Project Management
advertisement

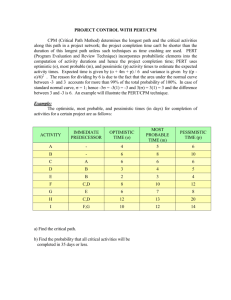
Project Management Why project management? Re: Any Marketing/Advertising PM's out there? Posted by: "kquain" kquain@walmart.com kquain Wed Mar 7, 2007 10:29 am (PST) I had a number of direct responses to this post which I really appreciate (I just joined yesterday, and am already pleased with my decision to join). My inquiry was driven by the fact that we are having some difficulty finding PM's experienced in marketing/advertising and or large scale retail. I'm honestly getting alot of applicants who are designers or copy writers which, as you can imagine, makes me a bit hesitant. As the Director of Process & Production at Wal-Mart, my team manages all Marketing Creative projects for Wal-Mart. We work on everything from the instore signage, to billboards, to tv advertising, to our biweekly printed circular. I need PM's with print and broadcast experience that aren't just robotic PM's but also really understand customer service and account management. We have PM openings and Sr. PM openings. If you are seriously interested, I encourage folks to send their resumes to me. We're making some very big changes here at WalMart; people who join us now have the chance to make a big impact on the way Wal-Mart works. I truly believe this is a chance/experience of a lifetime for passionate PM's. Thanks again for all the responses! Kelley Troia Why project management? New Member Posted by: "kelly_boatright" kelly_boatright@dell.com kelly_boatright Wed Mar 14, 2007 8:38 am (PST) Hello WiPM, I am a new member, and happy to see so many members in the PM world. I think PM is a perfect fit for women as we are natural multitaskers, yes? I am a member of Dell Global Services, the consulting arm of our company. We are looking for talented women across all areas of Services, but especially to lead our larger accounts as a Sr. PM or Program Executive. There are also opportunities in TAM (Technical Account Manager) positions in many markets as well. We have current and potential accounts across the U.S., therefore our roles are located in major marketsNY/NJ, Seattle, Washington D.C., Southern CA. In addition to sourcing out talent for DGS, I do incorporate some PM into my role keeping one foot in the business. After a few years in NYC I've moved to Austin. Most of my time is spent with my two dogs (adopted mixed are the best), and my husband. We like taking long walks, hiking and, of course, going to the dog park. If interested in opportunities with Dell Global Services, you may send your resume to my email, or feel free to contact me in order to learn more. Kelly Boatright Talent Acquisition Dell | Global Services Cell: (512) 672-9893 Desk: (512) 723-4373 Email: kelly_boatright@dell.com Linked In: http://www.linkedin.com/in/kellyboatright Dell Careers: www.dell.com/careers Overview What is project management Work breakdown structure Project scheduling Gantt charts CPM Project Characteristics Single unit Many related activities Difficult production planning and inventory control General purpose equipment High labor skills Examples of projects Personal Obtain a degree Obtain a job Plan a wedding Move Have a baby Thanksgiving dinner Rebuild a car Company/Non-profit Build a house Plan Olympics Intro. new product Install a new software Plan a military operation Hoover dam Produce a movie Project Management Questions What activities are required to complete a project and in what sequence? When should each activity be scheduled to begin and end? Which activities are critical to completing the project on time? What is the probability of meeting the project completion due date? How should resources be allocated to activities? Elements of Project Management Planning •Set goals •Define project •Develop work breakdown schedule •Identify team/resources Elements of Project Management Schedule •Sequence activities •Assign people •Schedule deliverables •Schedule resources Elements of Project Management Control •Monitor resources, costs, quality •Revise/change plans •Shift resources The Role of the Project Manager Project Plan and Schedule Revisions and Updates Project Manager Information regarding times, costs, problems, delays Resources Performance Reports Project Team Feedback Loop Top Management Organizational structures for projects Pure project structure - a self-contained team works full-time on the project Functional project structure - housed within a functional division; team members remaining part of the functional units and typically are not dedicated to the project Matrix project – blends the function and pure project structures. The project uses people from different function areas. A dedicated project manager decides which determines and schedules tasks but the functional manager assigns people. Pure Project Structure Advantages The project manager has full authority over the project Team members report to one boss Shortened communication lines Team pride, motivation, and commitment are high Pure Project Structure Disadvantages Duplication of resources Organizational goals and policies are ignored Lack of technology transfer Team members have no functional area "home" Functional Project President Research and Development Project Project Project A B C Engineering Project Project Project D E F Manufacturing Project Project Project G H I Example, Project “B” is in the functional area of Research and Development. Functional Project Structure Advantages A team member can work on several projects Technical expertise is maintained within the functional area The functional area is a “home” after the project is completed Critical mass of specialized knowledge Functional Project Structure Advantages Aspects of the project that are not directly related to the functional area get shortchanged Motivation of team members is often weak Needs of the client are secondary and are responded to slowly Matrix Project Structure President Research and Engineering Manufacturing Development Manager Project A Manager Project B Manager Project C Marketing Matrix project structure Advantages Enhanced communications between functional areas Pinpointed responsibility Duplication of resources is minimized Functional “home” for team members Policies of the parent organization are followed Matrix project structure disadvantages Too many bosses Depends on project manager’s negotiating skills Potential for sub-optimization Work Breakdown Structure 1. Project 1.1 Major task 1 1.1.1 Subtask 1 of major task 1 1.1.1.1 Activity 1 of subtask 1 1.1.1.2 Activity 2 of subtask 1 1.1.2 Subtask 2 of major task 2 1.2 Major task 2 1.2.1 Subtask 1 of major task 2 1.2.2 Subtask 2 of major task 2 1.3 Major task 3 Work Breakdown Structure How is this project structured? List the 1st level of the work breakdown structure. Project Scheduling Techniques Gantt chart Critical Path Method (CPM) Program Evaluation & Review Technique (PERT) (SKIP) © 1984-1994 T/Maker Co. PERT and CPM Network techniques Developed in 1950’s CPM by DuPont for chemical plants PERT by U.S. Navy for Polaris missile Consider precedence relationships and interdependencies Each uses a different estimate of activity times Consumer Product Development A company has 16 weeks for the development of a consumer product from initiation through the market test phase. Every week after 16 that this project is not completed the company is losing $1000 in profit. Activity Symbol Preceding Activities Time estimate (weeks) A B --- 3 1 Conduct promotional cost analysis C D -A 5 1 Manufacture prototype models E C 6 Perform product cost analysis F E 1 Perform final pricing analysis G B,D,F 2 Conduct market test H G 8 Investigate demand Develop pricing strategy Design product Network for Product Development A Start D G B C E F H Gantt Chart for Product Development Questions Which May Be Addressed by PERT & CPM Is the project on schedule, ahead of schedule, or behind schedule? Is the project over or under cost budget? Are there enough resources available to finish the project on time? If the project must be finished in less than the scheduled amount of time, what is the way to accomplish this at least cost? Steps in the CPM 1. Activity Identification 2. Activity Sequencing and Network Construction 3. Determine the critical path From the critical path all of the project and activity timing information can be obtained Network closeup Node: Activity B – Construct collection stack Arrow: Activity A precedes Activity B A Node: Activity A – Build internal components B Activity Relationships A Start B Critical path for House Building Example Activity Description Immediate Predecessor(s) S Pour foundation and frame — T Buy shrubs, etc. — U Roof S V Do interior work S W Landscape T, U Network for House Building Example Start Network for House Building Example S (6) Start Network for House Building Example S (6) Start T (3) Network for House Building Example S (6) U (2) Start T (3) Network for House Building Example S (6) V (3) U (2) Start T (3) Network for House Building Example S (6) V (3) U (2) Start T (3) W (4) Network for House Building Example S (6) V (3) U (2) Start T (3) End W (4) Critical path for House Building Example S (6) V (3) U (2) Start T (3) End W (4) Critical path for House Building Example S (6) V (3) U (2) Start T (3) End W (4) Gantt Chart Earliest Start and Finish Build House Project Activity S Fdn & frame T Buy shrubs U Roof V Interior work W Landscape 1 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 Gantt Chart Latest Start and Finish Build House Project Activity 1-2 Fdn & frame 1-3 Buy shrubs 2-3 Roof 2-4 Interior work 3-4 Landscape 1 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 Example CPM Consider the following consulting project: Activity Assess customer's needs Write and submit proposal Obtain approval Develop service vision and goals Train employees Quality improvement pilot groups Write assessment report Designation Immed. Pred. Time (Weeks) A None 2 B A 1 C B 1 D C 2 E C 5 F D, E 5 G F 1 Develop a critical path diagram and determine the duration of the critical path and slack times for all activities. Example: First draw the network Act. Imed. Pred. Time A None 2 B A 1 C B 1 D C 2 E C 5 F D,E 5 G F 1 A(2) B(1) D(2) C(1) F(5) E(5) G(1) Example: Determine the critical path Act. Imed. Pred. Time A None 2 B A 1 C B 1 D C 2 E C 5 F D,E 5 G F 1 A(2) B(1) D(2) C(1) F(5) E(5) G(1) Critical Path Analysis Provides activity information Earliest (ES) & latest (LS) start Earliest (EF) & latest (LF) finish Slack (S): Allowable delay Identifies critical path OM Go to Excel Longest path in network Shortest time project can be completed Any delay on critical path activities delays project Critical path activities have 0 slack Project management software Microsoft Project Benefits of CPM Useful at many stages of project management Mathematically simple Uses graphical displays Gives critical path & slack time Provides project documentation Useful in monitoring costs Limitations of CPM Assumes clearly defined, independent, & stable activities Specified precedence relationships Subjective time estimates Over-emphasis on critical path