occurring and teach the child new skills?
Understanding Challenging
Behaviors
Form vs. Function
Form
What does the behavior look like?
Function
What is the purpose of the behavior from the child’s perspective?
Forms of Challenging Behavior
Aggression Tantrum
Hitting
Scratching
Kicking
Biting
Throwing things
Pinching
Threatening
Screaming
Crying
Whining
Cussing
Noncompliance
Refuses to respond to a request
Passive when a request is made
Forms of Challenging Behavior
Social
Withdrawal
Primarily plays alone
Doesn’t respond to peers attempts to play
Self Injury/
Repetitive
Scratching self
Biting self
Hitting self
Rocking back and forth
Spinning objects
Others?
Challenging Behavior Works
Children engage in challenging behavior because “it works” for them.
Challenging behavior results in the child gaining access to something or someone (i.e., obtain/request) or avoiding something or someone (i.e., escape/protest).
Obtain
Functions of
Challenging Behavior
Attention
Escape
Adult
Peer
Adult
Peer
Tangible/
Activity
Toys/Items
Food
Activity
Toys/Items
Food
Activity
Sensory
Stimulation
Sensory
Stimulation
Sensory
Stimulation
Behavior Equation
Trigger
Joey is asked to come to circle.
Teacher provides physical prompt to move him to group.
Behavior
Joey resists, cries, and hits teacher.
Maintaining
Consequence
Teacher moves away from Joey and allows Joey to select a different activity.
Setting Event
Event that occurs at another time that increases the likelihood the child will have challenging behavior. Setting events serve to “set the child up” to have challenging behavior.
Behavior Equation
Setting
Event
Trigger Behavior Maintaining
Consequence
Quan approaches computer and sees child working on program.
Quan moves his picture to indicate that he is next.
Quan observes and waits for his turn.
Child leaves computer and
Quan sits down and begins working.
Behavior Equation
Setting
Event
Quan was up most the night with an asthma attack.
He arrives at school looking sleepy and with dark circles under his eyes.
Trigger
Quan approaches computer and sees child working on program.
Behavior
Quan hits child and pushes his body on the child’s chair.
Maintaining
Consequence
Child leaves computer and
Quan sits down and begins working.
What is the function?
Sevon, a 3 year old hits the teacher and says
“no” when give a puzzle to complete. The teacher removes Sevon from the table and places him in a chair away from the group.
Franz, a preschooler with Downs Syndrome, cries when the teacher is passing out popcorn and accidentally skips him. The teacher quickly gives him some popcorn.
What is the function?
Christina, who has autism, rocks back and forth when there is free play in the classroom. The class ignores her.
Mary, a 4 year old, “smarts off” to her teacher and the entire class laughs.
Kirby, who is 3 years old, runs to the play area when his teacher tells him it is time to sit at the table. The teacher says “no” and brings Kirby back to the table.
Observation Vignette
Observation Vignette
What is the function?
Setting
Event Trigger Behavior
Maintaining
Consequence
Function:
Behavior Incident Report
Procedure
Complete all areas of the form for each instance of problem behavior using the instructions provided for completing the
Behavior Incident Report
Behaviors that……
Cause injury to self, or others
Cause damage to the physical environment
Interfere with learning new skills
Socially isolate a child
Behavior Incident Report
Procedure
The BIR is completed for any behavior that is perceived as challenging.
Look at the situation in which the behavior occurs
Identify and describe the challenging behavior
Identify what events, people, activities, are associated with the behavior
Share Information
Use Bar Graph or other visual to display TPOT
Summary results
Tabulate BIR’s.
Define the behavior
Identify factors related to the behavior
When, where the behavior occurs
Persons the behavior occurs with
Activities and time related to the behavior
Identify the functions/outcomes for the behavior
October
Next Steps for TPOT
Develop a Professional Development Plan based on the TPOT Summary
Use the needs of the teaching team
Fidelity Checklist to determine the degree to which interventions are carried out as planned
Next Steps for BIR’s – Facilitating the
Development of a Positive Behavior Support
Plan
Learn how to use a team work approach in conducting a functional behavioral assessment, developing a hypothesis, creating a behavior support plan and monitoring outcomes.