Practice Exam 1 - Iowa State University
advertisement

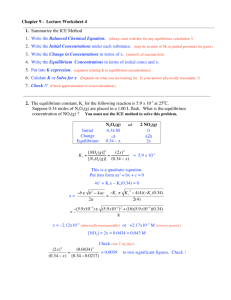
Leader: Lindsey and Tyler Course: Chem 178 Instructor: Bonaccorsi/Meyer Supplemental Instruction Date: Feb 9 Iowa State University 1. For the combustion of octane, if octane is consumed at a rate of 1.67 M/s, what is the rate of production of carbon dioxide? Chem 178 SI: Exam 1 Review 2𝐶8 𝐻18 + 25𝑂2 → 18𝐻2 𝑂 + 16𝐶𝑂2 2. The following rate law is given for the reaction 𝐴 + 𝐵 → 𝐶: 𝑟𝑐 = 𝑘[𝐴]2 [𝐵] What is the overall order of the reaction, and the order of each reactant? 3. Use the following data to determine a rate law for the reaction 𝐴 + 2𝐵 → 𝐴𝐵2. [A] (M) 0.6 1.8 1.8 0.6 [B] (M) r(AB2) (M/s) 0.8 1.4 0.8 12.6 3.2 12.6 4.5 1.4 4. Determine the half-life of the reactant A in the reaction 𝐴 → 𝐵 given that the initial concentration of A is 3 M and the rate constant k is 1.24 (units vary with reaction order): a. Assuming the reaction is zero order in A b. Assuming the reaction is first order in A c. Assuming the reaction is second order in A 5. Determine the rate law and the overall reaction given the following mechanism. 2𝑁𝑂2 → 𝑁𝑂3 + 𝑁𝑂 𝐶𝑂 + 𝑁𝑂3 → 𝐶𝑂2 + 𝑁𝑂2 (Rate determining step) 6. Find the reaction rate for a reaction that is 1st order in A and 2nd order in B with a rate constant of 4.5 M-2s-1. 7. Find the initial concentration of species A for a second-order reaction, given the concentration of species A at t = 575 seconds is 4.0 M and the rate constant is .056 M-1s-1. 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 sistaff@iastate.edu http://www.si.iastate.edu 8. Given the overall reaction and the mechanism, determine the reaction rate law. Overall: Steps: 2A + 2B → C A+B⇄D A + D → E Rate-determining step B+E→C 9. What is the rate law for the reaction A + B + C → 2D based on the given data? [A] (M) 0.7 1.4 1.4 1.4 [B] (M) 1.2 1.2 3.6 1.2 [C] (M) r(D) (M/s) 4.5 2.6 4.5 2.6 4.5 7.8 9 10.4 10. Give the rate law for the following reaction is R = k[B]2, ,identify the rate determining step. Overall: Steps: 2A + 3B → C + D 2B → C + E 2A + E → F B+F→D 11. The position of equilibrium for the reaction ZnO(s) + H2(g) ⇌ Zn(s) + H2O(g) does not depend upon which of the following (pick multiple): (1) concentration of ZnO(s) (2) concentration of H2(g) (3) concentration of Zn(s) (4) concentration of H2O(g) (5) the value of Kc? 12. Which way will each of the following reactions, initially at equilibrium, shift when the temperature is decreased at constant pressure? 1.) 2C2H2(g) + 5O2(g) ⇌ 4CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) ΔH = -1297 kJ 2.) CO2(g) ⇌ O2(g) + C(s) ΔH = +393 kJ 3.) 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) ⇌ 2Fe2O3(s) ΔH = -1644 kJ 13. What is the value of Kc for the following reaction if the equilibrium concentrations are [A] = 0.60 M [B] = 0.35 M [C] = 0.55 M? 2 A (aq) + B (aq) ⇌ 2 C (aq) 14. Initially 0.035 moles of SO2, 0.5 moles of SO2Cl2, and 0.08 moles of Cl2 are combined in a 5 liter flask. What is the value of Q and which direction will the reaction proceed to establish equilibrium? SO2Cl2 (g) ⇄ SO2 (g) + Cl2 (g) Kc = 0.078 15. What is Kc for the following reaction if Kp is 0.76 at 900 K? 2SO3(g) ⇌ 2SO2(g) + O2(g) 16. 6. A 0.700 mole sample of N2O4 (g) is allowed to come to equilibrium with NO2 (g) in a 0.750 L flask. At equilibrium 0.420 M N2O4 remains. Calculate the equilibrium concentration of NO2. N2O4 (g) 2NO2 (g) 17. 7. What is the correct Keq expression for the following reaction? 2 NO(g) + 2 H2 (g) N2(g) + 2 H2O(g) a. Keq = [N2 ][H2O] [NO][H2 ] [NO][H2 ] b.Keq = [N2 ][H2O] [N ][H O]2 2 2 c. 𝐾𝑒𝑞 = ([NO] 2 [𝐻 2 2] ) [NO]2 [H2 ]2 d. 𝐾𝑒𝑞 = [N2 ]2 [H2O] 18. 8. N2O4 and NO2 have the following equilibrium equation: 2NO2 (g) N2O4 (g) A closed container held at 298K is filled with N2O4 at a partial pressure of 0.50 atm and NO2 at a partial pressure of 0.60 atm. At equilibrium the partial pressure of N2O4 is measured to be 0.54 atm. What is the value of the equilibrium constant? 19. The type of chemical equilibrium exemplified by the following reaction is: BaSO4(s) ⇌ BA2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) a. Chemical equilibrium b. Haber c. Heterogeneous d. Homogeneous e. Mass action 20. Which of the following is not affected when a catalyst influences a gaseous chemical reaction? a. Forward and reverse reaction rates b. Initial reaction rate c. Value of equilibrium constant d. Reaction mechanism pathway 21. Given 2NOCl (g) 2NO (g) + Cl2 (g) What would happen when equilibrium is disturbed by an increase of volume? (Would more product or reactant or neither form?)