Ch 2 - sierackichem

Slope
Rise = y
2
-y
1 = m
2
-m
1 =
Run x
2
-x
1 v
2
-v
1 mass volume
Pick 2 points.
Write the coordinates (x
1
Calculate the density
,y
1
)(x
2
,y
2
)
Do this on your graph.
Computer Graphing
• Excel
• A- x axis,Time
• B- Y axis, volume of Na2S2O3
• Highlight all 2columns
• Insert
• X,Y scatter middle chart left column
• Chart layout first box Title (include your name), label both axis
• right click , move chart , New sheet
• Unshade background
• Print 2 to lexchem
More Dimensional Analysis
1. Convert 45 miles/hour to: in/sec
2. Convert 14.6 Kg/L to: dg/mL
Observing
• Card Trick
• Zooley
• Always make at least 4 observations: state of matter (solid,liquid,gas) color clarity odor
Energy
Energy
Capacity to do work or produce heat
Measuring Energy
• Calorie the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 o C.
1000 cal.=1 Kcal=1 Calorie (food)
• Joule
1 cal.=4.184 J
Practice
1. A student uses 30 J of energy putting books on a shelf. How many calories is this?
2. The energy content of a bag of potato chips is 350 Calories
How many J is this?
Energy Types
• Nuclear
• Chemical
• Electrical
• Solar
• Thermal
• Mechanical
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy is neither created nor destroyed (its converted from one form to another)
Energy Conversion
Hair dryer
Temperature
• Amount of hotness or coldness
• Temperature is not heat
• C= K-273 ( Celsius is smaller so subtract)
• K= C+ 273
Pure Matter
Elements cannot be broken down by chemical processes
Compound
Chemical combination of elements
(share or transfer of electrons)
Changes in Matter
• Physical changes
• Involve no change in composition
P hysical properties:
Boiling/melting point, density, color, odor, ductile
• Chemical changes
• Involves a change in composition
Heat change
Color change
Gas evolved
Precipitate formed
Chemical properties: combustion, reactivity
Lab: Physical/Chemical Changes
Title
Purpose: To determine physical and chemical changes as indicators for a chemical reaction
Safety:
Data table:
Law of Conservation of Matter
Matter is neither created nor destroyed, it is conserved
(not in nuclear reactions)
Matter
Anything that has mass and volume do not copy in notebook
Density Pressure Container
Solid High not affected own shape
Liquid High not affected takes shape
Gas low affected fills
Plasma low affected fills
Mixtures
(Not pure substances physical combination)
Homogeneous (solution)
1 phase visible
Heterogeneous
2 or more phases visible
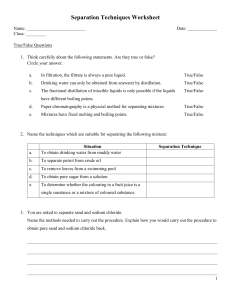
Separation of Mixtures
Homogeneous:
Distillation
Crystallization
Chromatography
Heterogeneous:
Filtration
2.3 RR
2.4 RR
2.5 RR
Practice
Physical/Chemical Processes
Types of Energy
• Kinetic energy of motion
• Potential stored energy
Lab: Separation of Mixture
• Title
• Partner, date
• Goal: To separate a mixture of salt and sand and to determine the percent sand and salt
• Write your own specific step by step procedure
• Make your own data table
• Show percent calculations and percent error
• Specific error analysis
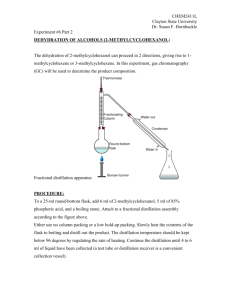
Pre-lab quiz - Fractional distillation
1. State 1 safety hazard to remember with ethyl alcohol (ethanol)
2. What will be recorded periodically through the distillation?
3. List 2 physical properties observed or recorded
4. State 1 safety hazard to remember about the flask at the end.
5. What observation/measurement will indicate to change beakers to collect each fraction?