Stockholders' Equity
advertisement

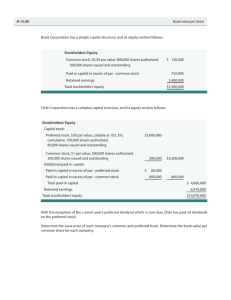
12-1 CHAPTER 12 STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY: CLASSES OF CAPITAL STOCK 12-2 The Corporation A business entity recognized by law with existence separate and distinct from its owners. Sue and be sued Hire and fire employees Enter into contracts A corporation can . . . Borrow money Buy, sell, or hold property 433 12-3 Advantages of the Corporate Form of Business* Limited liability Easy transfer of ownership Easy capital generation Continuous existence Professional management Separation of owners and entity 434 * Relative to a Partnership 12-4 Disadvantages of the Corporate Form of Business* Double taxation Governmental regulation Entrenched, inefficient management Limited ability to raise creditor capital 434 * Relative to a Partnership 12-5 Corporations General Terminology Incorporators Articles of incorporation Persons who form corporation Application for corporate charter Corporate Charter Contract between state and incorporators granting legal existence to corporation 12-6 Corporations General Terminology Corporate bylaws Rules adopted by board of directors to govern conduct of corporate affairs Organization costs Intangible assets subject to amortization e.g., Legal and accounting costs Domestic vs. Foreign Corporation Depends on state in which chartered 12-7 Directing the Corporation Stockholder Rights To dispose of their shares Preemptive right to buy new shares in proportion to shares already owned To share in dividends when declared To share in assets in event of liquidation To participate in management by voting at stockholders’ meetings 12-8 Directing the Corporation Hires corporate officers Formulates corporate policies Elected by whom? Board of Directors Composition of board? 12-9 Directing the Corporation Includes president, vice presidents, secretary, and treasurer Responsible for routine corporate operations Carry out the policies set by the board of directors Corporate Officers 12-10 Directing the Corporation Corporate Organization Chart Stockholders Board of Directors President (CEO) Secretary Treasurer Vice President Vice President Production Sales 12-11 Capital Stock A share of stock is a transferable unit of ownership. 100 Shares Stock Certificate VidTel, Inc. Common Stock Stock ownership records may be kept by external parties called stock-transfer agents and stock registrars. 12-12 Capital Stock The two classes of capital stock are common and preferred. 100 Shares Stock Certificate VidTel, Inc. Common Stock Capital Stock may have Par value No par value No par value with a stated value 12-13 Capital Stock Par value is an arbitrary amount assigned to each share of stock 100 Shares Stock Certificate VidTel, Inc. Common Stock $5 par value Par is not an indication of market value!!! 12-14 Capital Stock No-par stock has no par or stated value. (This is permitted in most states.) 100 Shares Stock Certificate VidTel, Inc. Common Stock No-par value Why would no-par stock be used? 12-15 Capital Stock No-par, stated value stock 100 Shares Stock Certificate VidTel, Inc. Common Stock No-par, $5 stated value Stock without par value, but to which a stated value has been assigned by the board of directors. 12-16 Capital Stock Market Value Price at which a seller is willing to sell for and a buyer is willing to buy for in the marketplace. 12-17 Capital Stock Liquidation Value Amount each share of stock would receive if assets are sold, liabilities are paid, and remainder is distributed to shareholders. 12-18 Capital Stock Three Important Numbers No. of shares authorized No. of shares issued No. of shares outstanding 12-19 Capital Stock Authorized Shares The maximum number of shares the corporation may issue as designated in its charter is the authorized number of shares. 12-20 Capital Stock Authorized Shares Issued shares are authorized shares of stock that have been sold. Unissued shares are authorized shares of stock that have never been sold. 12-21 Capital Stock Authorized Shares Issued Shares Outstanding Shares Treasury Shares Outstanding shares are shares that were sold and issued and are still held by stockholders. Unissued Shares Treasury shares are issued shares that have been reacquired by the corporation. 12-22 Question Ace Company’s corporate charter authorizes 1,000,000 shares of common stock. Ace issued 600,000 shares and later reacquired 100,000 shares. How many shares are outstanding and how many are unissued respectively? a. b. c. d. 600,000 & 300,000 500,000 & 500,000 500,000 & 400,000 400,000 & 500,000 12-23 Question Ace Company’s corporate charter authorizes 1,000,000 shares of common stock. Ace issued 600,000 shares and later reacquired 100,000 shares. How many shares are outstanding and how many are unissued respectively? a. b. c. d. 600,000 & 300,000 500,000 & 500,000 500,000 & 400,000 400,000 & 500,000 Issued Reacquired Outstanding Authorized Issued Unissued 600,000 100,000 500,000 1,000,000 600,000 400,000 12-24 Classes of Capital Stock Common Stock Residual Equity - all other claims against corporation’s assets, including those of creditors, rank above the claims of common stockholders. 1. Is not automatically entitled to dividends 2. Does not have asset preference in liquidation 12-25 Classes of Capital Stock Preferred Stock Preferences include 1. Dividends 2. Priority in case of liquidation A dividend rate is usually expressed either as a percent of par value or as a dollar amount per share 12-26 Classes of Capital Stock Companies issue preferred stock to avoid Using bonds with fixed interest charges Issuing so many additional shares of common stock Diluting the common stockholders’ control of the corporation 12-27 Attributes of Preferred Stock Voting or Nonvoting Preferred stock normally does not vote. Cumulative or Noncumulative Right to dividends accumulates if not paid. Unpaid dividends (called what?) must be paid before dividends may be paid to common shareholders. 12-28 Attributes of Preferred Stock Convertible or Nonconvertible May be exchanged for shares of common stock - a “sweetener” Callable or Noncallable Corporation may require shareholders to surrender shares of stock for a specified amount of cash 12-29 Types of Preferred Stock Preference as to dividends: Noncumulative Cumulative Unpaid current dividends need not be paid in future years. Unpaid dividends must be paid before any distribution to common stockholders. 12-30 Balance Sheet Presentation On the Balance Sheet, stockholders’ equity is divided into two parts. Paid-in Capital Investment by owners in exchange for shares of stock Retained Earnings Earnings that have been retained and reinvested in the business 12-31 Balance Sheet Presentation Stockholders’ Equity: Paid-in Capital Preferred Stock - $100 par, 7%, Cumulative; 10,000 shares authorized, issued, and outstanding Two Parts $ 1,000,000 Common Stock - $10 par, 300,000 shares authorized, 40,000 issued and outstanding Total Paid-in Capital Retained Earnings Total Stockholders' Equity (Similar) 444 400,000 $ 1,400,000 300,000 $ 1,700,000 12-32 Stock Issued for Cash Let’s take a closer look at the journal entries when stock is sold for cash. 12-33 Stock Issued for Cash Guidelines for Journal Entry Debit cash for number of shares times price per share. Credit common (or preferred) stock If Par Value Stock number of shares × par value per share If Stated Value Stock number of shares × stated value per share If No-Par Stock amount of cash received 12-34 Stock Issued for Cash Guidelines for Journal Entry If cash received differs from par or stated value Credit Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par Value for difference between cash received and total par value. Credit Paid-in Capital in Excess of Stated Value for difference between cash received and total stated value. 12-35 Stock Issued for Cash Par Value Example On September 1st, 10,000 shares of $20 par value common stock were sold for cash of $25 per share. GENERAL JOURNAL Date Description Page: PR Debit 1 Credit 12-36 Stock Issued for Cash Par Value Example On September 1st, 10,000 shares of $20 par value common stock were sold for cash of $25 per share. GENERAL JOURNAL Date Description 9/1 Cash Common Stock Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par Value To record issuance of stock for cash Page: PR Debit 1 Credit 250,000 200,000 50,000 12-37 Stock Issued for Cash Par Value Example On September 1st, 10,000 shares of $20 par value common stock were sold Dollars for cash perof $25 per share. Shares share Total Cash 10,000 × $ 25 = $ Page: 250,000 1 GENERAL JOURNAL Common stock 10,000 × (Par) 20 = 200,000 Paid-inDescription capital 10,000 × 5PR = Debit 50,000 Credit Date 9/1 Cash 250,000 Common Stock 200,000 Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par Value 50,000 To record issuance of stock for cash 12-38 Stock Issued for Cash Stated Value Example On September 1st, 10,000 shares of no-par, $20 stated value common stock were sold for cash of $25 per share. GENERAL JOURNAL Date Description Page: PR Debit 1 Credit 12-39 Stock Issued for Cash Stated Value Example On September 1st, 10,000 shares of no-par, $20 stated value common stock were sold for cash of $25 per share. GENERAL JOURNAL Date Description 9/1 Cash Common Stock Paid-in Capital in Excess of Stated Value To record issuance of stock for cash Page: PR Debit 1 Credit 250,000 200,000 50,000 12-40 Stock Issued for Cash Stated Value Example On September 1st, 10,000 shares of no-par, $20 stated value common stock were sold for cash of $25 per share. Stated value is treated just like GENERAL JOURNAL Page: 1 par value for accounting purposes. Date Description 9/1 Cash Common Stock Paid-in Capital in Excess of Stated Value To record issuance of stock for cash PR Debit Credit 250,000 200,000 50,000 12-41 Stock Issued for Cash No-Par Example On September 1st, 10,000 shares of no-par value common stock were sold for cash of $25 per share. GENERAL JOURNAL Date Description 9/1 Cash Common Stock To record issuance of stock for cash Page: PR Debit 1 Credit 250,000 250,000 12-42 Stock Issued for Cash No-Par Example On September 1st, 10,000 shares of no-par value common stock were sold for cash of $25 per share. For true no-par stock, credit the GENERAL JOURNAL Page:for the 1 Common Stock account total cash received. Date Description 9/1 Cash Common Stock To record issuance of stock for cash PR Debit Credit 250,000 250,000 12-43 Stock Issued for Property or Services Record transaction at fair value of property or services received or fair value of stock issued, whichever is more clearly evident. Fair value of stock Fair value of property 12-44 Stock Issued for Property or Services On May 1st, 10,000 shares of $20 par value stock were exchanged for land valued at $350,000. GENERAL JOURNAL Date Description Page: PR Debit We do not know the fair value of the stock issued because it is not actively traded in the market. 1 Credit 12-45 Stock Issued for Property or Services On May 1st, 10,000 shares of $20 par value stock were exchanged for land valued at $350,000. GENERAL JOURNAL Date Description 5/1 Land Common Stock Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par Page: PR Debit 1 Credit 350,000 200,000 150,000 12-46 Balance Sheet Presentation Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par Value The following slide illustrates a typical Balance Sheet presentation of Stockholders’ Equity. All numbers are assumed and are not taken from previous or text examples. 12-47 Balance Sheet Presentation Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par Value Paid-in Capital Preferred Stock - $100 par, 7%, Cumulative; 10,000 shares authorized, issued, and outstanding Common Stock - $10 par, 300,000 shares authorized, 40,000 issued and outstanding Paid-in Capital in excess of Par Value Preferred Stock $ 100,000 Common Stock 80,000 Total Paid-in Capital Retained Earnings Total Stockholders' Equity $ 1,000,000 400,000 180,000 $ 1,580,000 300,000 $ 1,880,000 12-48 Book Value in Total Not per share book value The theoretical liquidation value [Rice] i.e., Total stockholders’ equity i.e., Net assets (assets minus liabilities) 12-49 Book Value Per Share If no Preferred Stock is outstanding Book Value per share of common stock equals total Stockholders’ Equity divided by number of shares of common stock outstanding. If Preferred Stock is outstanding To get BV per share for common, subtract: (1) liquidating value of preferred and (2) cumulative preferred dividends in arrears from Stockholders’ Equity, before dividing by no. of common shares outstanding. 12-50 Book Value Per Share No Preferred Stock Book value per share = Total stockholders’ equity Number of common shares outstanding. Preferred Stock Outstanding Book value = per share Total stockholders’ equity Less: Liquidating value of preferred Less: Cumulative dividends in arrears Number of common shares outstanding 12-51 End of Chapter 12