Light! Now See This!
advertisement

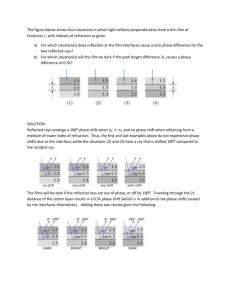
Light! Now See This! Mrs. Erickson Core Curriculum (What you will learn) Standard VI: Students will understand properties and behavior of heat, light, and sound. Objective 2: Describe how light can be produced, reflected, refracted, and separated into visible light of various colors. A. Compare light from various sources (e.g., intensity, direction, color). Remember… Light is a form of energy just like sound and heat. It travels in waves. So it has wavelength and frequency. Make a List…#1 Make a list of everything you know of that gives us light (you must have at least 10 items on the list). 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Sun ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ 6. ____________________ 7. ____________________ 8. ____________________ 9. ____________________ 10. ____________________ Make a List…#2 Make a list of all of the things light provides for us. 1. Heat _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio Waves (including Microwaves) Infrared Rays Visible Light Ultraviolet Rays X-Rays Gamma Rays Long Wavelength & Low Frequency Short Wavelength & High Frequency Electromagnetic Spectrum Assignment Name two things each of the waves in the electromagnetic spectrum is used for (see pages 80-88 of your book). For example, one thing radio waves are used for is communication. Radio waves: • 1. communication • 2. _________________________________________ Infrared Rays: • 1. _______________________________________ • 2. _______________________________________ Electromagnetic Spectrum Assignment Visible Light: • 1. _______________________________ • 2. _______________________________ UV Rays: • 1. ____________________________________ • 2. ____________________________________ X-Rays: • 1. ___________________________________ • 2. ___________________________________ Gamma Rays: • 1. ____________________________________ • 2. ____________________________________ Vocab Words Vocab Words: (look up the definition of each word and write it beside the word) Luminous: _______________________________ __________________________________________ Electromagnetic spectrum : _________________ __________________________________________ Ultraviolet (UV) rays : _______________________ __________________________________________ visible light: ______________________________ __________________________________________ Visible Light What is visible light? Visible light is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that we can see. Why do we see different colors? We see different colors because each different wavelength of light has a different color. Visible Light ROY G. BIV Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Indigo Violet Visible Light Assignment Fill in the table on the next slides in your notes. Use your book (pages 90-93) and own knowledge to fill in the tables on the visible light slides. We will share information after. Visible Light Incandescent lights Fluorescent lights Neon lights Halogen lights Bioluminescence Visible Light Assignment Kind of Light Definition Where can we What color Is it a good find it? does it source of appear to be? light? Why or why not? Incandescent Glow when a filament inside them gets hot Indoor & outdoor lighting; car headlights; flashlights; decorative lighting White (but can be other colors) get hot; inexpensive to make Visible Light Assignment Kind of Light Definition Where can we What color Is it a good find it? does it source of appear to be? light? Why or why not? Fluorescent (compact & linear) Glass tube w/ School, office, white gas inside & kitchen coated inside w/a powder Yes; high efficiency; low cost Visible Light Assignment Kind of Light Definition Where can we What color Is it a good find it? does it source of appear to be? light? Why or why not? Neon A sealed glass tube filled w/neon Bright, flashy signs Red (other no gasses produce other colors) Visible Light Assignment Kind of Light Definition Where can we What color Is it a good find it? does it source of appear to be? light? Why or why not? Tungsten Halogen Tungsten filament & contain a gas Projectors; floor lamps yellow Yes (provide bright light from small bulb); little electricity; become hot Visible Light Assignment Kind of Light Definition Where can we find it? What color does Is it a good it appear to be? source of light? Why or why not? Bioluminescence Organisms that produce their own light Jellyfish, deep sea fish, firefly, fungi & mushrooms, bacterial Depends on organism For the organism, not for us Visible Light Assignment Kind of Light Definition Where can we What color Is it a good find it? does it source of appear to be? light? Why or why not? LED (Light Emitting Diode) Diodes allow electricity pass in only one direction; emit visible light when electricity is applied Aviation; traffic lights; auto lighting; communicatio n; remote controls; small electronics Core Curriculum B. Compare the reflection of light from various surfaces (e.g., loss of light, angle of reflection, reflected color). Vocab Words: angle of incidence angle of reflection ray reflection concave mirror convex mirror Vocabulary Vocab Words: angle of incidence: ______________________________ ________________________________________________ angle of reflection: ______________________________ ________________________________________________ ray: ___________________________________________ reflection: ______________________________________ _________________________________________________ concave mirror: _________________________________ _________________________________________________ convex mirror: __________________________________ _________________________________________________ Core Curriculum/Vocabulary E. Predict and test the appearance of various materials when light of different colors is shone on the material. Vocab Words: opaque: ____________________________________ _____________________________________________ transparent: _________________________________ _____________________________________________ translucent: _________________________________ _____________________________________________ When Light Strikes an Object 3 Things Can Happen, Light is: Reflected (page 113 of book) (the bouncing of light waves from a surface) Absorbed (takes in colors—may be some or all) Transmitted (light goes through the object) Regular Reflection Happens when parallel rays of light hit a smooth, or even, surface All the rays are reflected at the same angle What are some examples? I.E. if you look at a shiny sheet of metal, you can see your own reflection Shiny metal (or other smooth surface) Diffuse Reflection Happens when parallel rays of light hit an uneven, or a bumpy, surface The rays are reflected at different angles. Most objects reflect this way. What are some examples? Mirrors What is a mirror? How does a mirror A mirror is a sheet of reflect an image? When light passes through the glass, the coating on the back reflects the light, allowing you to see the image. (Which kind of reflection is it?) glass that has a smooth, silver coating on one side. Mirrors can be flat or curved. This shape determines if an image appears the same size, smaller, or larger. Flat, or Plane, Mirrors Mirror is flat (smooth). Image appears about the same size and distance as well as right side up but backwards. Write two examples of a flat mirror in your notes. __________________ 2. __________________ 1. Concave Mirrors Mirror looks “caved” in. It is curved inward. Surface curves inward like the inside of a bowl. Reflects light rays so they meet at a point, called a “focal point.” A mirror to make things look bigger. Focal point Turn to page 115 in your book and copy diagrams A, B, and C in your notes. Write 2 examples in your notes. 1. ________________ 2. ________________ Convex Mirrors Mirror looks “curved out.” Rays spread out but appear to come from a focal point behind the mirror. Widens the viewpoint but images appear further away than they really are. Convex Mirrors Write 2 examples in your notes. 1. _________________ 2. _________________ Turn to page 116 in your book and copy the diagram at the top of the page. Mirrors? Answers these questions in your notes: 1. How would you look in a concave mirror? __________________________________________ 2. How would you look in a plane (flat) mirror? __________________________________________ 3. How would you look in a convex mirror? __________________________________________ Opaque Objects reflect or absorb all of the light that strike it cannot be seen though examples: wood, metal, wool & cotton fabrics Most objects are opaque. Transparent Objects transmit light (light passes right through it) allow you to see through to the other side examples: clear glass, water, air Translucent Objects allow some light to pass through scatter light as it passes through you can tell there is something behind but no details examples: frosted glass, wax paper Light Transmission Assignment Write 5 objects that transmit light each way in your notes: Opaque (1-5) 1. _________________ 2. _________________ 3. _________________ 4. _________________ 5. _________________ Transparent (6-10) 6. _________________ 7. _________________ 8. _________________ 9. _________________ 10. _________________ Translucent (11-15) 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. _________________ _________________ _________________ _________________ _________________ Remember!! When light hits an object, what three things can happen? •Light can be: •Reflected (two types-what are they?) 1. __________ 2. ___________ •Transmitted (three ways-what are they?) 1. ___________ 2. ____________ 3. __________ •Absorbed Core Curriculum Investigate and describe the refraction of light passing through various materials (e.g., prisms, water). Vocab Words: prism: ______________ _____________________ _____________________ refraction D. Predict and test the behavior of light interacting with various fluids (e.g., light transmission through fluids, refraction of light). Vocab Word: refraction: __________ _____________________ _____________________ Absorption Means object takes in colors; may be some or all. All colors are reflected if an object appears white. All colors are absorbed if an object appears black. Most objects reflect more than one color. Absorption: Everything reflects light! The color of an object is the color of the light it reflects. For example, when we look at a red apple it reflects red and absorbs all the other colors. Color Objects appear different colors in different colors of light. We see objects in: White light (like from the Sun) Colored light (like from a light bulb, p. 125 in book) Through filters (like lights on a stage) Primary Colors of Light The primary colors of light are: Red, Blue, Green Any 2 primary colors combined produce a secondary color. When all amounts of 3 primary colors are equal, we see white light. (p. 126) When there are unequal amounts, we see another color. Absorption- Make a list of 10 items and what color(s) each reflect(s). Object Color/s 1. __________________________________________ 2. __________________________________________ 3. __________________________________________ 4. __________________________________________ 5. __________________________________________ 6. __________________________________________ 7. __________________________________________ 8. __________________________________________ 9. __________________________________________ 10. __________________________________________ Color Writing Assignment On a lined sheet of paper, answer the following questions: In what way(s) does light (and different colors of light) effect the way we see color? (should be at least 4 sentences) ***This assignment should be turned in separately, not left with your notes. Light & Refraction When light rays enter a new medium at an angle, the change in speed causes them to bend, or change direction. This is called refraction. This is how convex and concave lenses and mirrors work. Prisms, rainbows, and mirages are examples of refraction. Light & Refraction Turn to page 117 in your book. How many fish appear to be in the tank? ____________ How many are actually in the tank? ________________ What other examples can you think of? ____________________________________________ Write at least 2 other examples of refraction in your notes. __________________________________________ 2. __________________________________________ 1. Light & Refraction Turn to page 118. •Look at Figure 8. Copy this in your notebook. MAKE SURE YOU COPY THE LINES LIKE THEY ARE IN THE DIAGRAM. Lenses- There are two basic types of lenses: Concave- makes images smaller. It is thinner in the center than at the edges Convex-makes images larger. It is thicker in the center than at the edges. Turn to page 120 in your book. Copy Figure 13 in your notebook. Notice how the shape of the lens are different. Lenses Lenses are different than mirrors because they refract light instead of reflect light. •Lenses are transparent or clear. •Mirrors are opaque. Prisms A prism is a clear piece of glass or plastic that bends or breaks up white light into the colors of the spectrum (p. 118) Rainbows How do rainbows work? A rainbow forms when sunlight is refracted and reflected by tiny water droplets. In other words, raindrops act like prisms when the white light hits them. Colors are always reflected in the same order: ROY G. BIV Mirages Have you ever looked down the road on a hot day and it looks wet? Then when you get there, it isn’t actually wet? •That is a mirage. •A mirage is an image of a distant object caused by refraction of light. •See page 119 in your text book. How do you see Paste eye diagram in your notebook at the end of your light notes. Parts of the eye: Cornea-light enters the eye through here; moistened by “windshield wiper” eyelids Iris-contracts and expands to let in more or less light; colored part of the eye Pupil-part of the eye that looks black; actually a hole; pupil can become larger or smaller How do you see-part 2 lens-convex lens; forms an image on your eyeball Retina-made up of millions of rods and cones which sends signals to brain (rods allow you to see white, black, and grey, as well as in dim light; cones allow you to see blue, red, and green) Optic nerve & brain-signals sent along optic nerve; brain flips them right side up Correcting Vision Nearsightedness (see near but not far)-eyeball is too long so concave lens forms image in right place Farsightedness (see far but not near)-eyeball is too short so convex lens forms image in right place