Chapter 13 - Equilibrium

Chemical Equilibrium Practice
Given the following equations, answer the questions indicating whether each substance will increase, decrease, or remain the same for the given change.
A.
aA(g) + bB(g) + heat
cC(g) + dD(g)
B.
aA(g) + bB(g)
cC(g) + heat
a = 2 b = 3 c = 4
1. In equation A, a decrease in the concentration of C will have what effect on the following? a. The concentration of B b. The concentration of A c. The concentration of D d. The equilibrium constant K c
2. In equation B, increasing the temperature will have what effect on the following? a.
The concentration of A b.
The concentration of C c.
The concentration of B d.
The equilibrium constant K c
3. In equation B, increasing the pressure will have what effect on the following? a. The equilibrium constant K c b. The concentration of C c. The concentration of B d. The concentration of A
Given the following equations, answer the questions indicated.
A.
aA(g) + bB(g) + heat
cC(g) + dD(g) a = 3 b = 4 c = 2 d = 5
B. aA(g) + bB(g)
cC(g) + heat
4. In equation B, decreasing the concentration of B will have what effect on the following? a.
The concentration of A b.
The concentration of C c.
The equilibrium constant K c
5. In equation A, decreasing the pressure will have what effect on the following? a.
The concentration of A b.
The concentration of C c.
The concentration of B d.
The equilibrium constant K c
6. In equation A, decreasing the temperature will have what effect on the following? a.
The concentration of A b.
The concentration of C c.
The concentration of B d.
The equilibrium constant K c
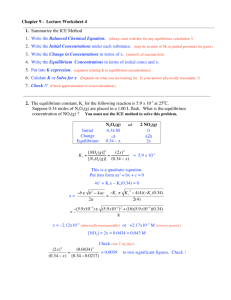
7. Calculate K p
for the equation: aA(g) + bB(g)
cC(g) + heat if:
A = 1.6 atm, B = 3.6 atm, C = 8.7 atm, and: a = 2; b = 3, c = 5.
8. Write the general equilibrium expressions for the following reactions (refer to notes): a. H
2
(g) + I
2
(g)
2HI(g) b. 2SO
2
(g) + O
2
(g)
2SO
3
(g) c. HF(aq) + H
2
O(l)
F
-
(aq) + H
3
O
+
(aq) d. 2NH
3
(aq) + 3I
2
(s)
2NI
3
(s) + 3H
2
(g) e. CO(g) + H
2
O(g)
CO
2
(g) + H
2
(g) f. Ba
+2
(aq) + SO
4
-2
(aq)
BaSO
4
(s) g. C
2
H
4
(aq) + 3O
2
(g)
2CO
2
(g) + 2H
2
O(g)
9. Calculate K eq
or concentrations as indicated for each reaction and then decide whether products or reactants are favored.
Assume all are (aq) unless otherwise noted. a.
2NO
2
N
2
O
4
NO
2
= 8.23 x 10
-3
M; N
2
O
4
= 1.46 x 10
-3
M b.
CH
4
+ H
2
O
CO + 3H
2
CH
4
= 0.200 M; H
2
O = 0.150 M; CO = 1.37 x 10
-2
M;
H
2
= 4.11 x 10
-2
M c. 2NO
2
Cl(g)
2NO
2
(g) + Cl
2
(g)
NO
2
Cl = 0.00106 M; NO
2
= 0.0108 M; Cl
2
= 0.00538 M. d. C(s) + H
2
O(g)
CO(g) + H
2
(g) Calculate the concentration of CO.
Keq = 4.251 x 10
-2
; H
2
O = 0.1990 M
CO
=
H
2
10. The reaction of gaseous sulfur with oxygen at high temperature is:
2S(g) + 3O
2
(g)
2SO
3
(g)
if the partial pressures at equilibrium are measured as
P s
= 0.0035 atmosphere; P
SO3
= 0.0050 atmosphere; and
P
O2
= 0.0021 atmosphere, calculate the equilibrium constant K p