PubMed - Nursing Focus
advertisement

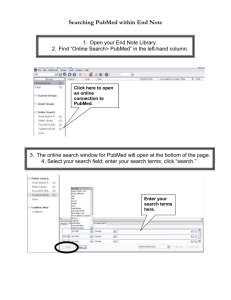
TTUHSC Preston Smith Library presents Searching PubMed® Nursing Focus Rev. 02/05/16 To begin... Hover mouse over Databases Click PubMed PubMed Database • Biomedical & life sciences journal literature - @6,000 journals • International scope • Developed and maintained by the: National Center for Biotechnology Information at the U.S. National Library of Medicine at the National Institutes of Health Accessing PubMed • Freely available over the Internet @ www.pubmed.gov • Also through library’s home page Creating a My NCBI Account Click Sign in to NCBI PubMed Home Page Click Register for an NCBI account Fill out form and click Create account Verifying your MY NCBI Account Open the email you used in the account: 1) Locate the link from NCBI 2) Click the link 3) Tells NCBI you are a real user requesting the account (not a computer robot) 4) Your user name will now appear on the top right-hand side Your username Click Sign into NCBI username Enter your username and password Click My NCBI Click Manage Filters Select database Select filters Filter activated Click Properties Selections Click Publication Types ttuhsc Activ e Name Meta-analysis Multicenter Study News Select Meta-analysis Practice Guideline Randomized Controlled Trial Newspaper Article Observational Study Overall Patient Education Handout Periodical Index Personal Narratives Portraits Practice Guideline Pragmatic Clinical Trial Published Erratum Randomized Controlled Trial Description ttuhsc Scroll to - Subsets and select Click PubMed Create a Search Strategy Plan Identify the question and key concepts: prevention and control of hypertension with life style changes Write the search program using medical subject headings (MeSH) Using MeSH Database MeSH Database is a “controlled vocabulary list” of more than 25,000 subject headings. Terms in the database are called Medical Subject Headings or MeSH. There are 10-15 MeSH assigned to each article in PubMed. It is like a keyword abstract of the article and is known as the MeSH Terms Index. Click MeSH Database Frequently Used Mesh Categories – 2016 A A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 A10 A11 A12 A13 A14 A15 A16 A17 A18 A19 A20 A21 Body Regions Musculoskeletal System Digestive System Respiratory System Urogenital System Endocrine System Cardiovascular System Nervous System Sense Organs Tissues Cells Fluids and Secretions Animal Structures Stomatognathic System Hemic and Immune Systems Embryonic Structures Integumentary System Plant Structures Fungal Structures Bacterial Structures Viral Structures B B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 Anatomy Organisms Eukaryota Archaea Bacteria Viruses Organism Forms C Diseases C1 Bacterial Infections & Mycoses C2 Virus Diseases C3 Parasitic Diseases C4 Neoplasms C5 Musculoskeletal Diseases C6 Digestive System Diseases C7 Stomatognathic Diseases C8 Respiratory Tract Diseases C9 Otorhinolaryngologic Diseases C10 Nervous System Diseases C11 Eye Diseases C12 Male Urogenital Diseases C13 Female Urogenital Diseases & Pregnancy Complications C14 Cardiovascular Diseases C15 Hemic & Lymphatic Diseases C16 Congenital, Hereditary, & Neonatal Diseases & Abnormalities C17 Skin & Connective Tissue Diseases C18 Nutritional & Metabolic Diseases C19 Endocrine System Diseases C20 Immune System Diseases C21 Disorders of Environmental Origin C22 Animal Diseases C23 Pathologic Conditions, Signs, and Symptoms C24 Occupational Diseases C25 Substance-Related Disorders C26 Wounds and Injuries D D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 Chemicals & Drugs Inorganic Chemicals Organic Chemicals Heterocyclic Compounds Polycyclic Compounds Macromolecular Substances Hormones, Hormone Substitutes, & Hormone Antagonists D8 Enzymes, & Coenzymes D9 Carbohydrates D10 Lipids D12 Amino Acids, Peptides, & Proteins D13 Nucleic Acids, Nucleotides, & Nucleosides D20 Complex Mixtures D23 Biologic Factors D25 Biomedical and Dental Materials D26 Pharmaceutical Preparations D27 Chemical Actions and Uses Other Categories Include: Analytical, Diagnostic, & Therapeutic Techniques & Equipment Psychiatry and Psychology Phenomena and Processes Disciplines and Occupations Anthropology, Education, Sociology & Social Phenomena Technology and Food and Beverages Humanities Information Science Persons Health Care Pharmacological Actions Publication Types Geographic Locations Enter hypertension and click a Search a (Note: If there is a Boolean OR relationship, start with the “OR” statement first.) Term Definitions Click the underlined term Sub-headings narrow the “meaning” of a MeSH term. M They are a “subset” of all the articles under the MeSH term: Hypertension. 82 SUBHEADINGS: abnormalities administrations & dosage adverse effects agonists analogs & derivatives analysis anatomy & histology antagonists & inhibitors biosynthesis blood blood supply cerebrospinal fluid chemical synthesis chemically induced chemistry classification complications congenital contraindications cytology deficiency diagnosis diet therapy drug effects drug therapy economics education embryology enzymology epidemiology ethics ethnology etiology genetics growth & development history immunology injuries innervation instrumentation isolation & purification legislation & jurisprudence manpower metabolism methods microbiology mortality nursing organization & administration parasitology pathogenicity pathology pharmacokinetics pharmacology physiology physiopathology poisoning prevention & control psychology radiation effects radiography radionuclide imaging radiotherapy rehabilitation secondary secretion standards statistics & numerical data supply & distribution surgery therapeutic use therapy toxicity transmission transplantation trends ultrasonography ultrastructure urine utilization veterinary virology 2) Select 1) Check the box next to the subheading AND a 3) Then click Add to search builder The first MeSH term is in the search program “box” Enter life style and click a Search a (Note: If there is a Boolean OR relationship, start with the “OR” statement first.) Full Display of Term Information MeSH terms arranged in tree structure hierarchy Terms are listed from broadest to narrowest. If Life Style yields zero results, try using a broader term: Psychology, Social. … unless you select the following command ✓ Note: PubMed automatically OR’s indented terms under a broader term… Click Add to search builder The second MeSH term is in the search program “box” Boolean Logic - AND hypertension/ prevention & control and life style Boolean Logic - OR life style OR diet The search program is complete. Click Search PubMed Search Results PubMed identifies 720 articles NOTE: Custom Filters set up in you’re My NCBI account. Click Meta-analysis, to quickly list those 4 articles Filters include:a A Article types Text availability Publication date Species such as: (human or animal) Languages Sex Subjects Journal categories Ages Search fields Limit to articles that were written in the past 5 years by clicking the selection on the left. Selection will turn blue: ✓ 5 years Click Humans Click Show additional filters Select Languages and click Show Click English Results are reduced From 720 to 123 Change [Mesh] to [Majr] Results are reduced From 123 to 40 Click Show additional filters Select Journal categories and click Show Click Nursing journals Results are reduced From 40 to 5 Select article # 3. X Click Summary Select Abstract Icons for full text. Click ∨ ∨ for MeSH terms. MeSH Database searches only the MeSH terms for: hypertension/dt AND The * indicates Major focus hypertension/pc AND life style Look at subject headings in the MeSH Terms Index for additional terms. You may want to write a new search program using: Risk Reduction Behavior Click Send to: and select File to save citations to a file on your computer or . Clipboard to temporarily store selected citations or E-mail to send citations to self or colleague …or click icon for full text. Linking to Full-Text Articles in Electronic Journals When Searching from Off Campus: Enter the Eraider username and password assigned to you by Information Services. A Problems with eRaider? a Call: 806-743-1234 Click PDF Full Text Article Close Article Saving Searches Click Advanced. Click 5 Click Create alert Click Yes, please. Select frequency Select day Select Report format Select Number of items: Click Save Click My NCBI Search is saved. Click Manage Saved Searches Delete saved search(es). Click to rerun search. See What’s new Click PubMed Click Clear all Other Searching Features a 1. MeSH, phrase, & title word searching using the [ti] pneumonic 2. Truncation Click MeSH Database Enter a human genome and click aSearch Click the underlined term Click Add to search builder Click Search PubMed PubMed identifies 21536 articles Enter AND “dark matter” and click Search PubMed identifies 11 articles Enter “dark matter” [ti] and click Search Results are narrowed to 8 Truncation Enter gene* to truncate. PubMed locates: gene genes genetic Generation is a “false drop” Online Tutorial Click Training & Tutorials for hands-on learning. Please email us: www.ttuhsc.edu/libraries Ask-ALibrarian The End