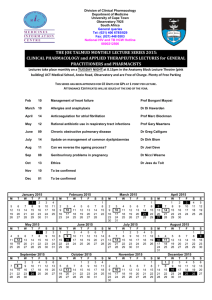
2- Presentation1 - INAYA Medical College
advertisement
Lecture 2 Dr. Dalia Mohsen prof. In Microbiology Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen CLS (311) Prof. in Microbiolog • Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog All living cells are classified into Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells, based on their structural and functional characteristics. Prokaryote comes from the Greek words for prenucleus. Eukaryote comes from the Greek words for true nucleus. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog PROKARYOTIC CELLS • Archaea • Bacteria EUKARYOTIC CELLS • Fungi • protozoa, • algae, • plants • animals Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Important • Viruses -Non-cellular elements that do not fit into any organizational scheme of living cells. (will be discussed later) Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Bacteria are unicellular. Most bacteria are 0.2 um in diameter and 2-8 um in length. Most bacteria are monomorphic – maintain a single shape. and few are pleomorphic – they can have many shapes. Ex – Rhizobium and Corynebacterium. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Basic shapes of bacteria COCCI • Cocci may be oval, elongated, or flattened on one side. • Cocci may remain attached after cell division. These group characteristics are often used to help identify certain cocci. Cocky that remain in pairs after dividing are called diplococci. Cocci that remain in chains after dividing are called streptococci. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Cocci that divide in two planes and remain in groups of four are called tetrads. Cocci that divide in three planes and remain in groups or cube like groups of eight are called sarcinae. Cocci that divide in multiple planes and form grape like clusters or sheets are called staphylococci. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Bacillus means rod shaped. Bacilli only divide across their short axis, so there are fewer groups. • Most bacilli appear as single rods. Diplobacilli appear in pairs after division. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Spiral bacteria have one or more twists. Vibrios look like curved rods Spirilla have a helical shape and fairly rigid bodies. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog •Spirochetes have a helical shape and flexible bodies. • Spirochetes move by means of axial filaments, which look like flagella contained beneath a flexible external sheath. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Stella are star-shaped. Haloarcula, a genus of halophilic archaea, are rectangular. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Streptobacilli appear in chains after division. Some bacilli are so short and fat that they look like cocci and are referred to as Coccobacilli. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog STRUCTURE OF A PROKARYOTIC CELL virulent factor movement attachment Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog The structure is described according to the following organization Structures, external to cell wall Structure of cell wall Structures, internal to cell wall Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Glycocalyx Flagella Axial filaments Fimbriae Pili Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog The glycocalyx (capsule, slime layer, or extra cellular polysaccharide) is a gelatinous polymer. A capsule is neatly organized A slime layer is unorganized & loose External to cell wall, composed of polysaccharide, polypeptide covering or both. The presence of a capsule can be determined by negative staining. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Capsules are important in contributing to the virulence of the bacteria. • Protect bacteria by preventing phagocytosis. • Allows the bacteria to adhere and colonize. • Important components of biofilm – protects cell Facilitates communication among them Enable to survive by attaching to various surfaces • Protects cell against dehydration • Inhibit the movement of nutrients out of the cell. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Capsulated bacteria – • Streptococcus pneumoniae • Klebsiella pneumoniae • Haemophilus influenzae • Bacillus anthracis • Streptococcus mutans • Yersinia pestis Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Streptococcus pneumoniae (in vivo) Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog K. pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog • Long filamentous appendages consisting of a filament, hook, and basal body • Made of chains of protein (flagellin) • Attached to a protein hook • Anchored to the wall and membrane by the basal body • Semi rigid, helical structure that moves the cell by rotating from the basal body. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Flagella are anchored by pairs of rings associated with the plasma membrane and cell wall. Gram positive bacteria have only the inner pair of rings Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Flagella Arrangement Peritrichous – distributed over the entire cell Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Monotrichous – single flagellum at one pole Prof. in Microbiolog Lophotrichous – a tuft of flagella coming from one pole Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Amphitrichous – flagella at both poles of cells Prof. in Microbiolog Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog • Rotate flagella to run or tumble • Move toward or away from stimuli (taxis) • The stimuli include chemicals like oxygen, ribose, galactose – Chemotaxis. • Stimuli can be light – Phototaxis. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog • Flagellar (H) protein functions as an antigen. • Flagella proteins are H - antigens - useful in distinguishing the variants within the species of gram-negative bacteria. • Example – 50 different H antigen for E. coli are identified. • E. coli O157:H7 – associated with food borne epidemics. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog •Also known as Endoflagella – are bundles of fibrils that arise at the ends of the cell beneath an outer sheath and spiral around the cell. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog • Spiral cells that move by means of an axial filament are called spirochetes. • Axial filaments are similar to flagella, except that they wrap around the cell. • Anchored at one end of a cell • Rotation causes cell the movement of the outer sheath that propels the spirochetes in a spiral motion. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog • Fimbriae and pili are short, straight, thin, hair like appendages. Made up of protein called Pilin. Arranged helically around a central core. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog • Fimbriae – – Occur at poles or evenly distributed. – Number can vary from few to several hundreds – Allow attachment to surfaces and adhere to each other • Pili – – Longer than Fimbriae – Only one or two per cell – are used to transfer DNA from one cell to another by Conjugation – (sex Pili). – Involved in motility called twitching motility – short jerky intermittent movements, seen in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. – Other type of motility is gliding motility – smooth gliding movement of mycobacterium. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Is a complex, semi rigid structure responsible for the shape of the cell. Surrounds the underlying, fragile plasma membrane. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Functions: • Prevents osmotic lysis • Keep or protect the cell shape • Point of anchorage for flagella • In some species it has the ability to cause disease and is the site of action for some antibiotics. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog • PEPTIDOGLYCAN - Main component of bacterial cell wall (also known as murein) - a polymer consisting of disaccharide N-acetyl glucoseamine (NAG) & N-acetyl muramic acid (NAM) linked by polypeptides chains. N-acetyl glucosamine (NAG) and N-acetyl muramic acid (NAM) joined as in peptidoglycan Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog • Alternating NAM and NAG molecules form a carbohydrate backbone (the glycan portion). • Rows of NAG and NAM are linked by polypeptides (the peptido - portion). •The structure of the polypeptide cross-bridges may vary but they always have a tetra peptide side chain, which consists of 4 amino acids attached to NAMs. The amino acids occur in alternating D and L forms. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog consist of many layers of peptidoglycan and also contain teichoic acids. Teichoic acids may: • bind and regulate movement of cations into and out of the cell • prevent extensive wall breakdown and possible cell lysis during cell growth • provide much of the cell wall's antigenicity Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog • Have a lipopolysaccharide-lipoprotein-phospholipid outer membrane surrounding a thin (sometimes a single) peptidoglycan layer. • Gram-negative cell walls have no teichoic acids. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog • Forms the periplasm between the outer membrane and the plasma membrane. • Protection from phagocytes, complement, antibiotics like penicillin, lysozyme, and other chemicals. . • O polysaccharide antigen, e.g., E. coli O157:H7. • Lipid A is an endotoxin – causes fever and shock • Porins (proteins) form channels through membrane Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog • Like Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium leprae • Contains Mycolic acid layer (waxy layer) instead of Peptidoglycan layer Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog • Mycoplasmas – Smallest known bacteria – Lack cell walls – Sterols in plasma membrane protect them from lysis. • Archaea – Wall-less, or – Walls of pseudomurein (lack NAM and D amino acids) Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Plasma membrane Cytoplasm Nucleoid Ribosomes Inclusions Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Cytoplasm is the aqueous solution or substances inside the plasma membrane Consists of 80% water and primary proteins (enzymes), carbohydrates, lipids, many low molecular weight compounds Inorganic ions are present in higher concentration It is thick, aqueous, semitransparent, and elastic containing DNA, ribosomes and inclusions. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Bacteria contains negative supercoiled single covalently closed circular chromosome (cccc) – single , long, continuous, and frequently circularly arranged thread of double stranded DNA called Bacterial Chromosome Nuclear area (nucleoid), there is no nucleus Bacteria can also contain plasmids, which are circular, extra-chromosomal DNA molecules. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog The cytoplasm of a prokaryote contains numerous 70s ribosomes; ribosomes consist of rRNA and protein. Protein synthesis occurs at ribosomes; it can be inhibited by certain antibiotics. The difference between prokaryotic (70s) and eukaryotic (80s) ribosomes allows antibiotics to selectively target the prokaryotic ribosomes while sparing eukaryotic ribosomes. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Endospores are resting structures formed by some bacteria for survival during adverse environmental conditions. •The process of endospore formation is called sporulation; the return of an endospore to its vegetative state is called germination.. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Eukaryotic organisms include algae, protozoa, fungi, plants and animals. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Flagella are few and long in relation to cell size; cilia are numerous and short. Flagella and cilia are used for motility, and cilia also move substances along the surface of the cells. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Figure 4.23a, b Both flagella and cilia are anchored to plasma membrane by a basal body and consists of nine pairs arranged in a ring, and two other single microtubules in the center of the ring called a 9 plus 2 array. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog The cell wall of many Algae and some Fungi contain cellulose. The main material of Fungal cell walls is chitin (a polymer of NAG units. Yeast cell wall consist of glucan and mannan (polysaccharide). Animal cells are surrounded by a glycocalyx, which strengthen’s the cell and provides a means of attachment to other cells. Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog PLASMA MEMBRANE Phospholipid bilayer Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Transmembrane proteins Sterols Glycocalyx carbohydrates Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog Cytoplasm – encompasses substance inside the plasma membrane and outside the cell Cytosol - Fluid portion of cytoplasm Cytoskeleton – provides support and shape and assists in transporting substances through the cell Cytoplasmic streaming - Movement of cytoplasm throughout cells helps distribute nutrients and move the cell over the surface Dr. Dalia M. Mohsen Prof. in Microbiolog